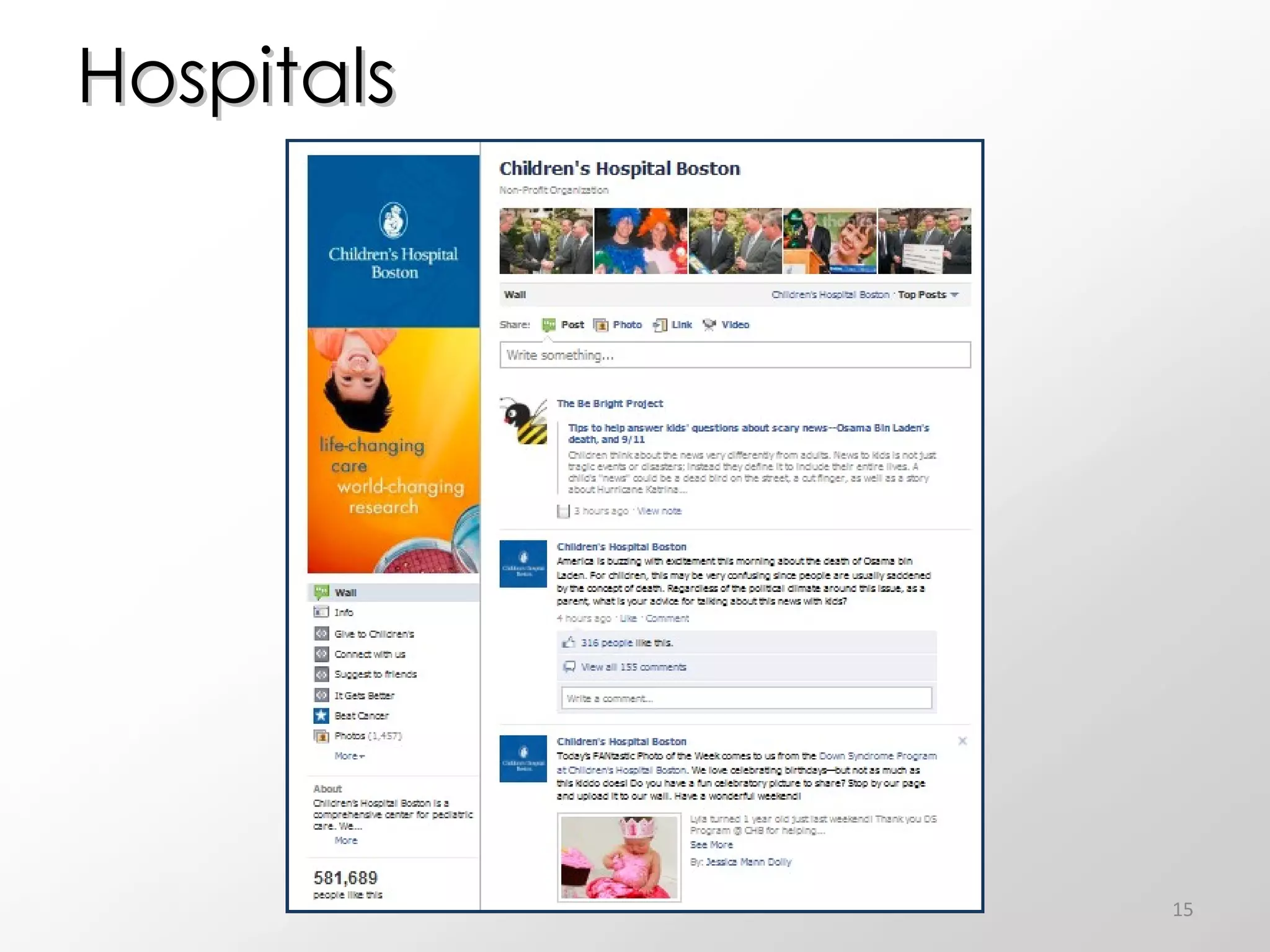
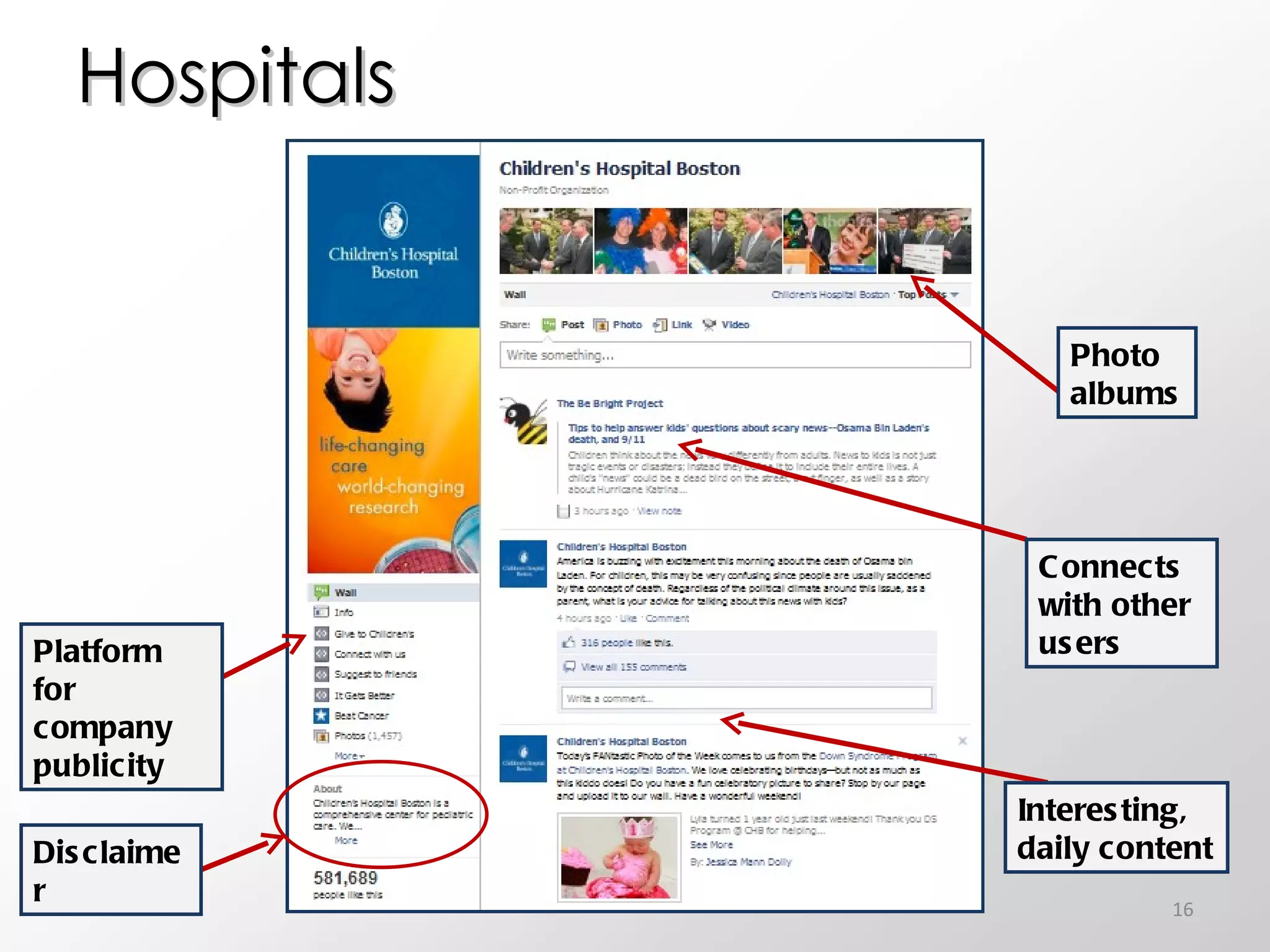
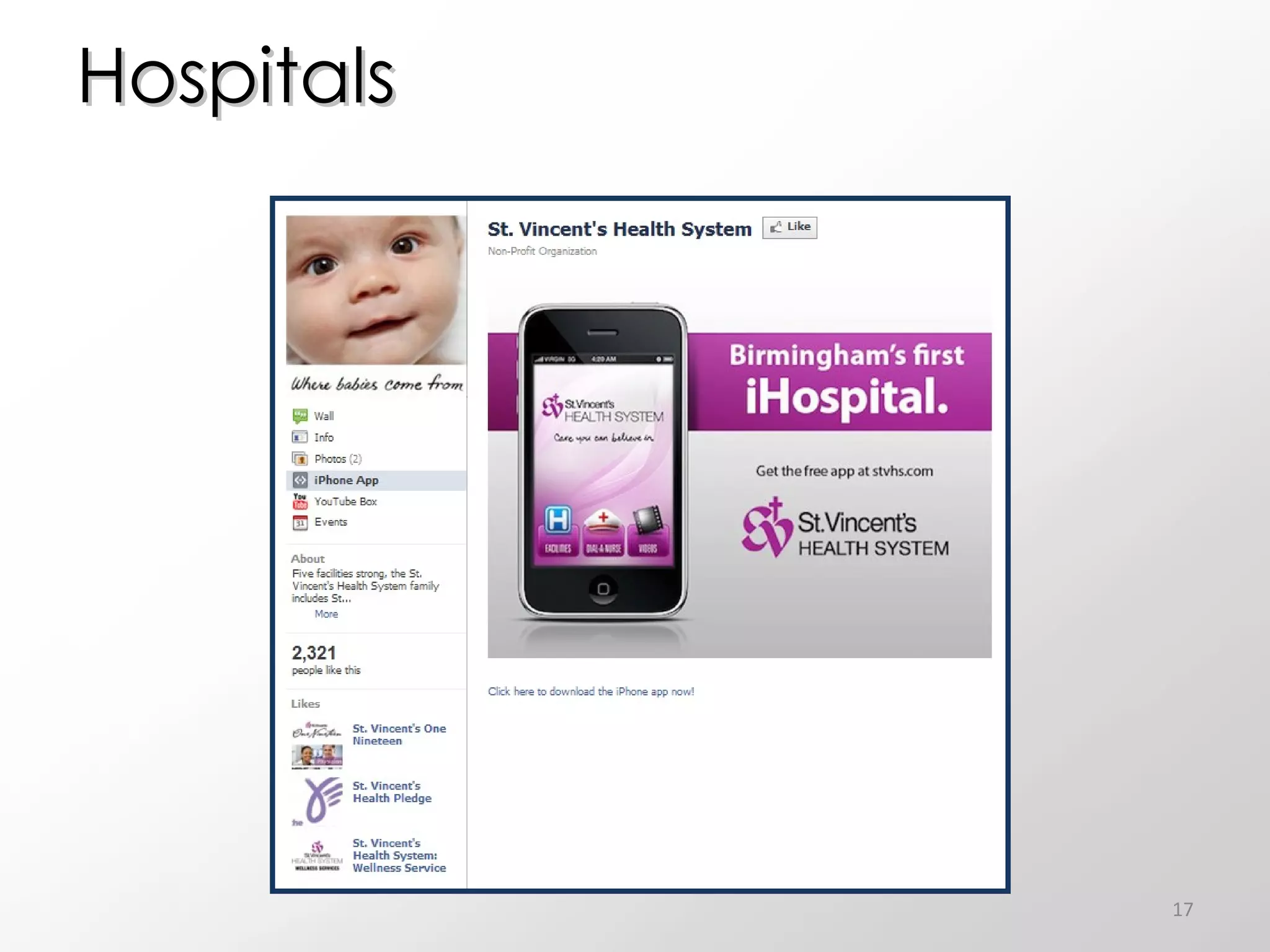
