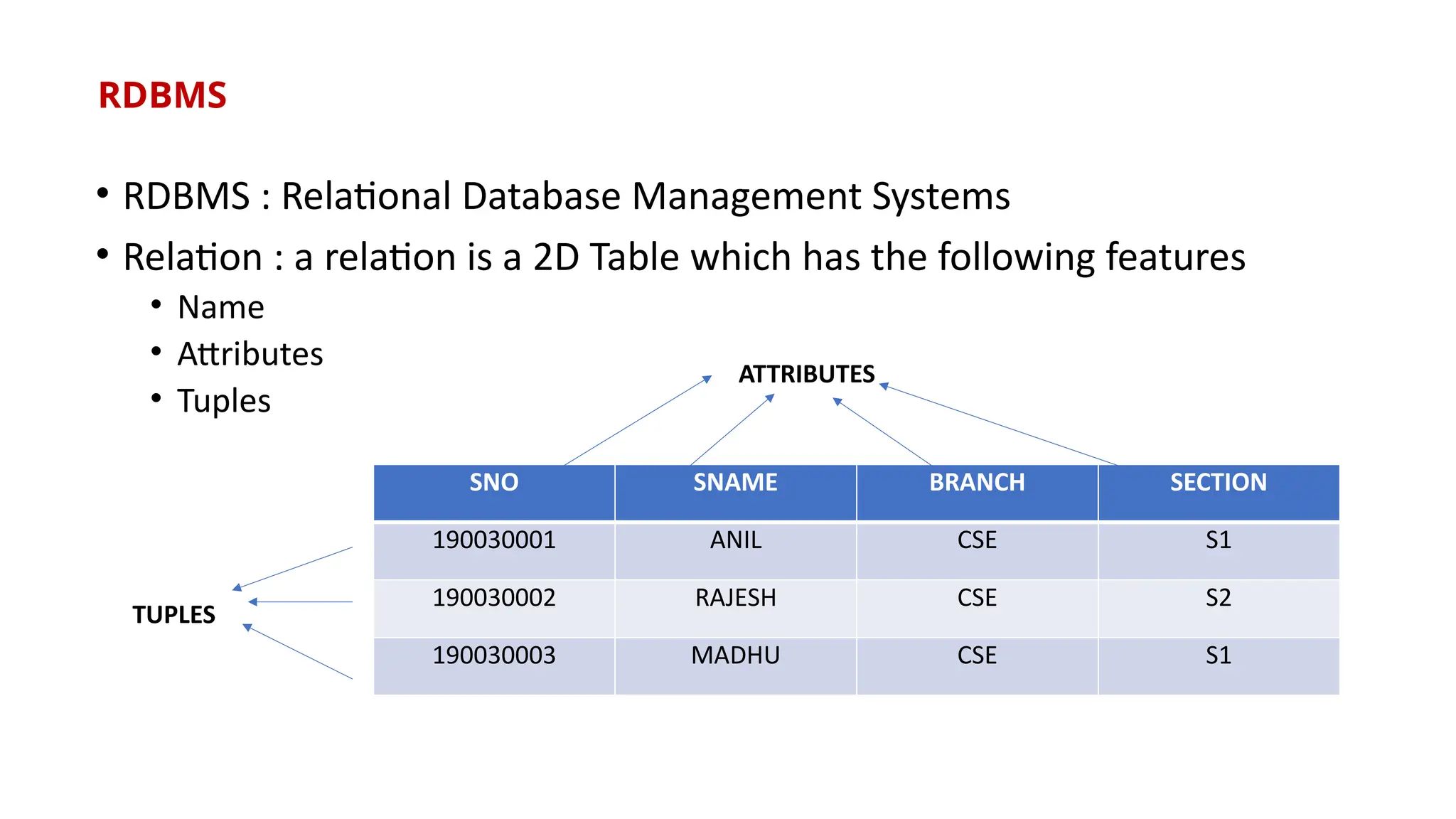
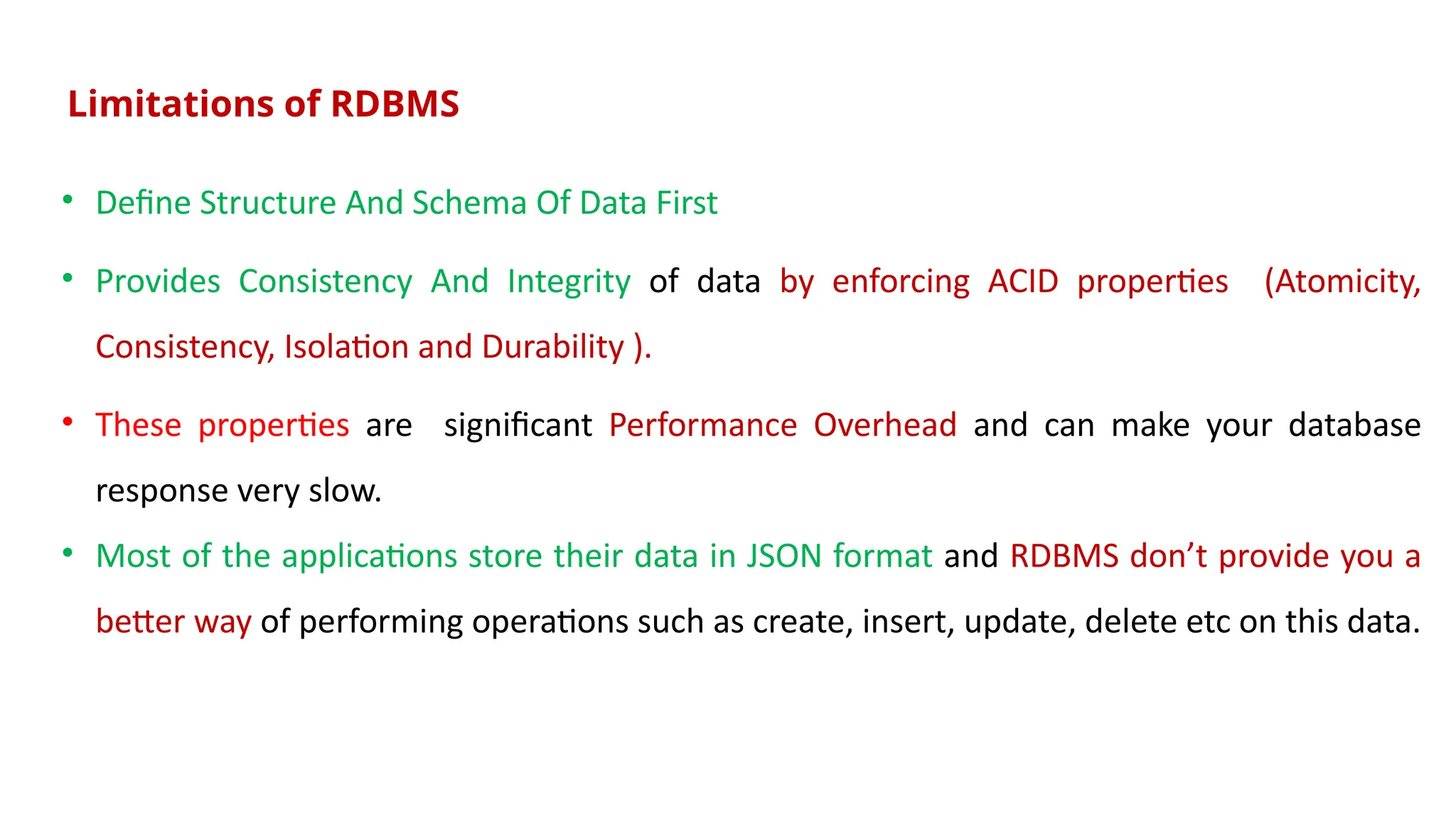
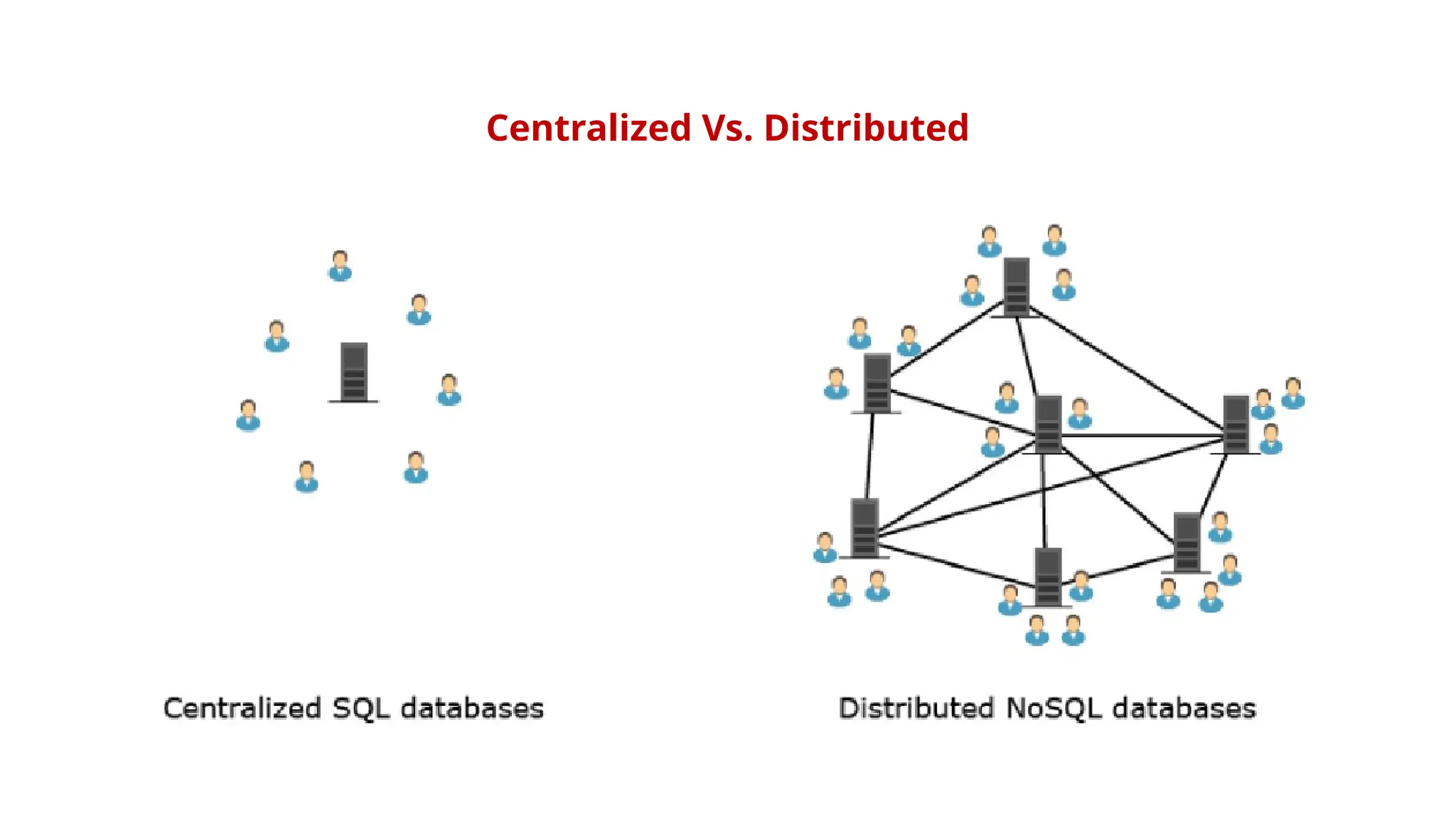
