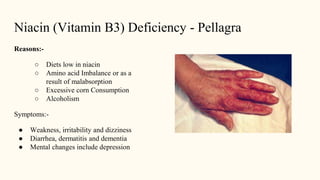
This document discusses malnutrition, its causes, types, and prevention. It defines malnutrition as an imbalance between nutritional needs and intake, leading to disorders. The main types are undernutrition and overnutrition. Causes include insufficient food intake and poor absorption. Consequences are discussed like protein-energy malnutrition conditions Kwashiorkor and Marasmus, as well as disorders from vitamin and mineral deficiencies such as beriberi, pellagra, rickets, and goiter. Prevention strategies covered include education, agriculture, food fortification, and public health programs.