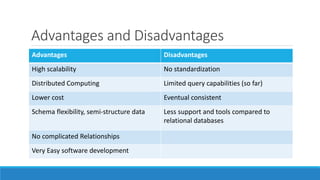
The document provides an overview of NoSQL databases, highlighting their advantages for handling large-scale, distributed data while noting the limitations of traditional relational databases regarding consistency and scalability. It discusses the CAP theorem, explaining the trade-offs between consistency, availability, and partition tolerance in distributed systems. Additionally, it describes various types of NoSQL databases, their use cases, and the emergence of NewSQL as a hybrid model combining aspects of both NoSQL and traditional relational approaches.