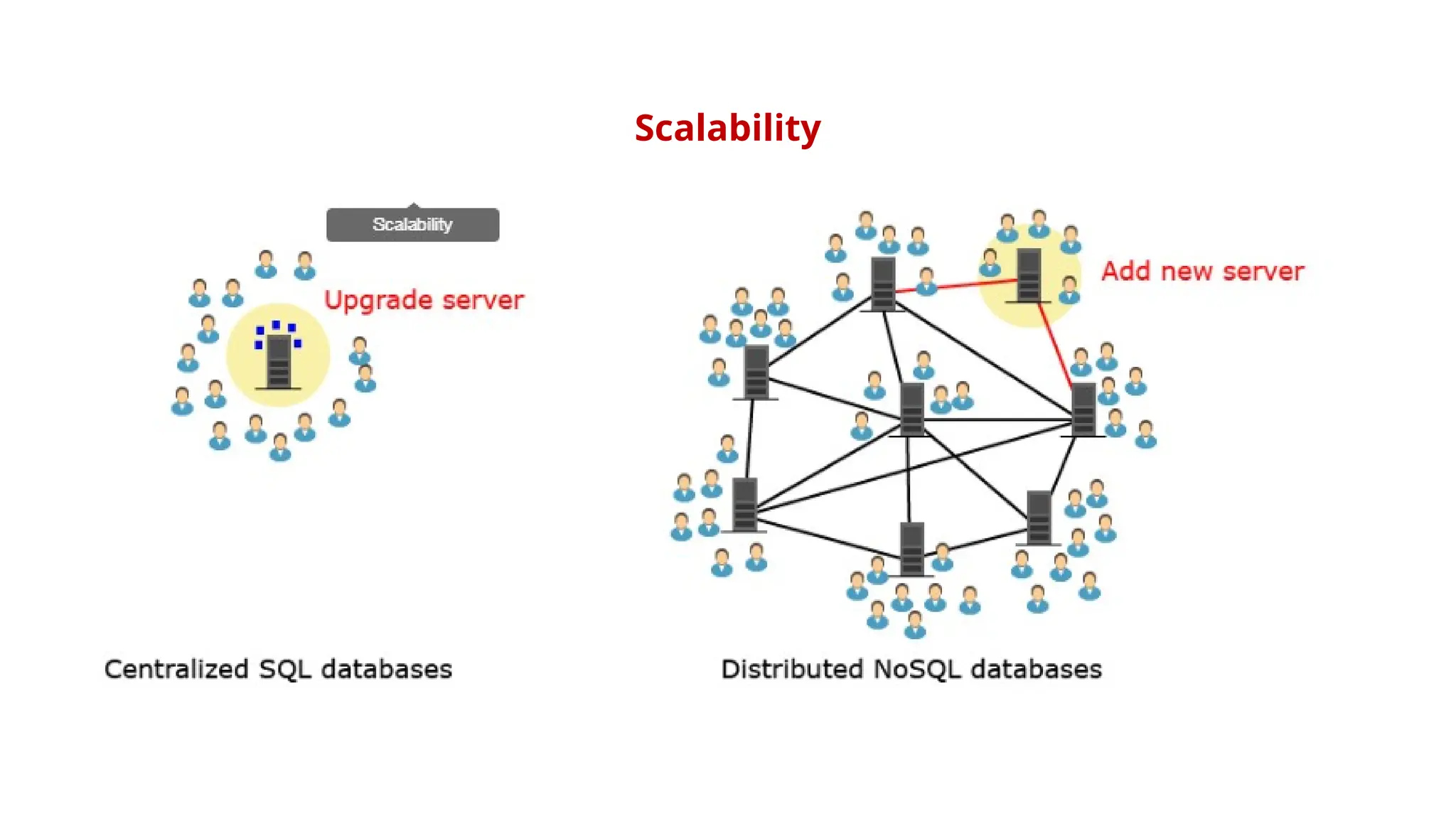
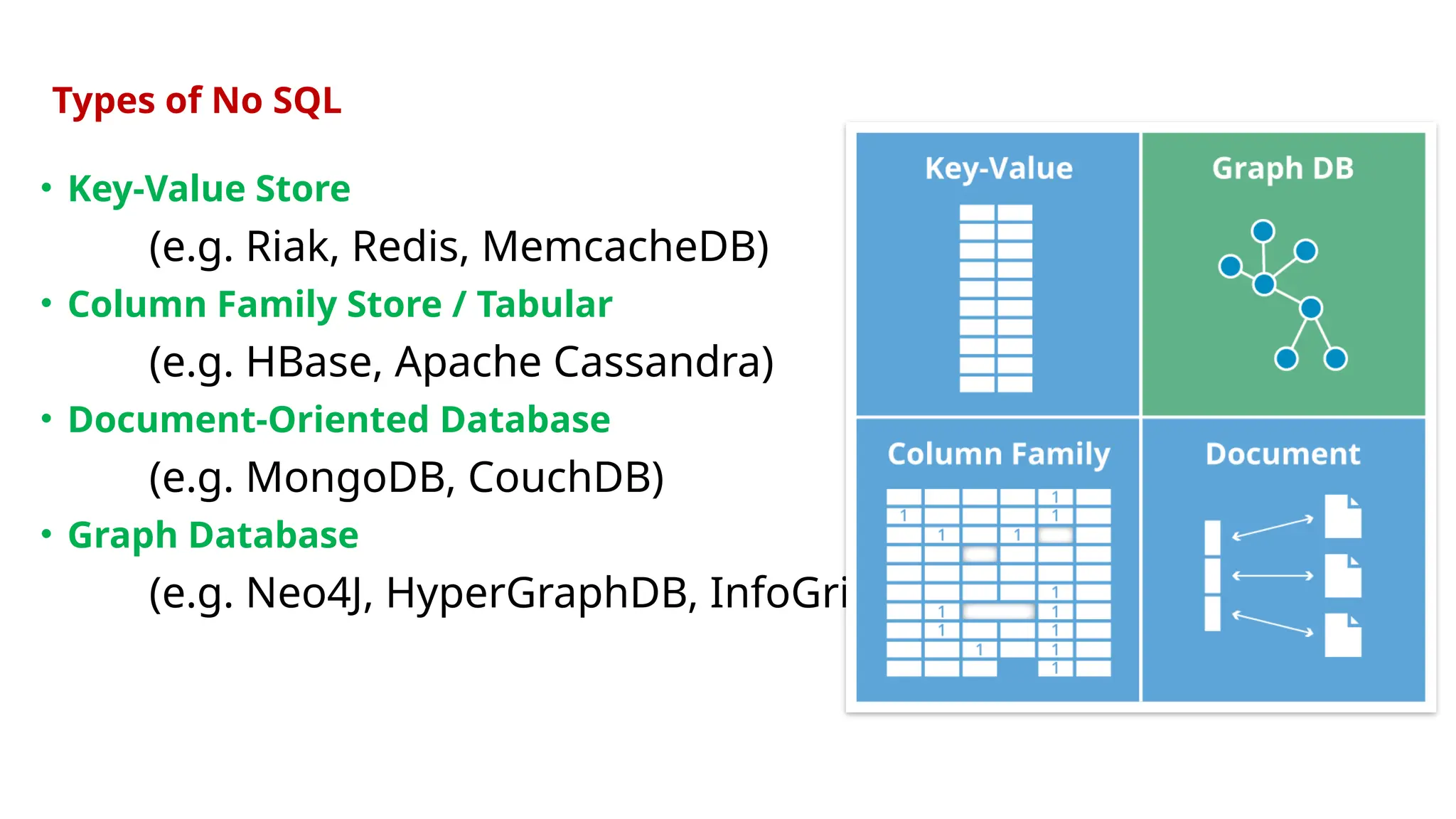
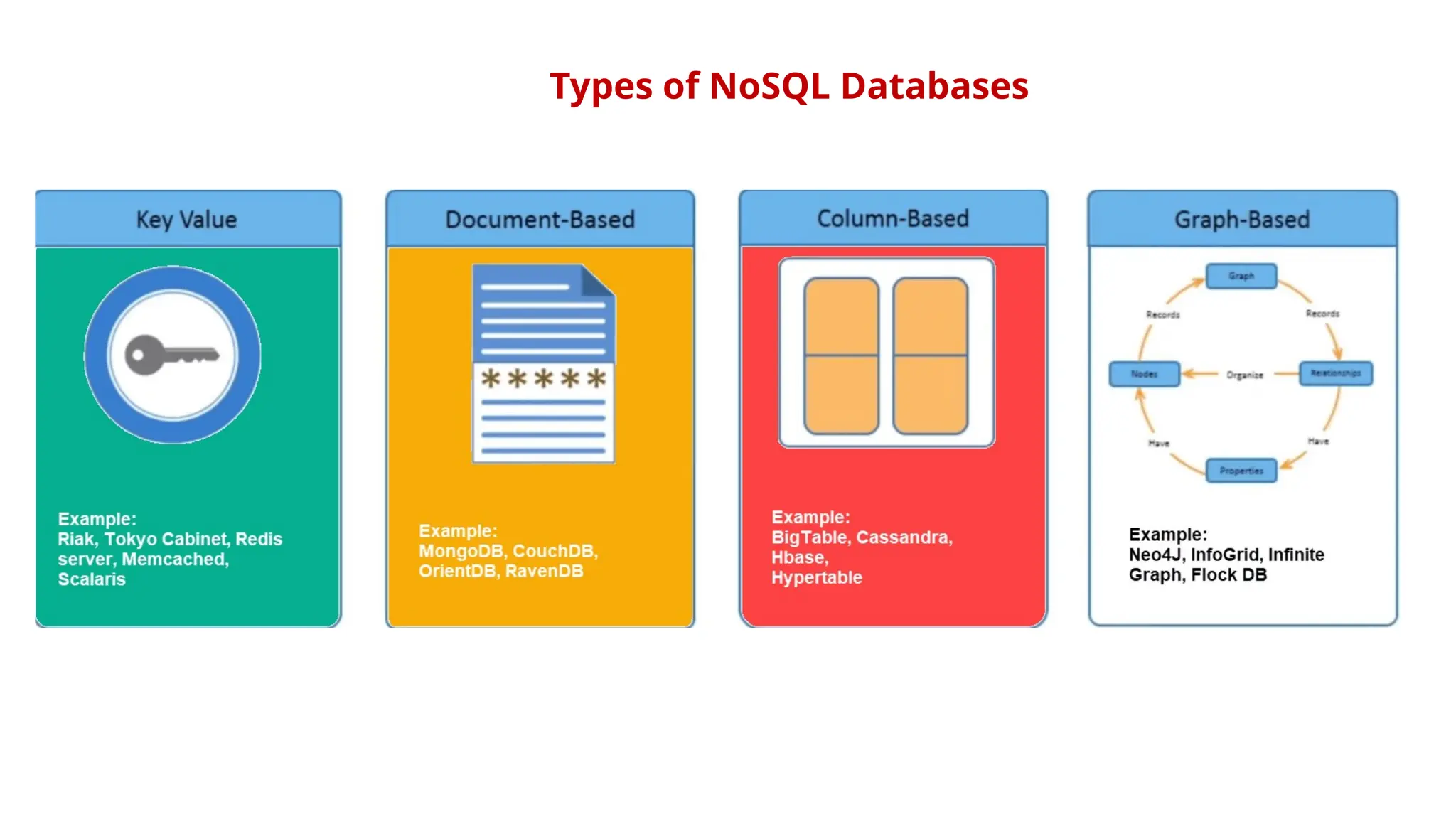
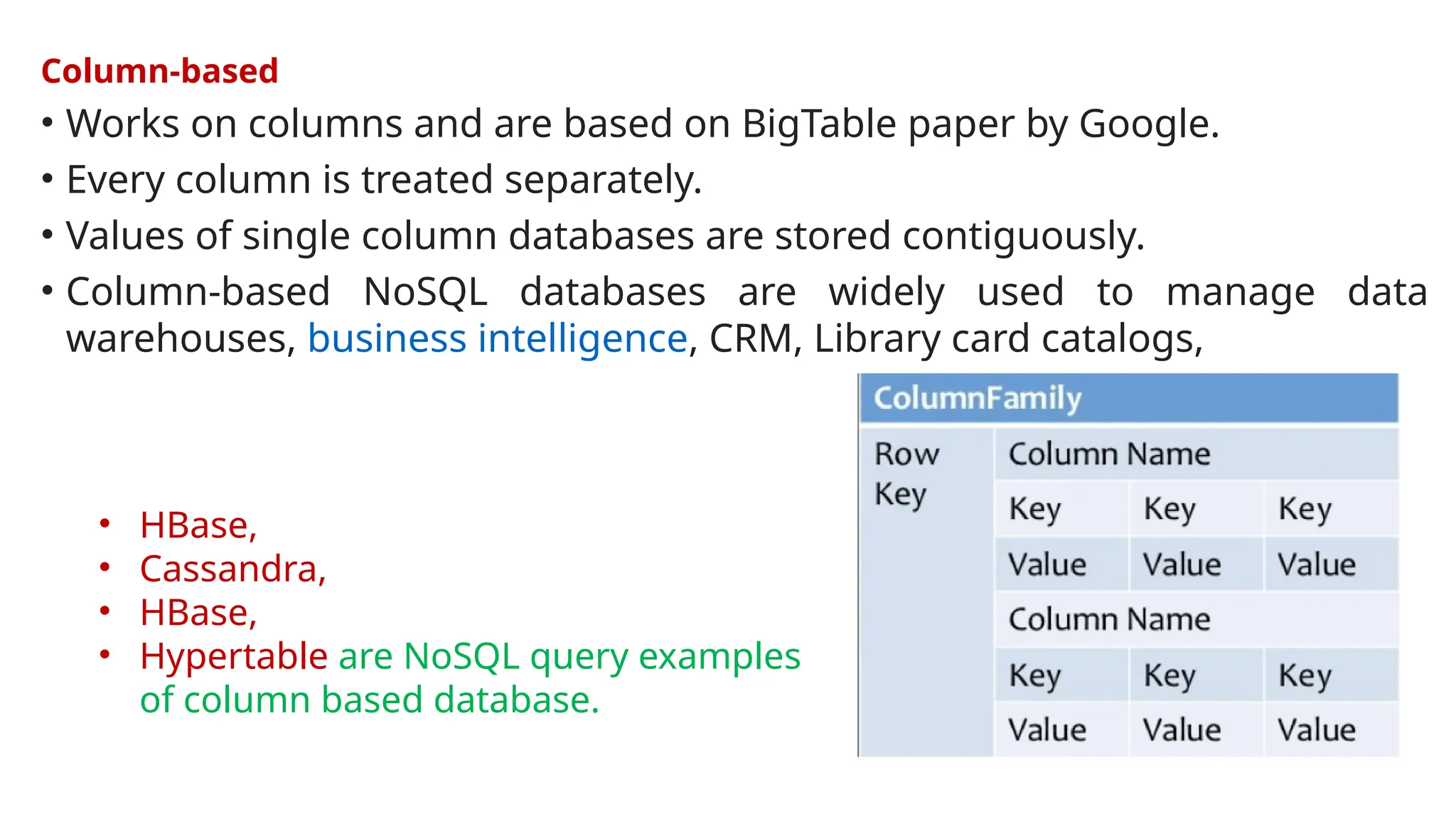