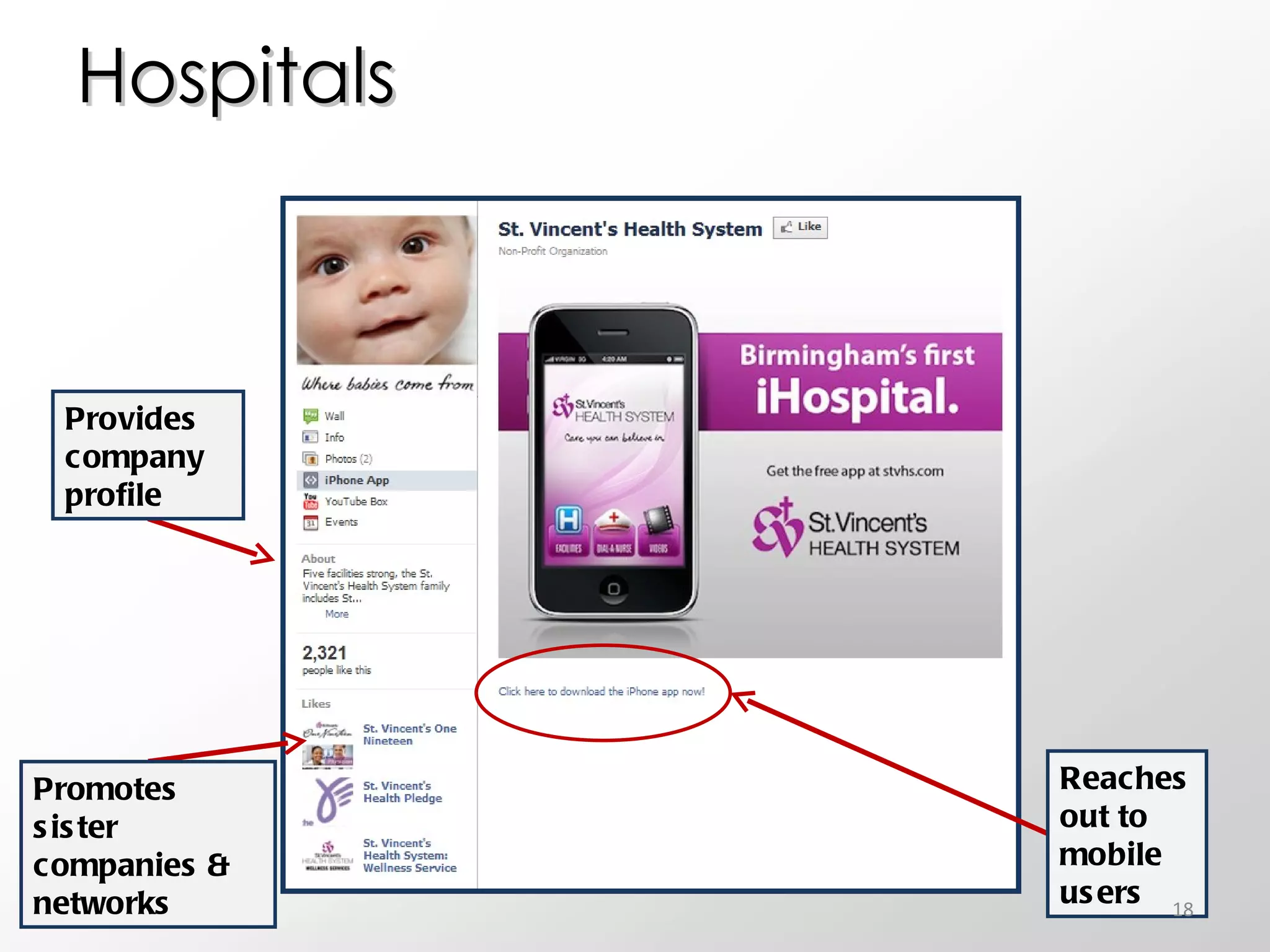
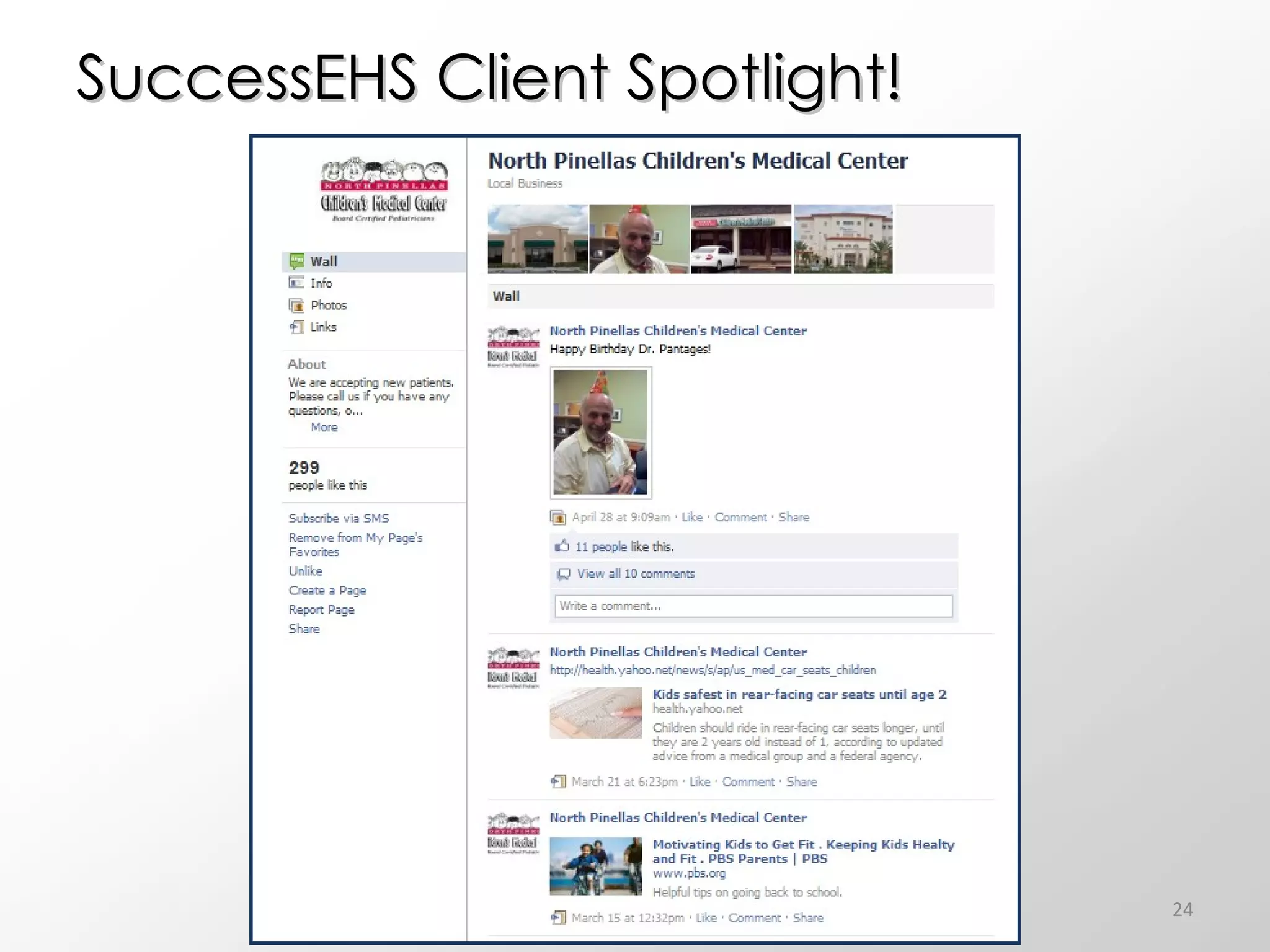
