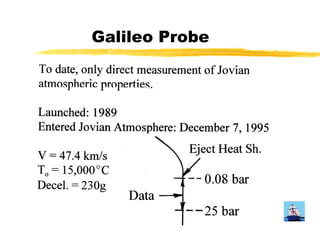
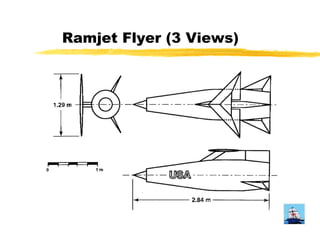
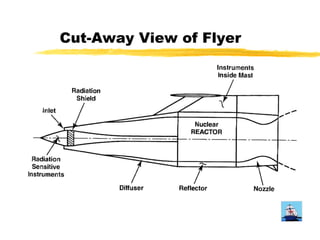
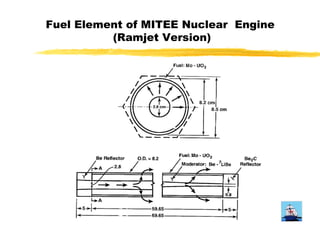
The document proposes exploring Jupiter's atmosphere using a nuclear ramjet flyer. It would use a Miniature Reactor Engine (MITEE) as its power source, allowing it to operate for months within Jupiter's atmosphere. A companion orbiter would also be launched. The flyer would separate upon atmospheric entry and use the atmosphere as propellant while mapping various characteristics like temperature, composition and cloud patterns over an extended period. Developing the MITEE nuclear engine could enable further solar system and interstellar exploration.