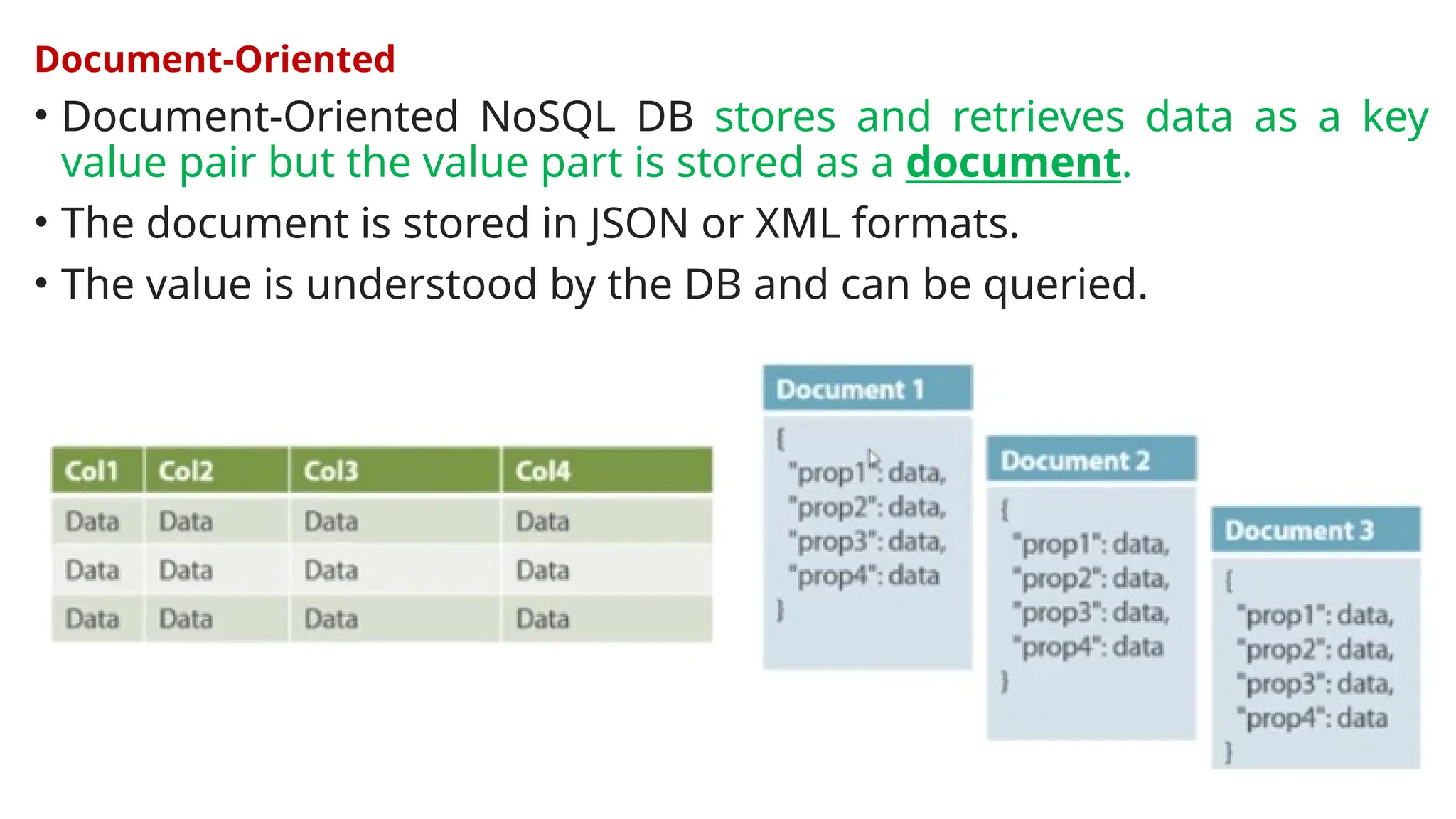
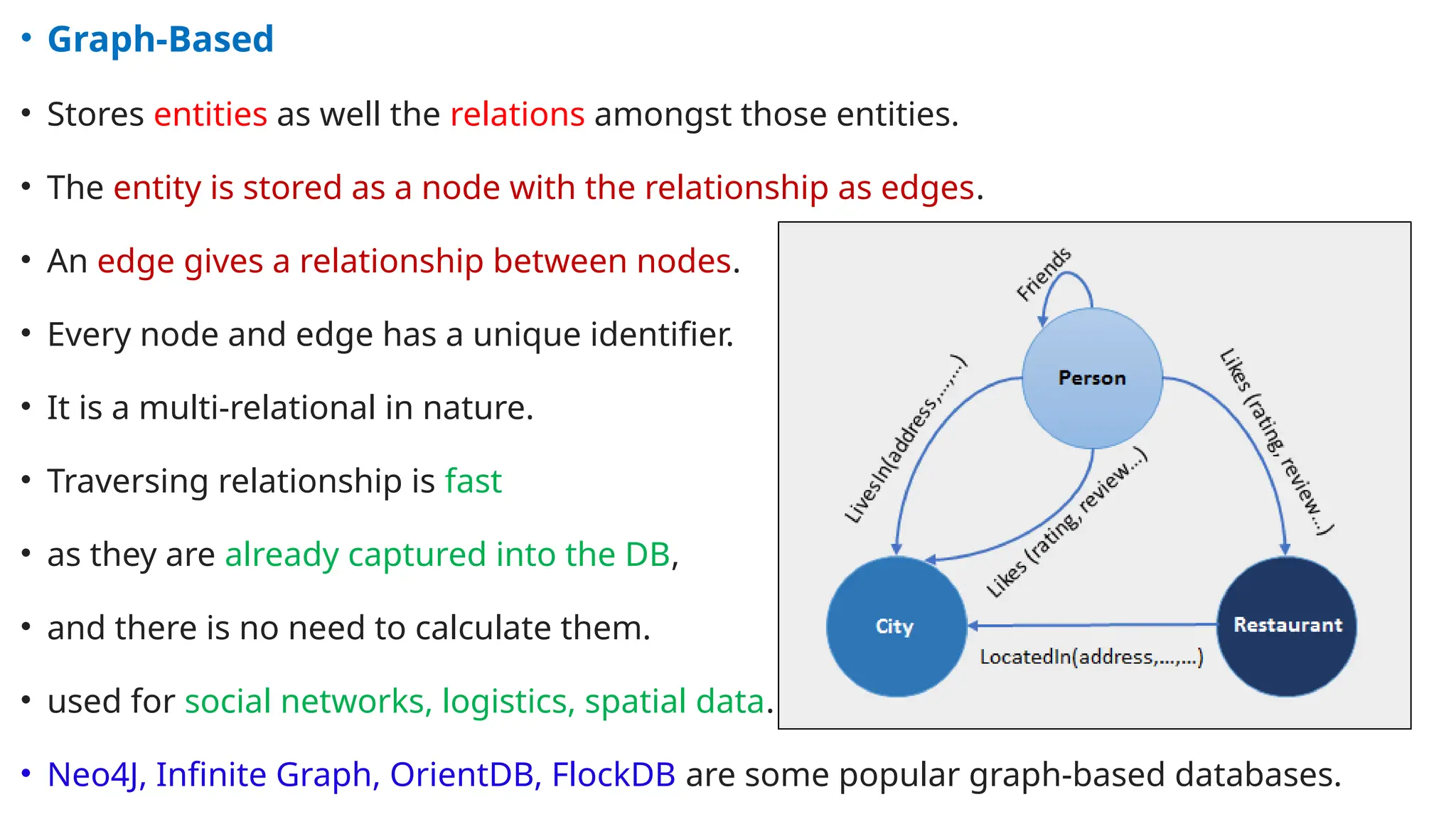
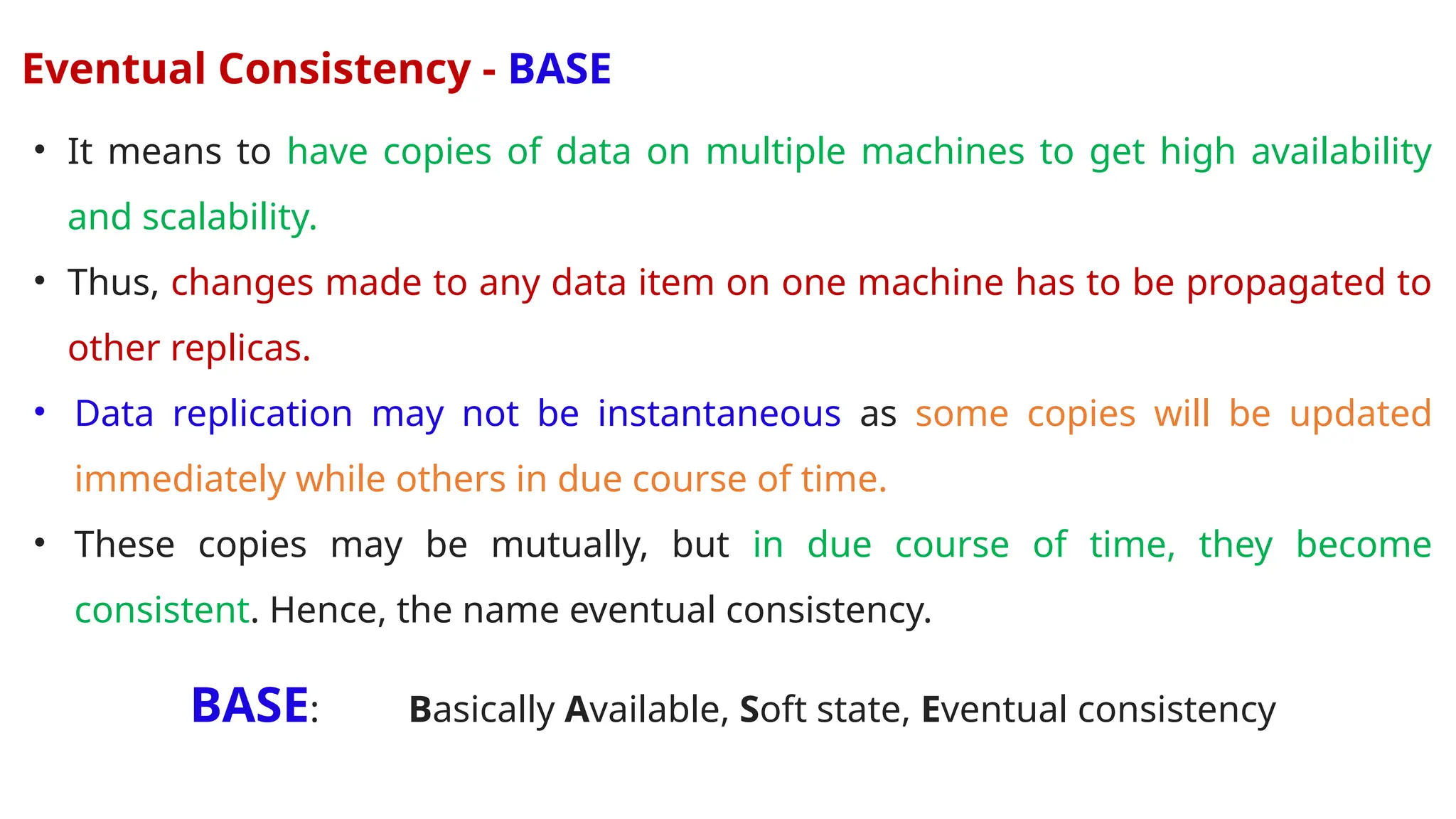
