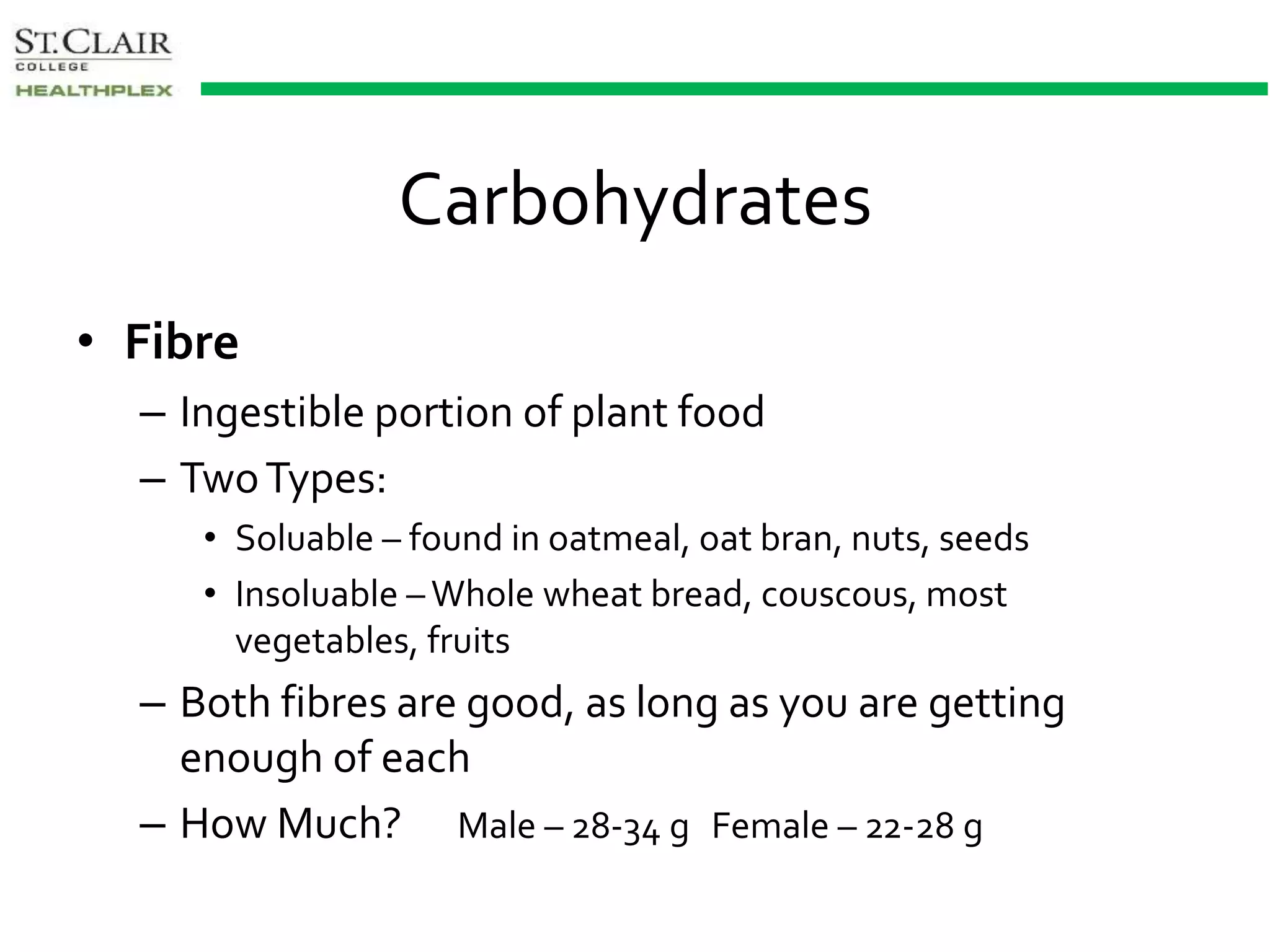
This document provides an overview of the macronutrients essential for healthy eating, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It details their functions, types, sources, and recommended daily intake, emphasizing the importance of balanced consumption. It also highlights the implications of different types of fats and the role of food labels in making informed dietary choices.