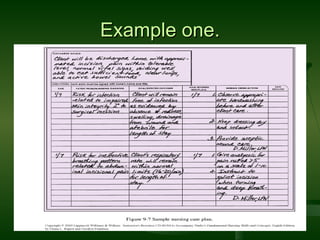
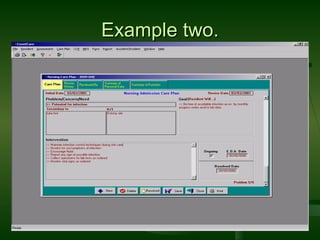
Care plans involve four stages: assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation (APIE). The assessment stage involves a multi-disciplinary evaluation of the client's individual needs and problems. The planning stage develops goals and strategies to address the identified needs. The implementation stage puts the plan into action using various resources. The evaluation stage reassesses the plan's effectiveness and determines if changes are needed.