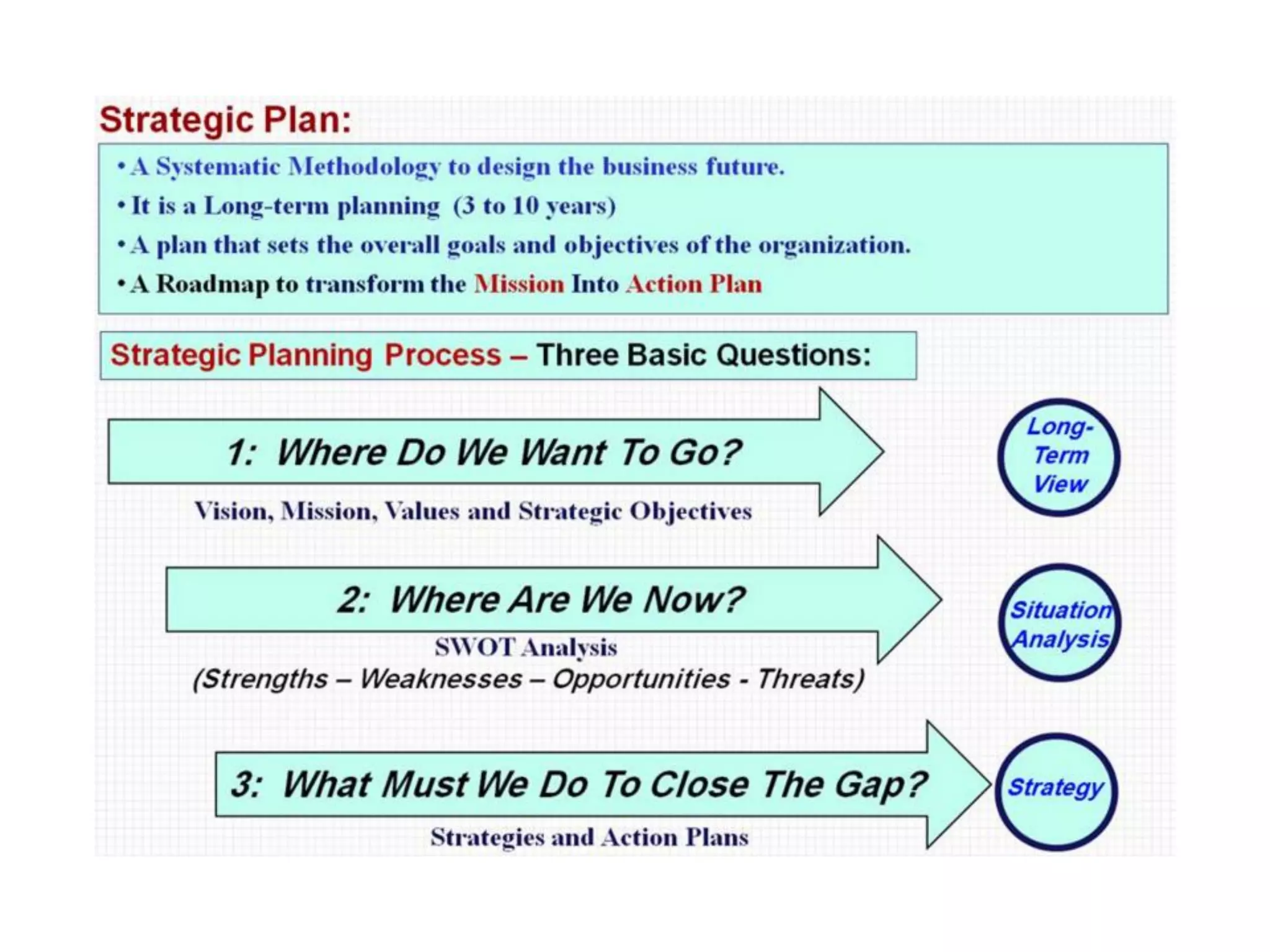
