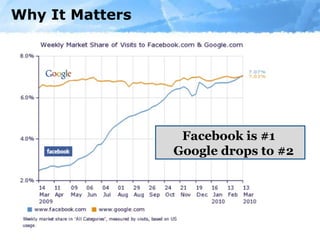
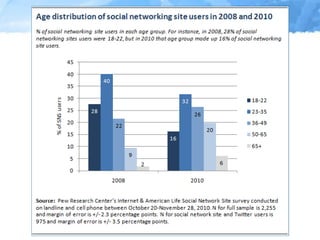
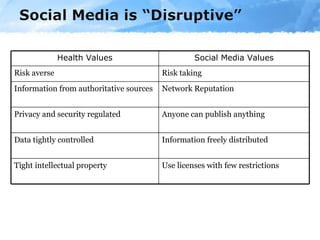
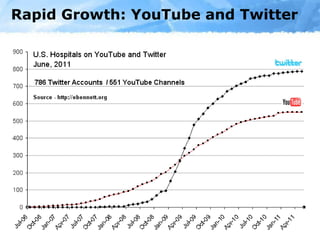
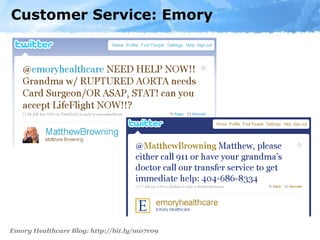
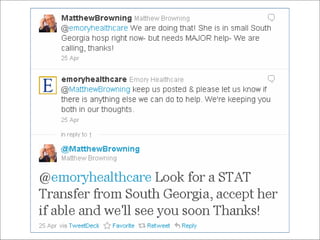
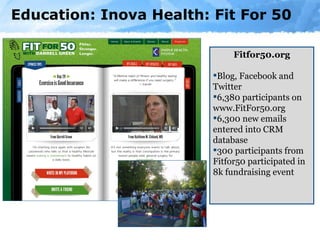
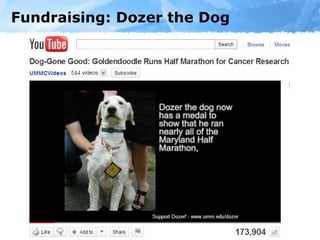
The document provides an overview of the role of social media in healthcare, highlighting its rapid adoption and significance for both patients and professionals. It discusses various uses of social media within hospitals, including customer service, education, and community outreach, while addressing the unique challenges healthcare faces regarding privacy and regulation. Notable statistics demonstrate the increased engagement of adults with social media platforms, emphasizing the need for healthcare institutions to adapt and integrate these tools into their operations.