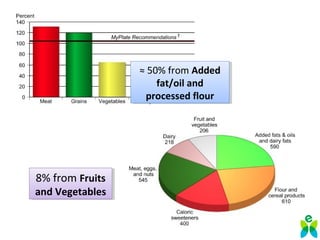
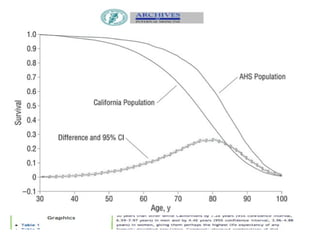
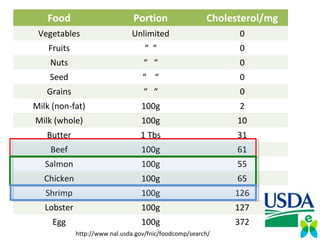
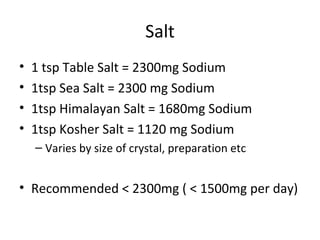
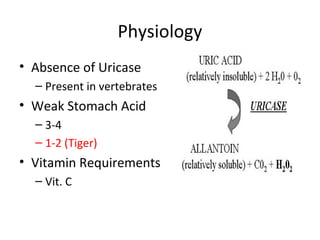
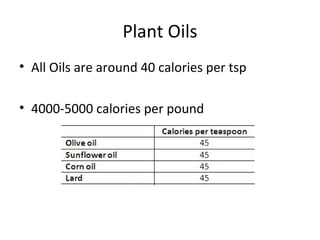
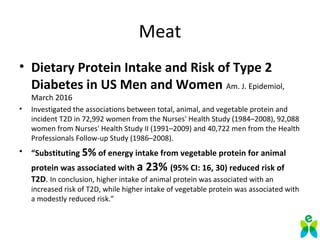
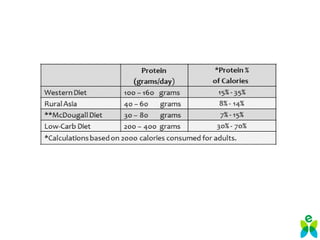
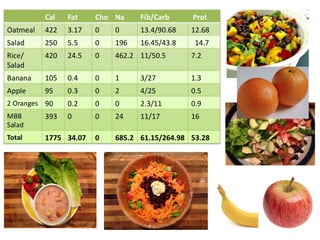
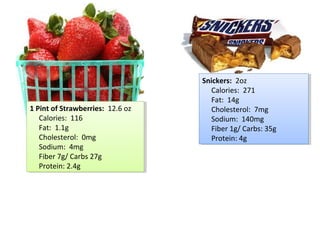
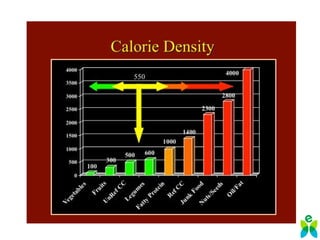
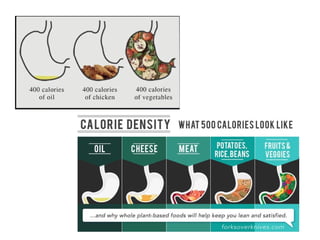
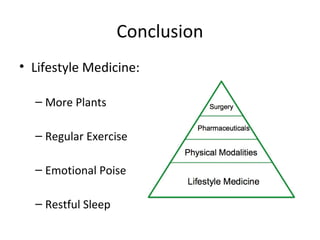
The lecture discusses the impact of diet and lifestyle choices on health, highlighting the rise of chronic diseases linked to poor nutrition and sedentary behavior. Evidence suggests that a plant-based diet can reduce the risk of various diseases, while high consumption of animal protein and processed foods has adverse effects on health. The presentation promotes a holistic approach to nutrition, emphasizing the importance of making informed dietary choices for long-term health benefits.