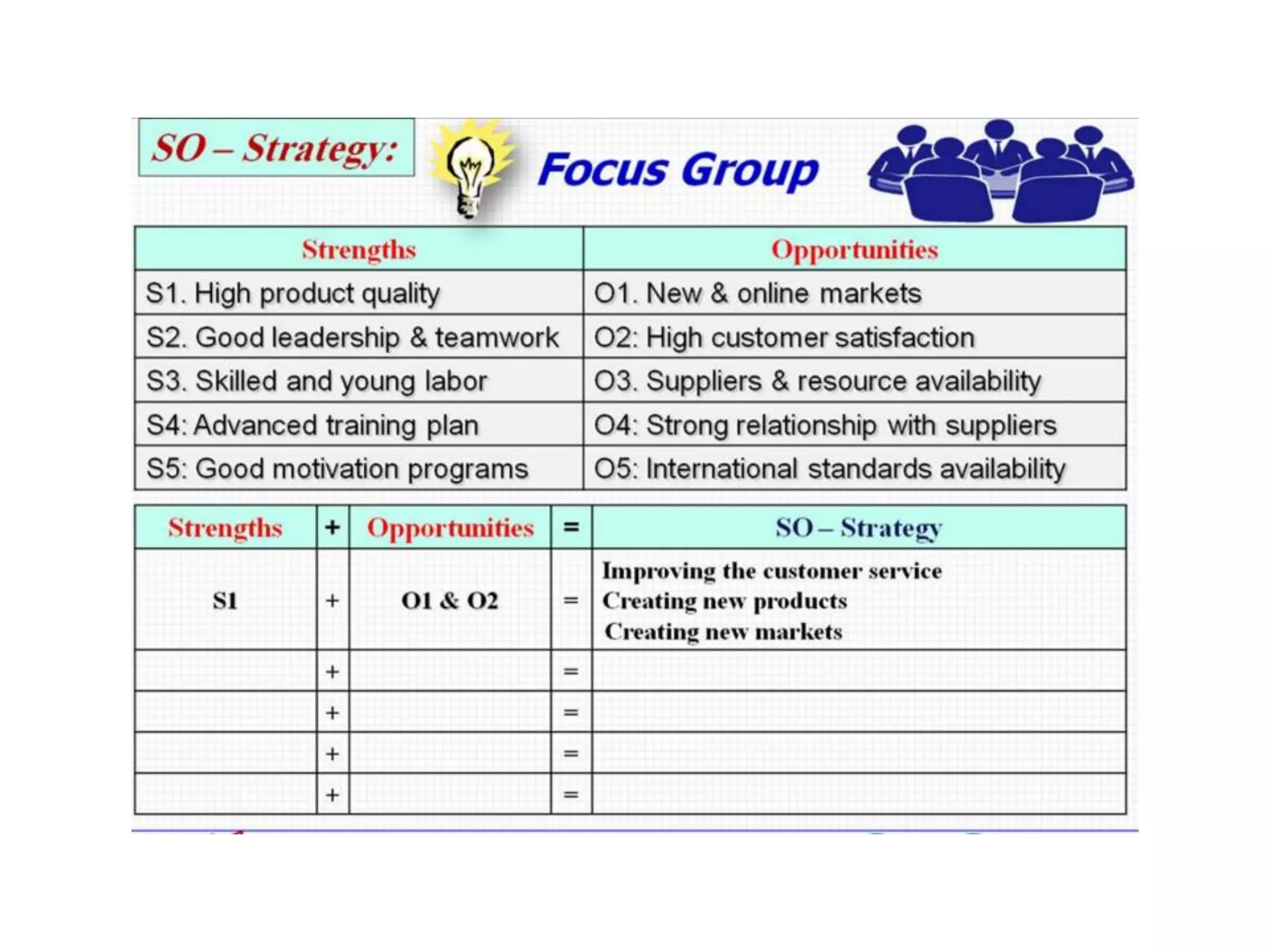
