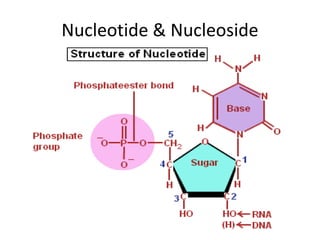
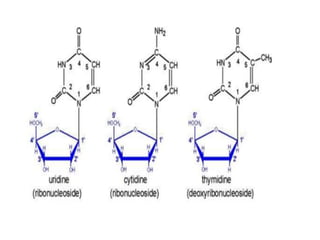
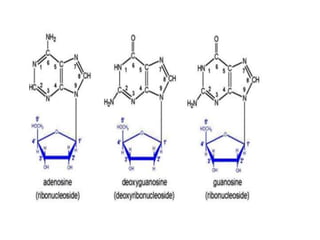
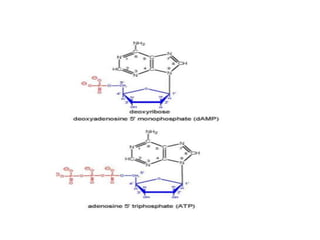
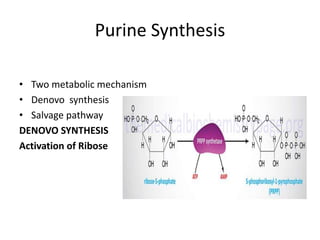
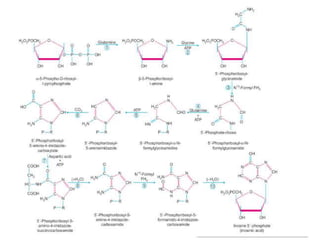
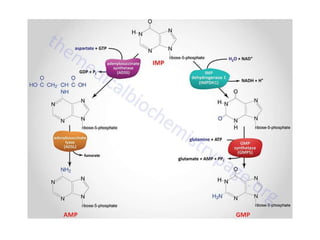
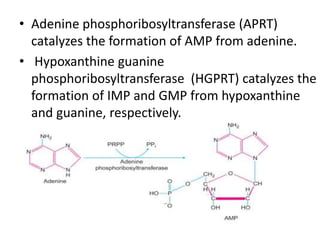
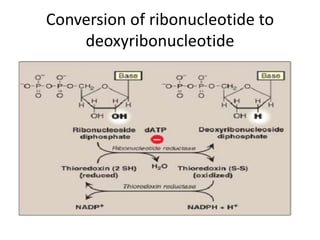
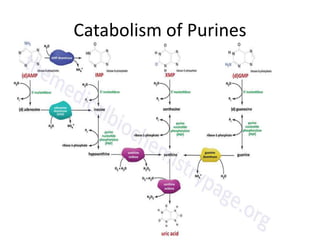
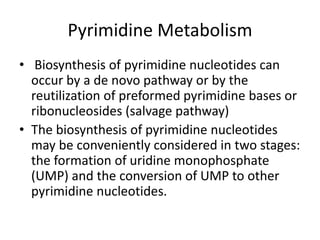
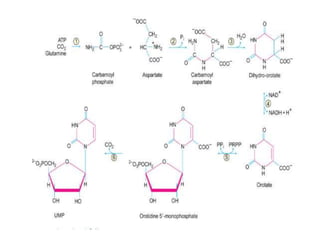
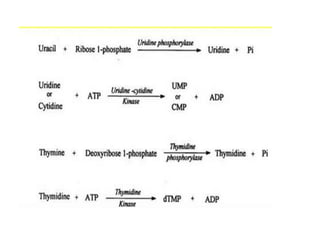
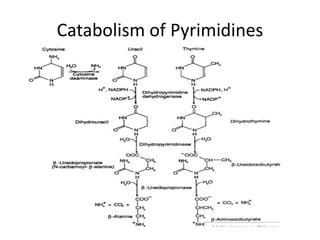
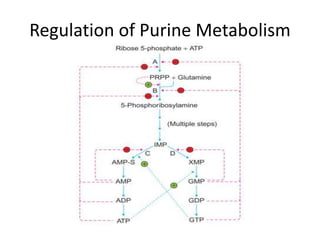
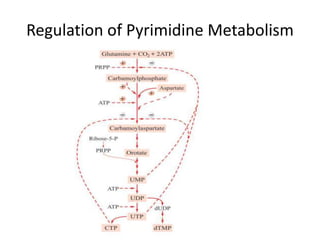
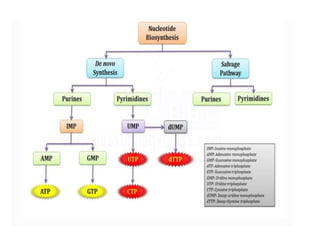
The document discusses nucleic acid metabolism, focusing on nucleotide and nucleoside components, including their synthesis pathways, such as the de novo synthesis and salvage pathway for purines and pyrimidines. It highlights the importance of various enzymes in these processes and the roles of different tissues, particularly the liver and extrahepatic tissues, in metabolizing and salvaging nucleotides. Additionally, it outlines the biosynthesis and catabolism of purines and pyrimidines, as well as the regulation mechanisms for both types of nucleotides.