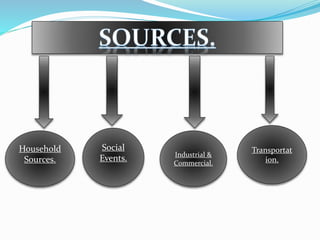
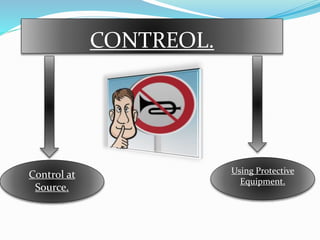
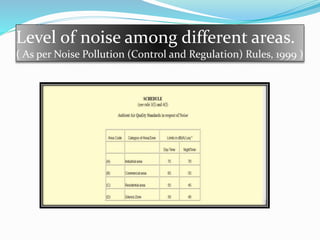
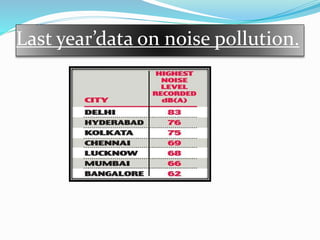
This document discusses noise pollution, including its sources, causes, effects, and controls. It defines noise pollution as unwanted sound that harms humans or animals. Major sources of noise pollution are listed as household appliances, social events, industries, commercial activities, and transportation. The effects of noise pollution on humans can include hearing loss, lack of concentration, fatigue, and cardiovascular issues. Animals are also negatively impacted through damage to the nervous system and problems with habitat. The document outlines ways to control noise pollution such as reducing sound levels, maintaining vehicles and machinery, and using protective ear equipment.