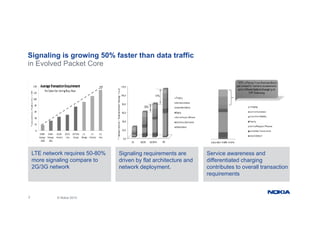
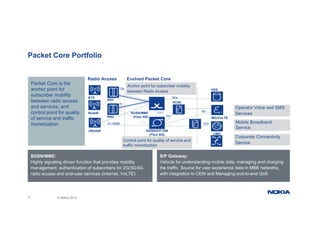
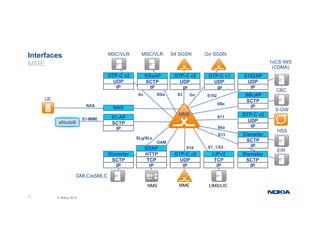
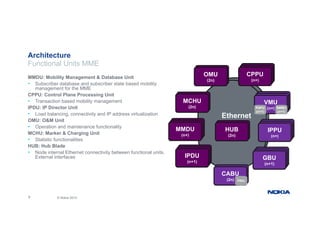
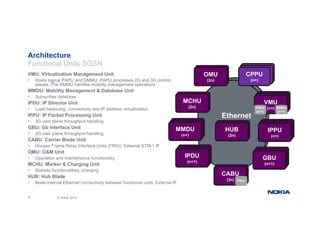
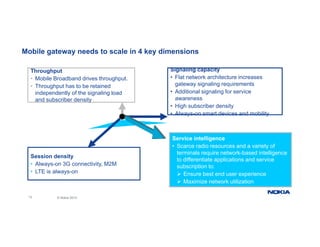
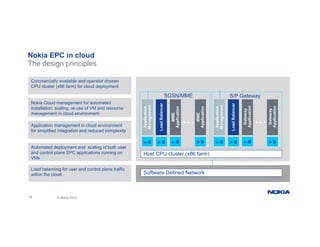
The document provides an overview of Nokia's Evolved Packet Core (EPC) solutions, detailing the increasing demand for signaling capacity as mobile broadband and IoT grow. It highlights Nokia's strategy to unify hardware platforms for core network elements and emphasizes the scalability, performance, and flexibility of their core solutions. Additionally, it discusses the cloud deployment of core network functions, optimizing traffic and monetization capabilities for operators.