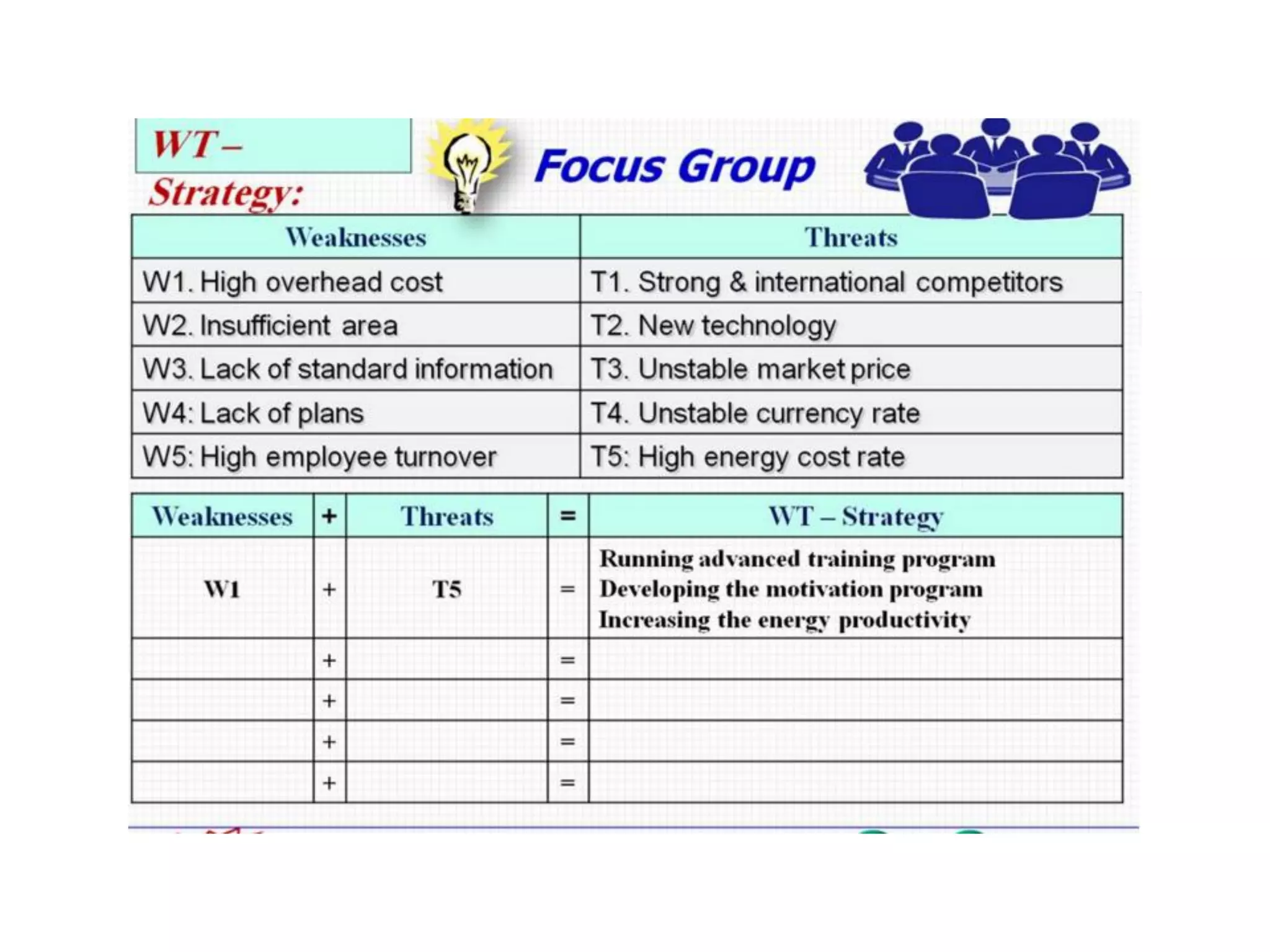