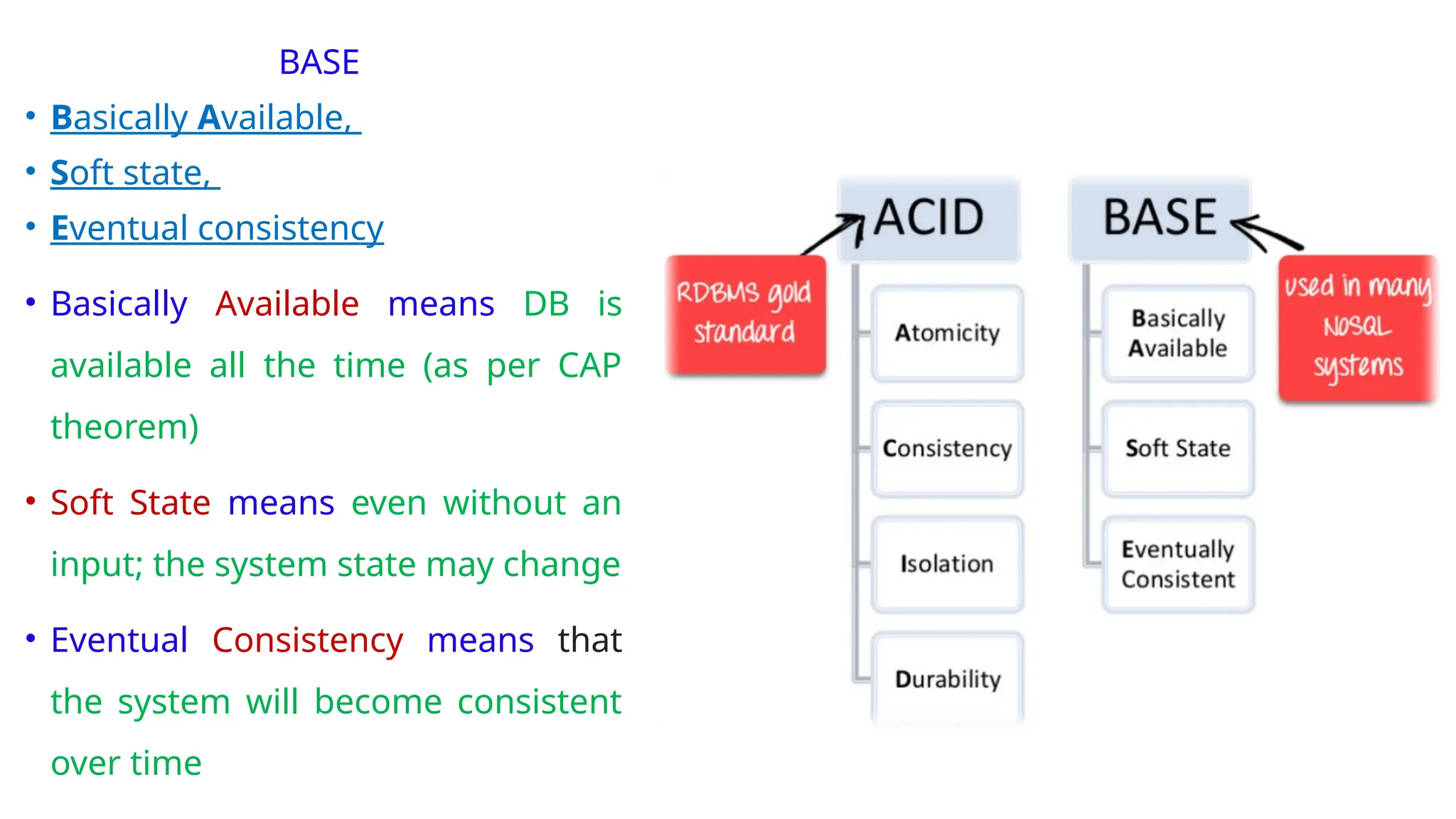
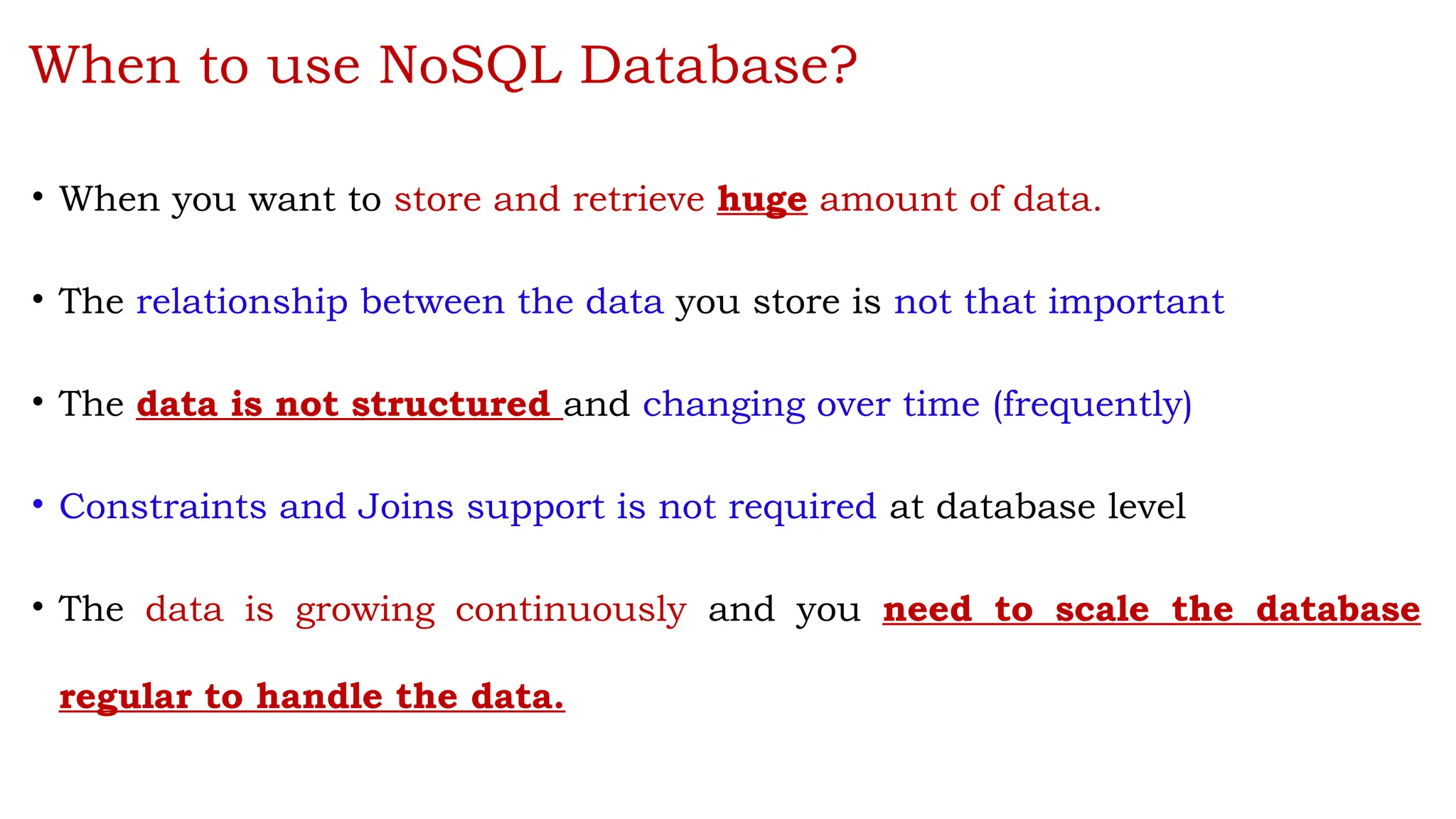
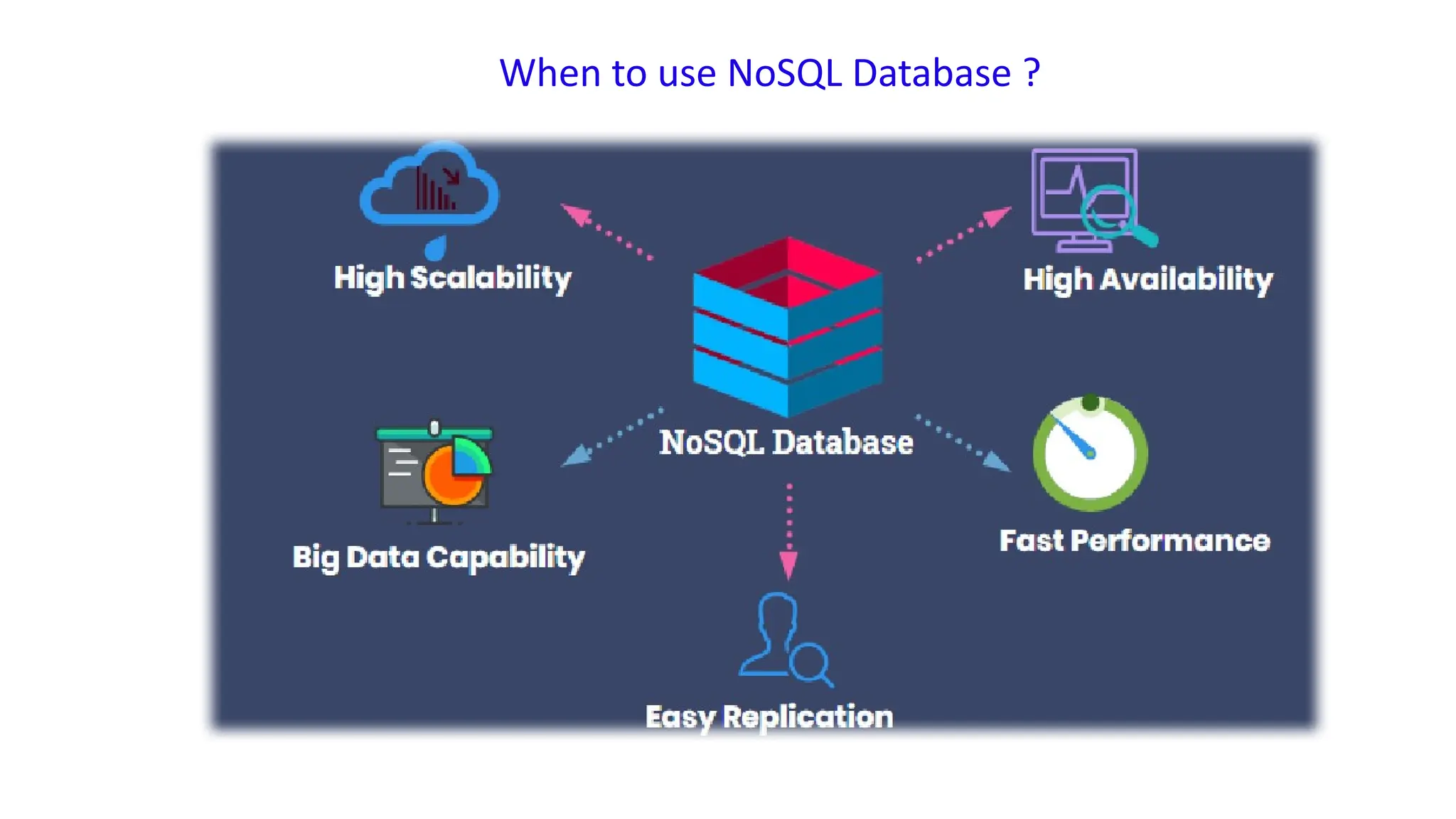
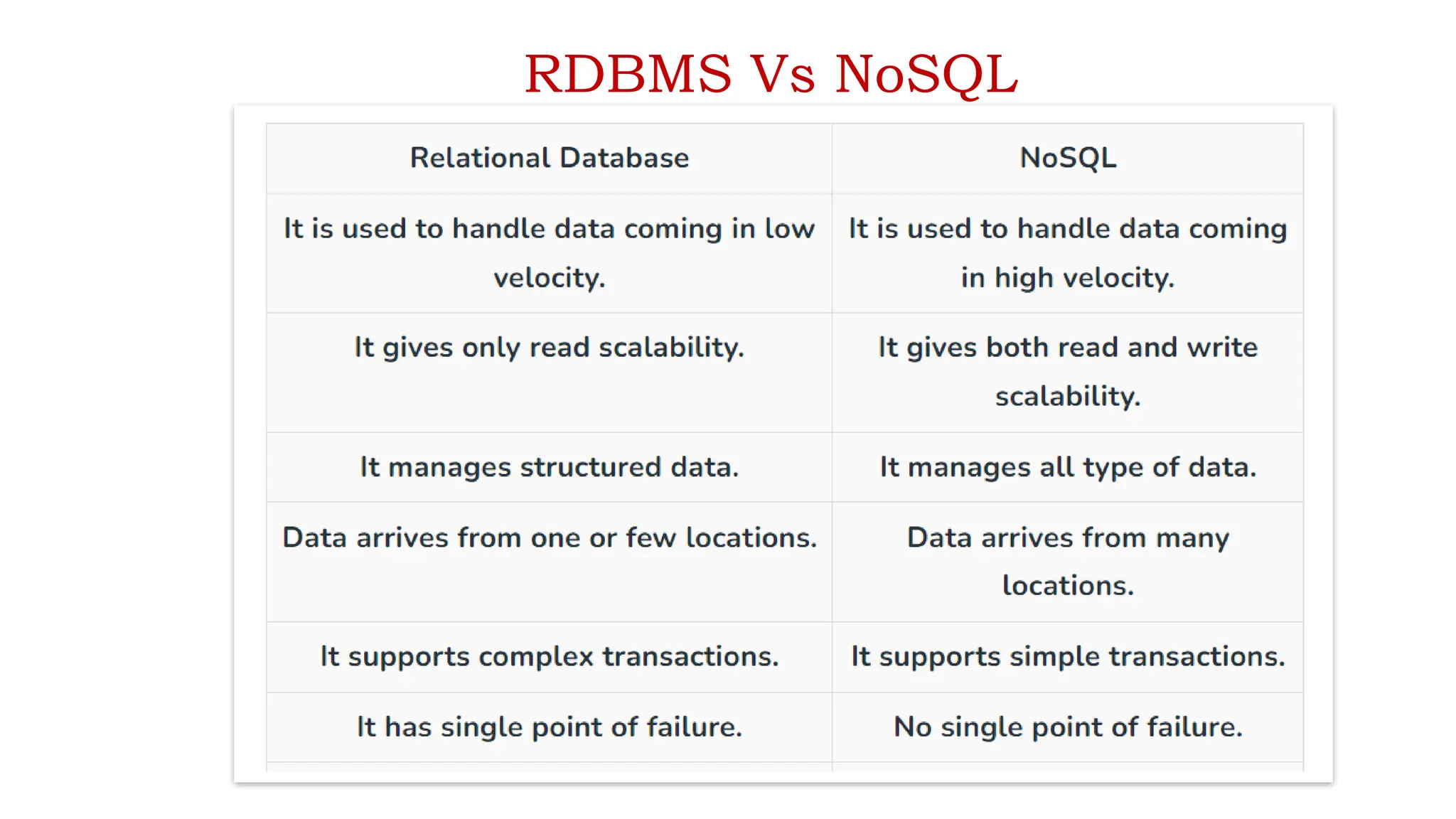
