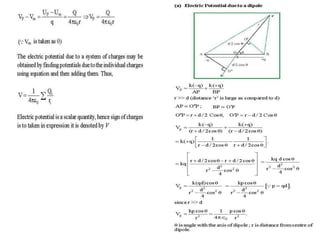
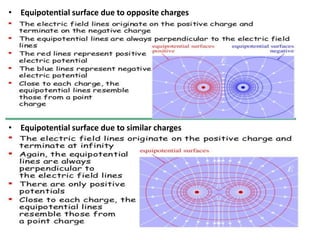
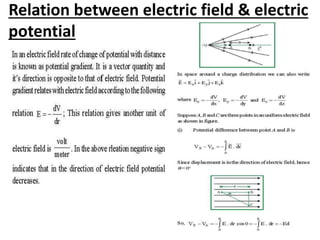
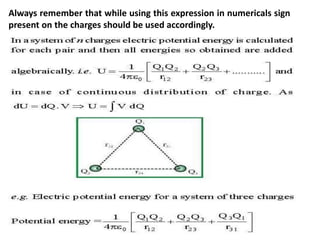
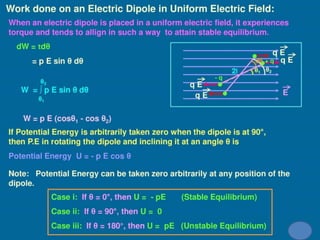
Electrostatic potential is a scalar quantity measured in joules (J) or electron volts (eV). Equipotential surfaces represent regions in space where the electric potential is constant around a charged body. They are always perpendicular to electric field lines and can be represented by concentric spheres or lines. The relationship between electric field and potential is such that the electric field is defined as the negative gradient of the potential.