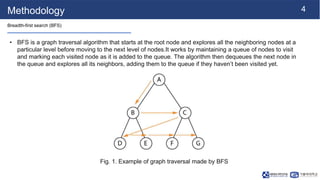
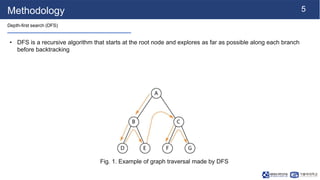
Node2Vec is an algorithm for learning continuous feature representations or embeddings of nodes in graphs. It extends traditional graph embedding techniques by leveraging both breadth-first and depth-first search to learn the local and global network structure. The algorithm uses a skip-gram model to maximize the likelihood of preserving neighborhood relationships from random walks on the graph. Learned embeddings have applications in tasks like node classification, link prediction, and graph visualization.