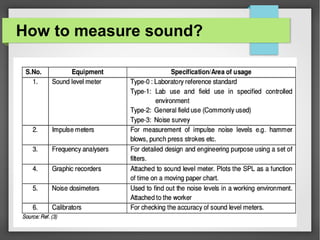
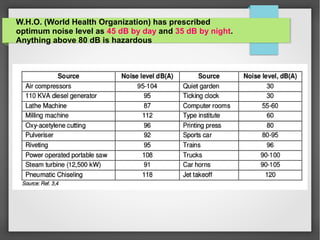
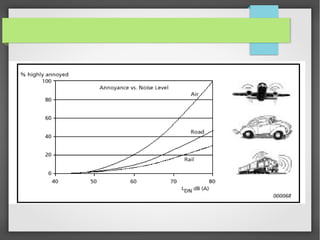
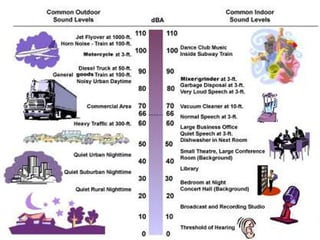
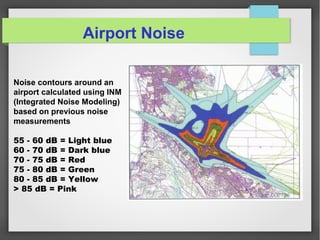
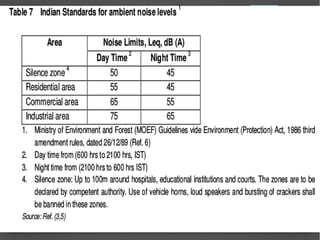
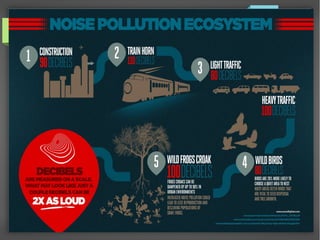
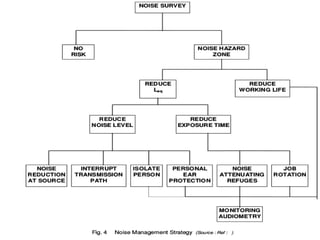
Noise pollution refers to unwanted sounds that penetrate the environment. Sources of noise pollution include domestic activities, natural sounds, commercial activities, industrial operations, and transportation. The World Health Organization recommends maximum noise levels of 45 dB during the day and 35 dB at night. Excessive noise can cause annoyance, physiological effects, hearing loss, reduced human performance, sleeplessness, and damage to materials. Prevention of noise pollution involves creating noise barriers, restricting loud sounds at night, maintaining vehicles, and planting green spaces.