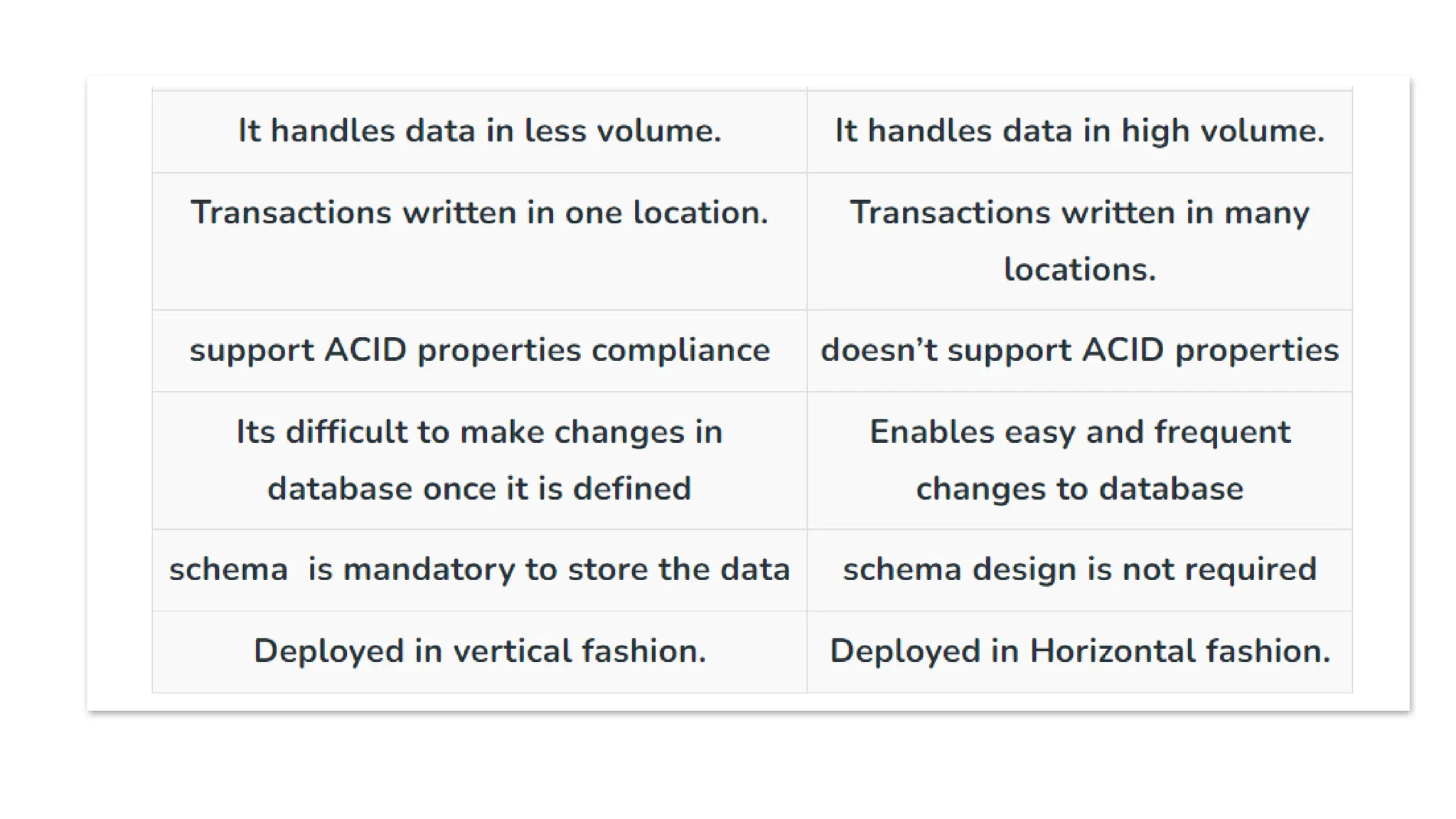
The document outlines a NoSQL database lab course for B.Tech students, highlighting prerequisites, course outcomes, and key differences between NoSQL and traditional RDBMS. It discusses various types of NoSQL databases, including key-value stores, column family stores, document-oriented databases, and graph databases, along with the CAP theorem and eventual consistency. The document emphasizes the advantages of NoSQL, such as handling big data and providing faster performance and flexibility compared to RDBMS.