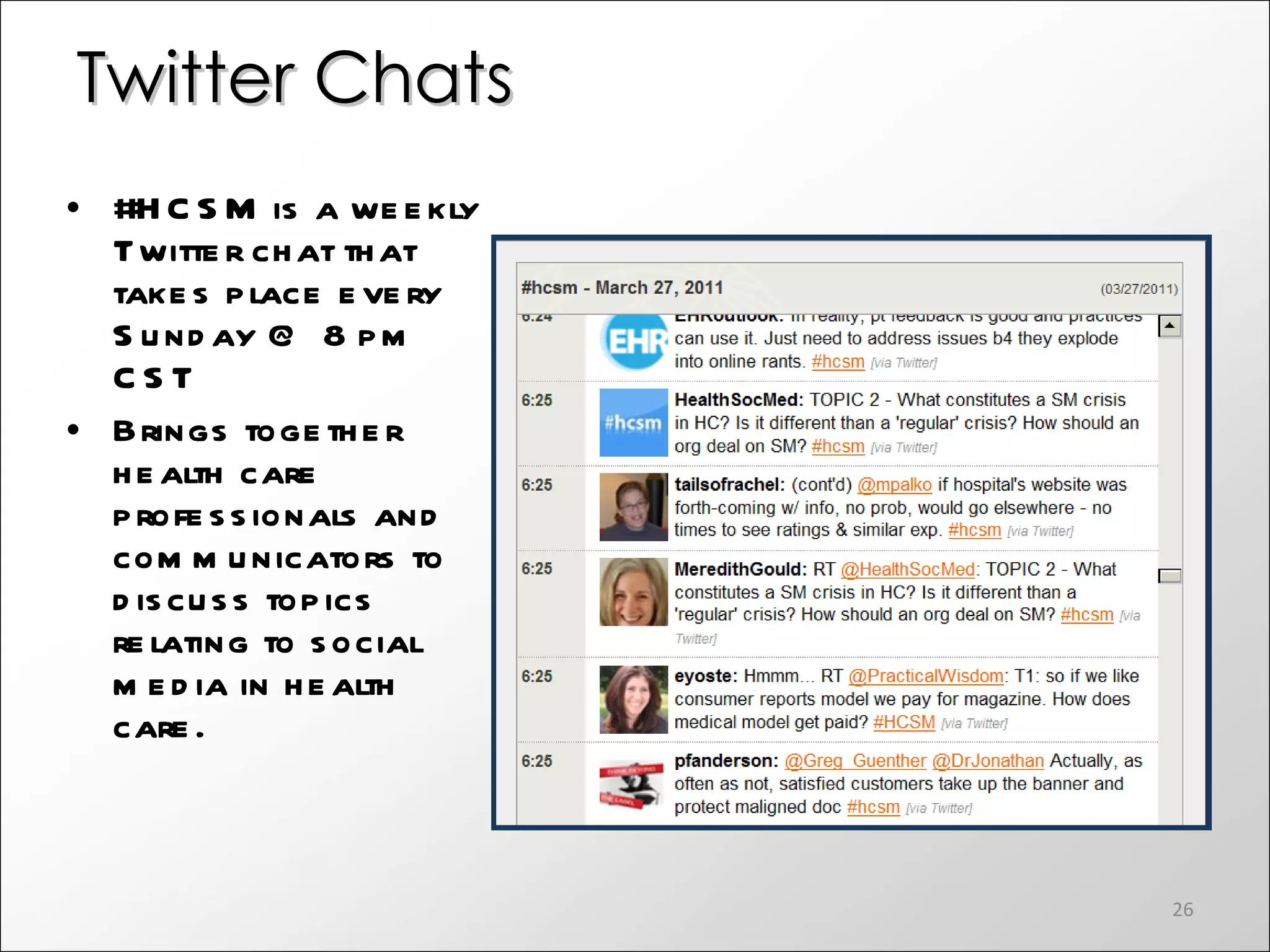
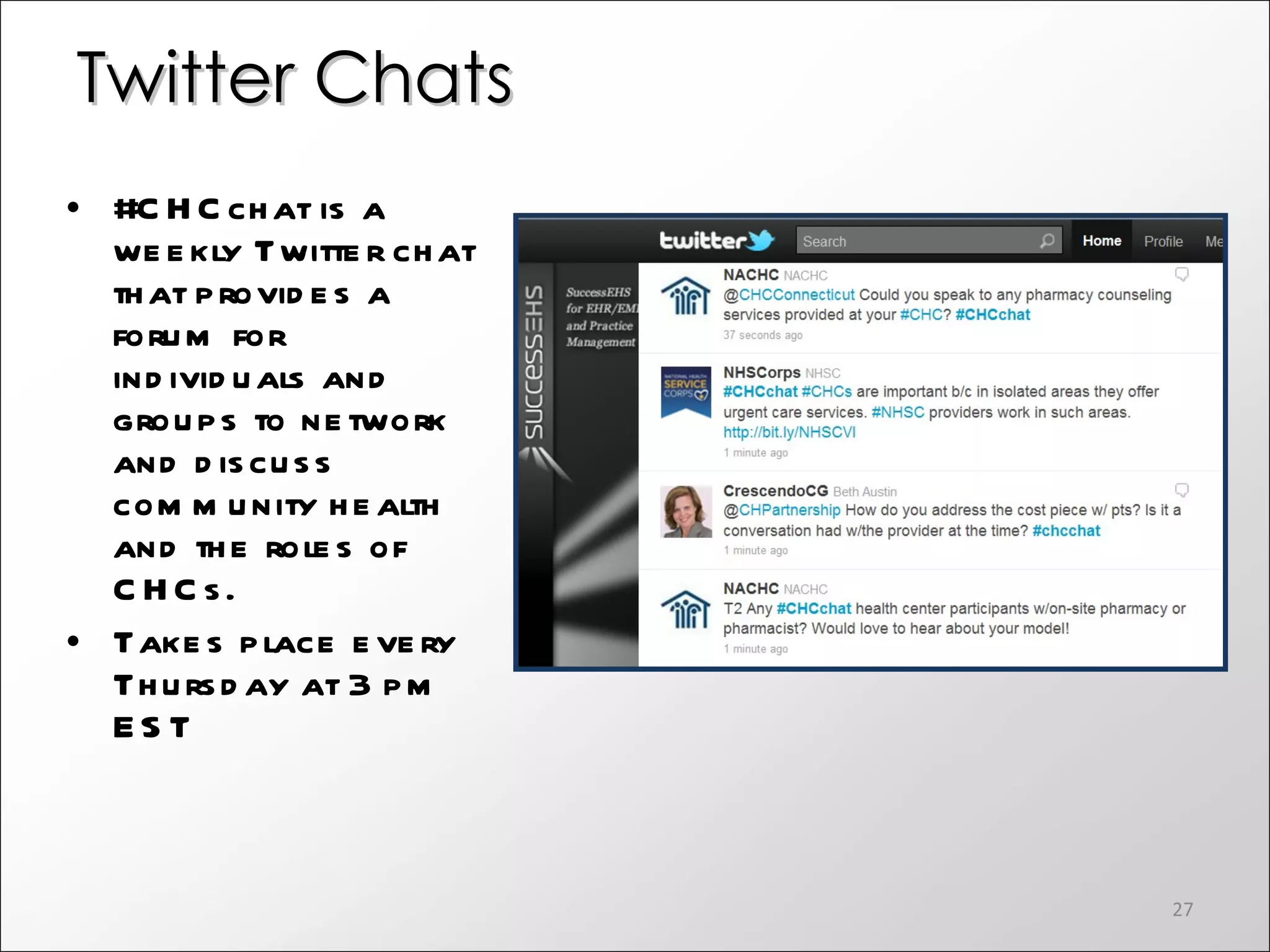
The document discusses the role of social media in healthcare, emphasizing its use for connecting with patients and fellow professionals while addressing industry trends and statistics. It highlights the benefits and challenges of using social media, including the importance of maintaining credibility and ethical standards. Additionally, it provides guidelines for healthcare providers on managing their online presence and engaging effectively with their audience.