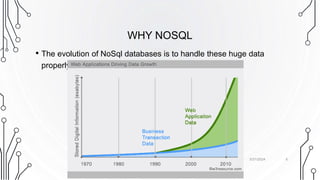
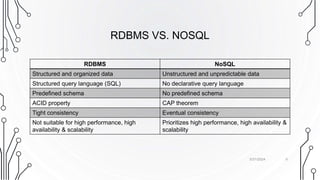
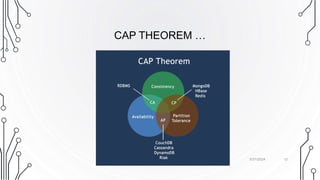
The document provides an overview of NoSQL databases, contrasting them with traditional RDBMS in aspects like data structure, scalability, and the CAP theorem. NoSQL databases accommodate unstructured data, prioritize flexibility, and often feature high scalability and performance. It categorizes NoSQL systems into key-value stores, column-oriented databases, graph databases, and document-oriented databases, each with distinct characteristics and use cases.