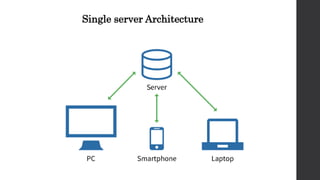
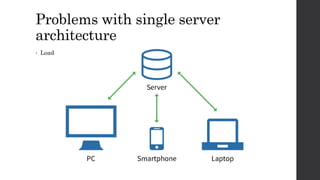
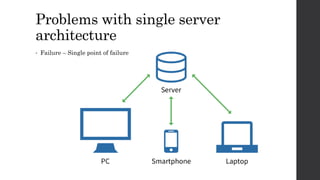
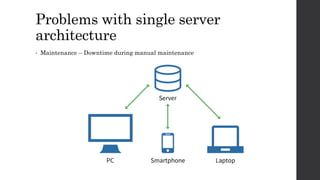
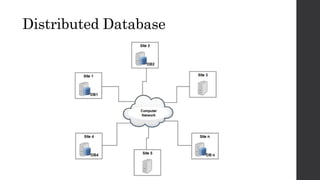
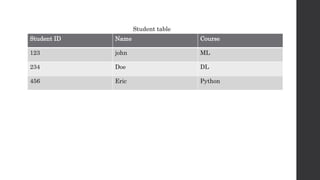
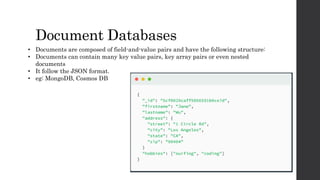
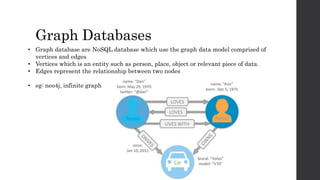
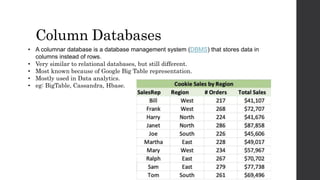
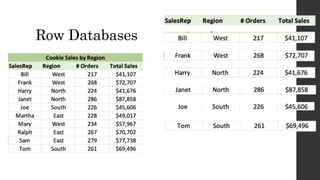
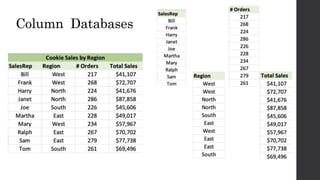
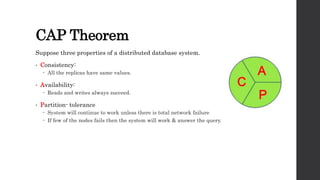
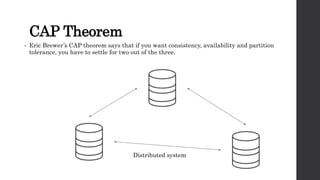
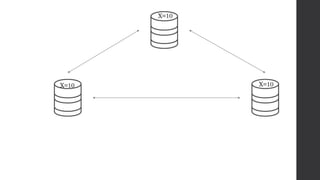
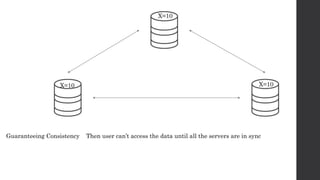
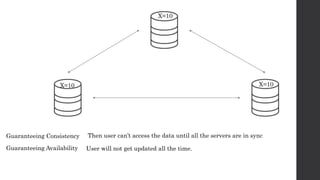
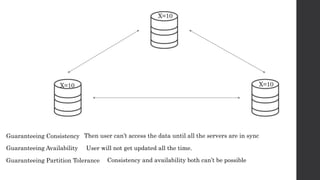
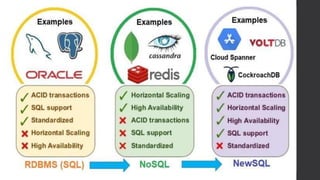
The document discusses the limitations of relational databases (RDBMS), highlighting issues such as rigidity of schema, costly scalability, and challenges with normalization and maintenance. It contrasts these with NoSQL databases, which are schema-less, support easier scaling, and are suitable for diverse data types and patterns, mentioning various NoSQL types like key-value, document, graph, and column databases. Additionally, it introduces NewSQL databases that aim to combine the transactional benefits of RDBMS with the scalability of NoSQL.


![Problems With RDBMS
• Should know the entire schema upfront
• Every record have same properties [rigid structure]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-220126121545/85/No-SQL-3-320.jpg)
![Problems With RDBMS
• Should know the entire schema upfront
• Every record have same properties [rigid structure]
• Scalability is costly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-220126121545/85/No-SQL-4-320.jpg)
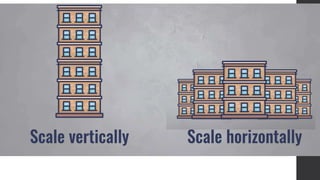
![Problems With RDBMS
• Should know the entire schema upfront
• Every record have same properties [rigid structure]
• Scalability is costly
• Scaling relational database is hard](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-220126121545/85/No-SQL-8-320.jpg)
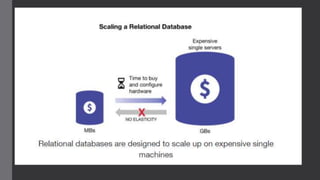
![Problems With RDBMS
• Should know the entire schema upfront
• Every record have same properties [rigid structure]
• Scalability is costly
• Scaling relational database is hard
• Normalization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-220126121545/85/No-SQL-10-320.jpg)
![Problems With RDBMS
• Should know the entire schema upfront
• Every record have same properties [rigid structure]
• Scalability is costly
• Scaling relational database is hard
• Normalization
• Altering schema on a running database is expensive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-220126121545/85/No-SQL-11-320.jpg)
![Problems With RDBMS
• Should know the entire schema upfront
• Every record have same properties [rigid structure]
• Scalability is costly
• Scaling relational database is hard
• Normalization
• Altering schema on a running database is expensive
• Horizontal scaling is a problem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosql-220126121545/85/No-SQL-12-320.jpg)