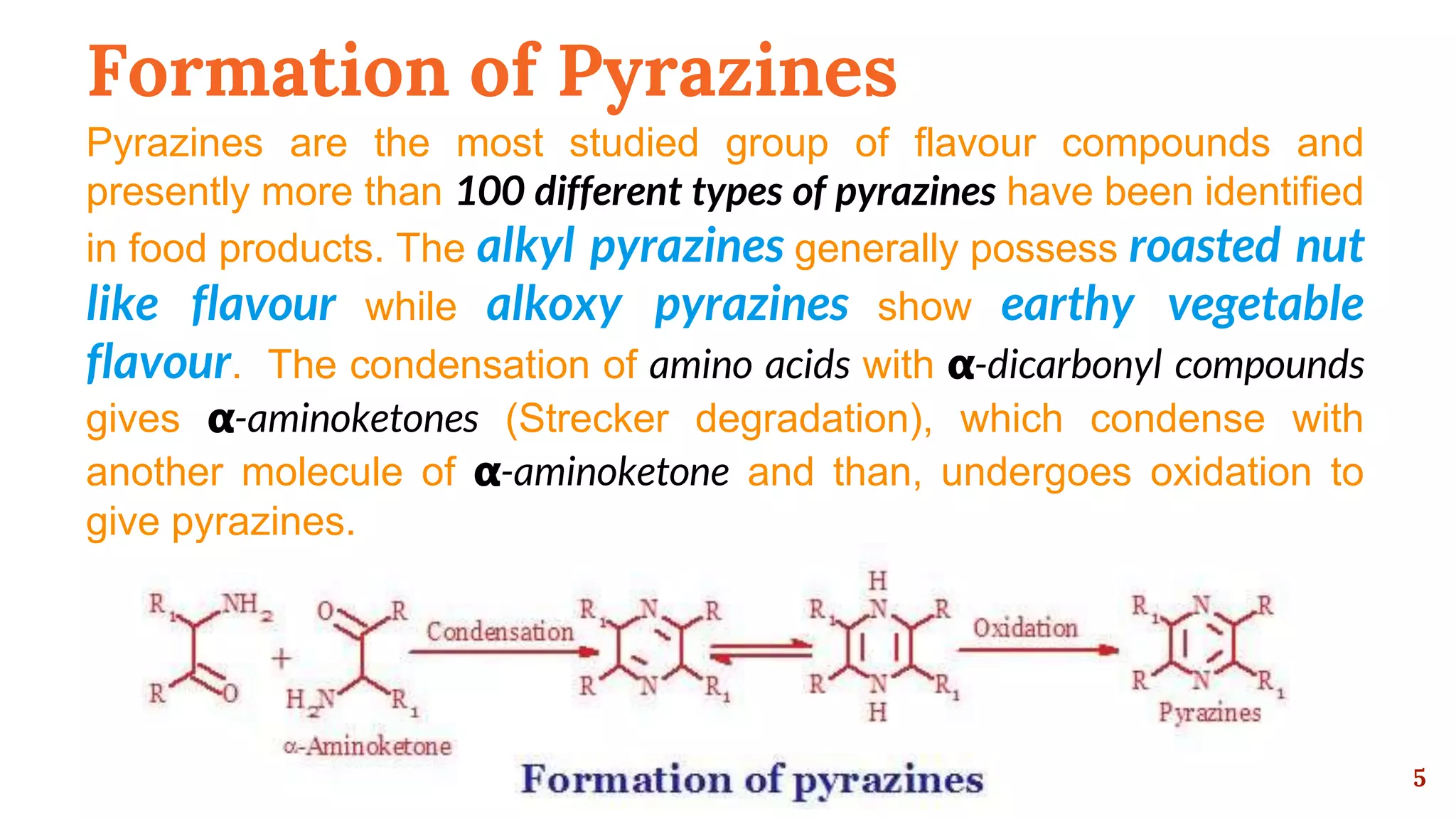
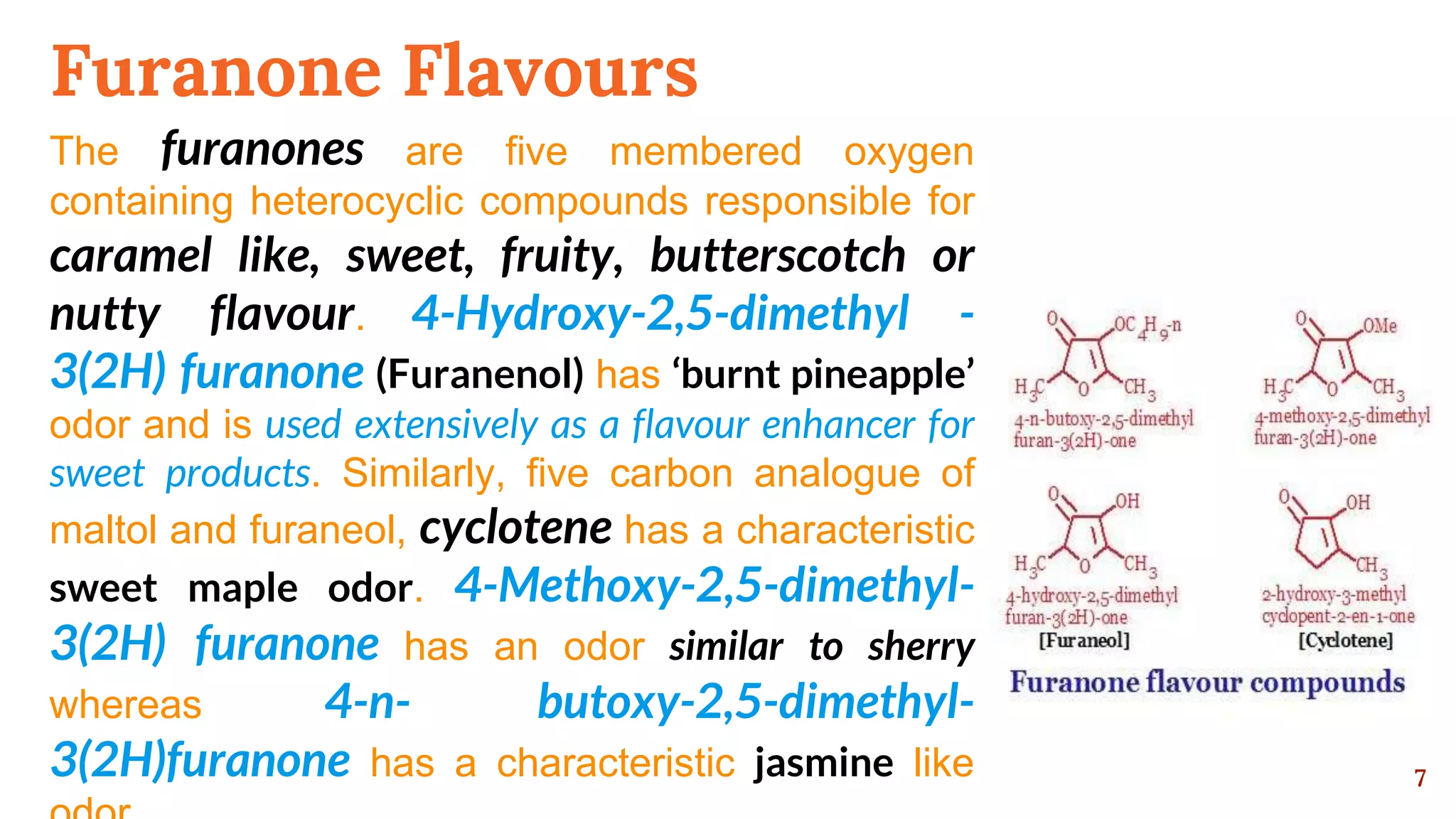
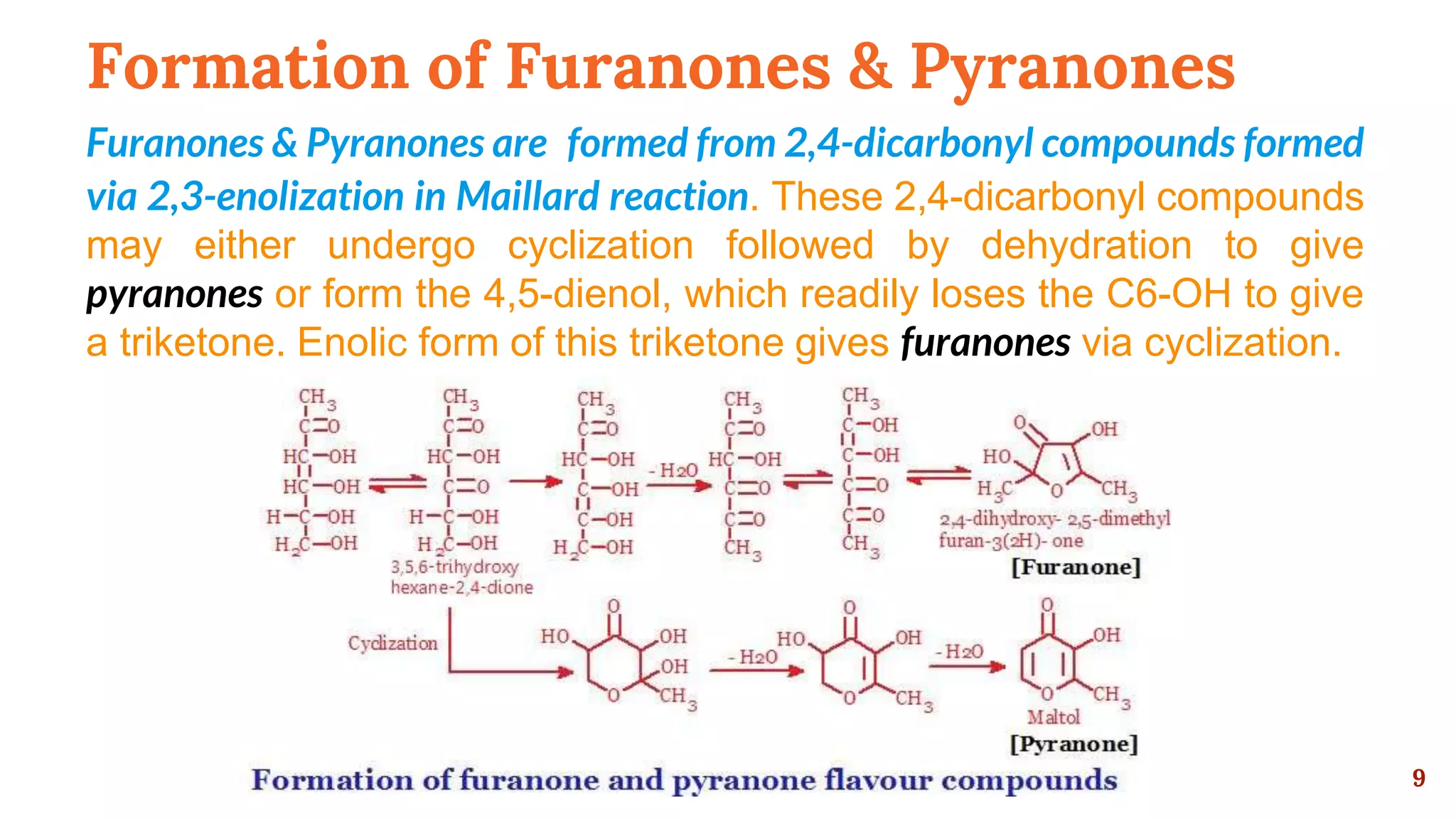
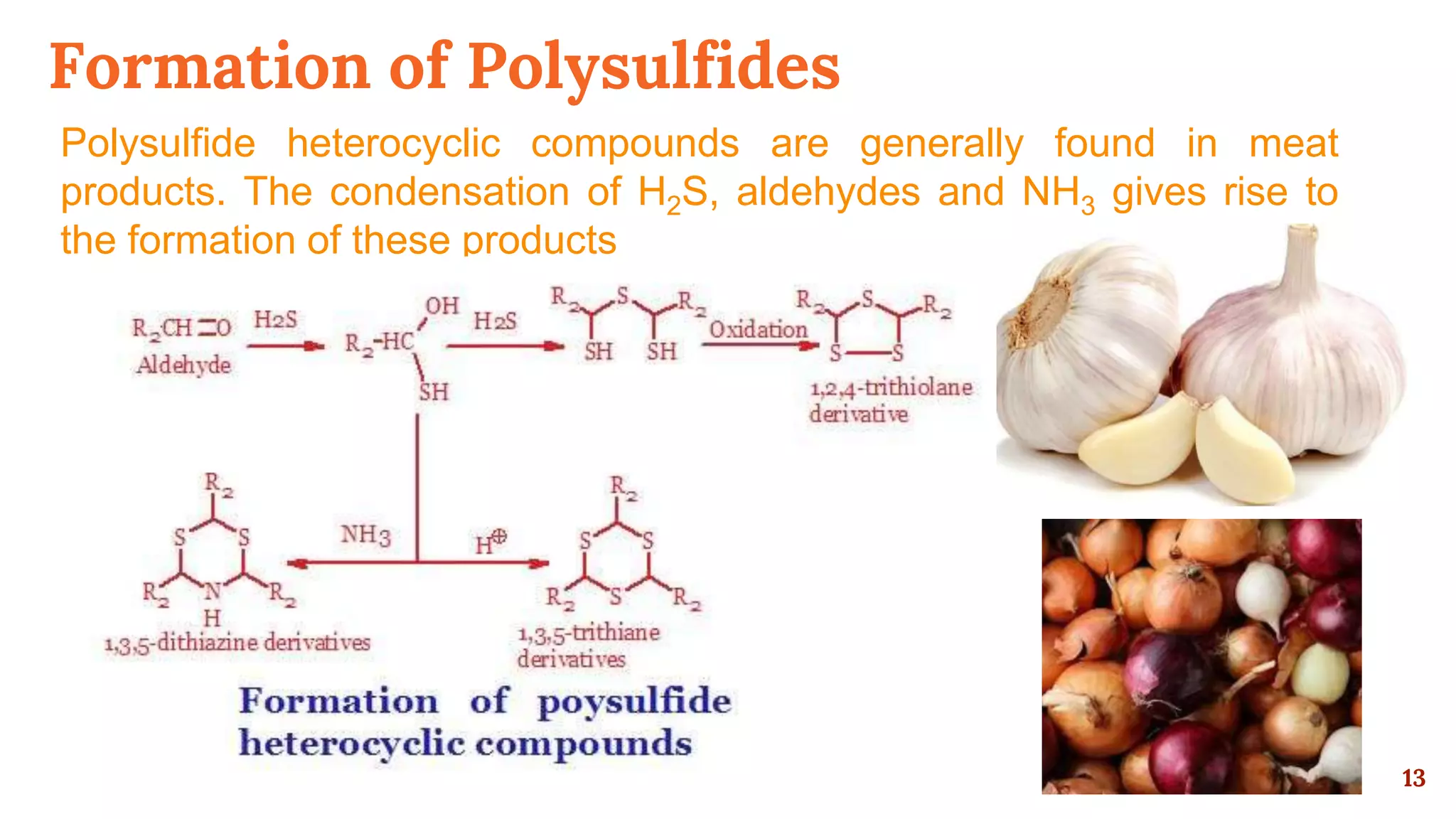
This document discusses the Maillard reaction, also known as non-enzymatic browning, which is responsible for pleasant flavors in foods like bread, coffee, and chocolate. It produces primary products through the condensation of reducing sugars and amino acids, which then undergo additional reactions to form secondary products that contribute flavor. These secondary products include carbonyls, pyrroles, pyrazines, oxazoles, thiazoles, pyridines, and imidazoles. The document outlines the specific chemical reactions that form several classes of these compounds, such as Strecker degradation producing carbonyls and pyrazines. It also discusses the formation of furanones, pyranones, pyrrolines