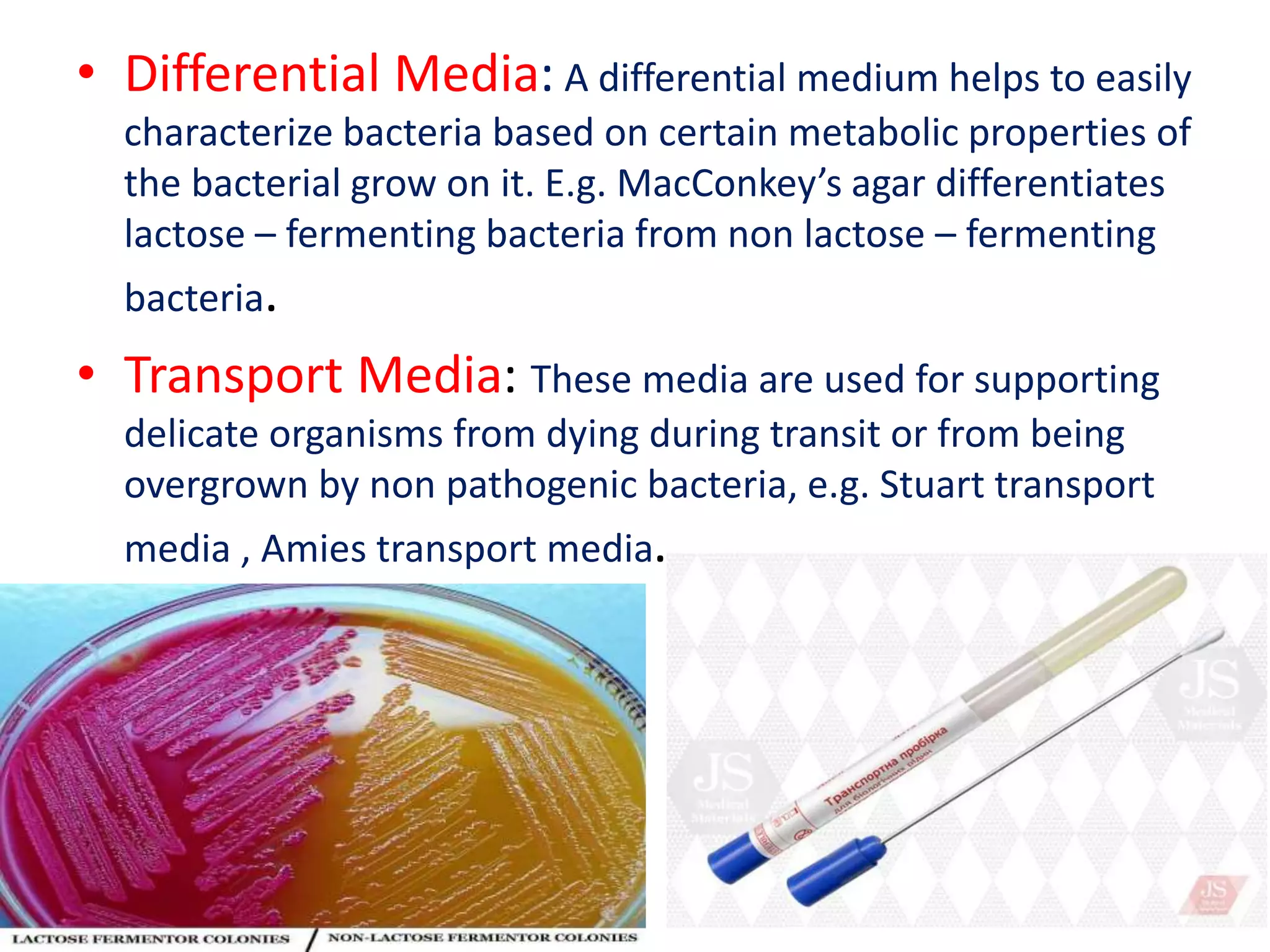
Media used in microbiology refers to the substances used to support the growth of microorganisms in laboratory cultures. Common ingredients in bacterial culture media include water, peptone, meat extract, carbohydrates, yeast extract, and mineral salts. Agar is often used as a solidifying agent. Culture media can be classified based on consistency (liquid vs solid), composition (simple vs complex), application (basal, enriched, selective, differential, transport), and more. Proper culture media selection is important for isolating and identifying microbes.