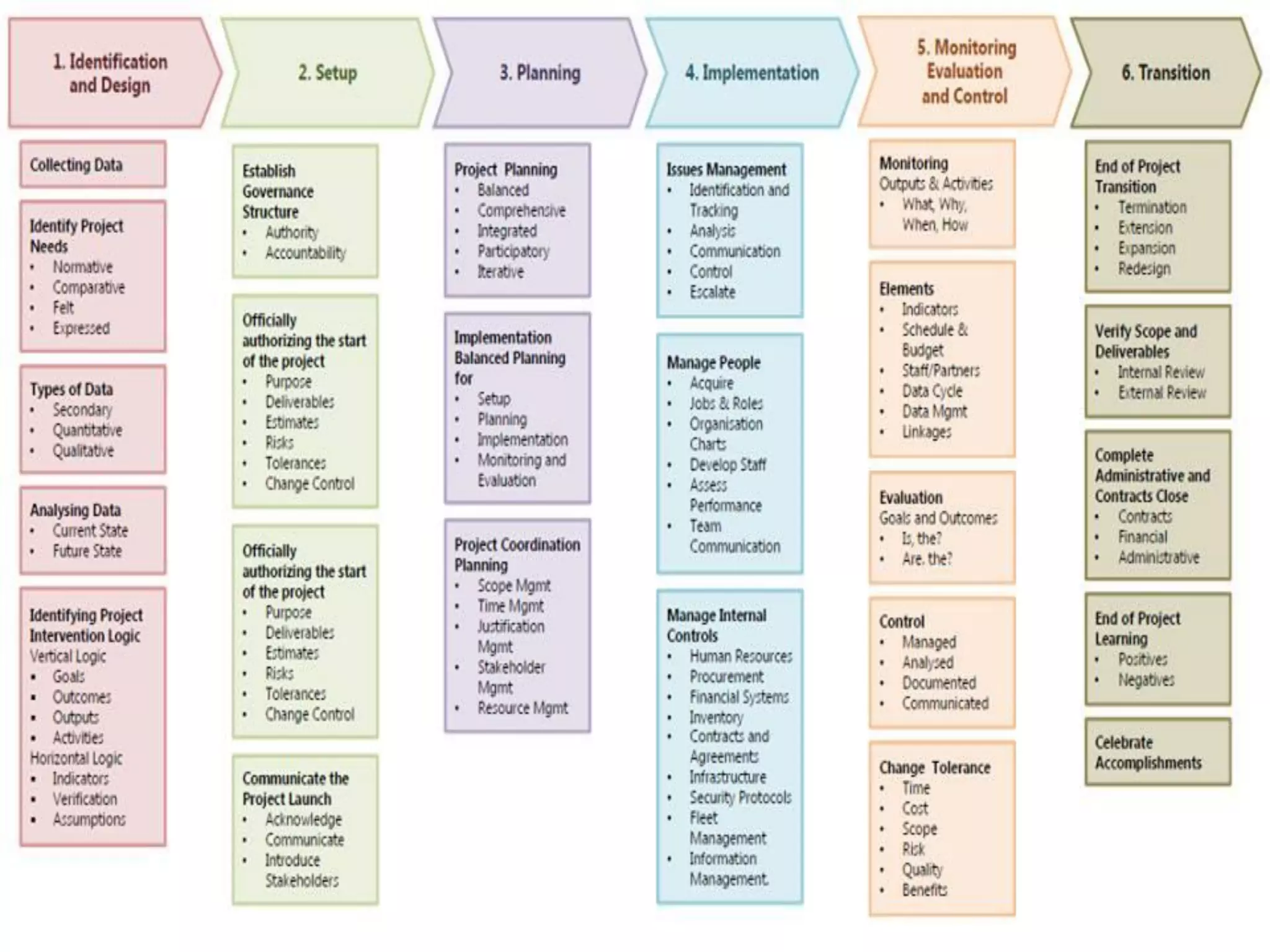
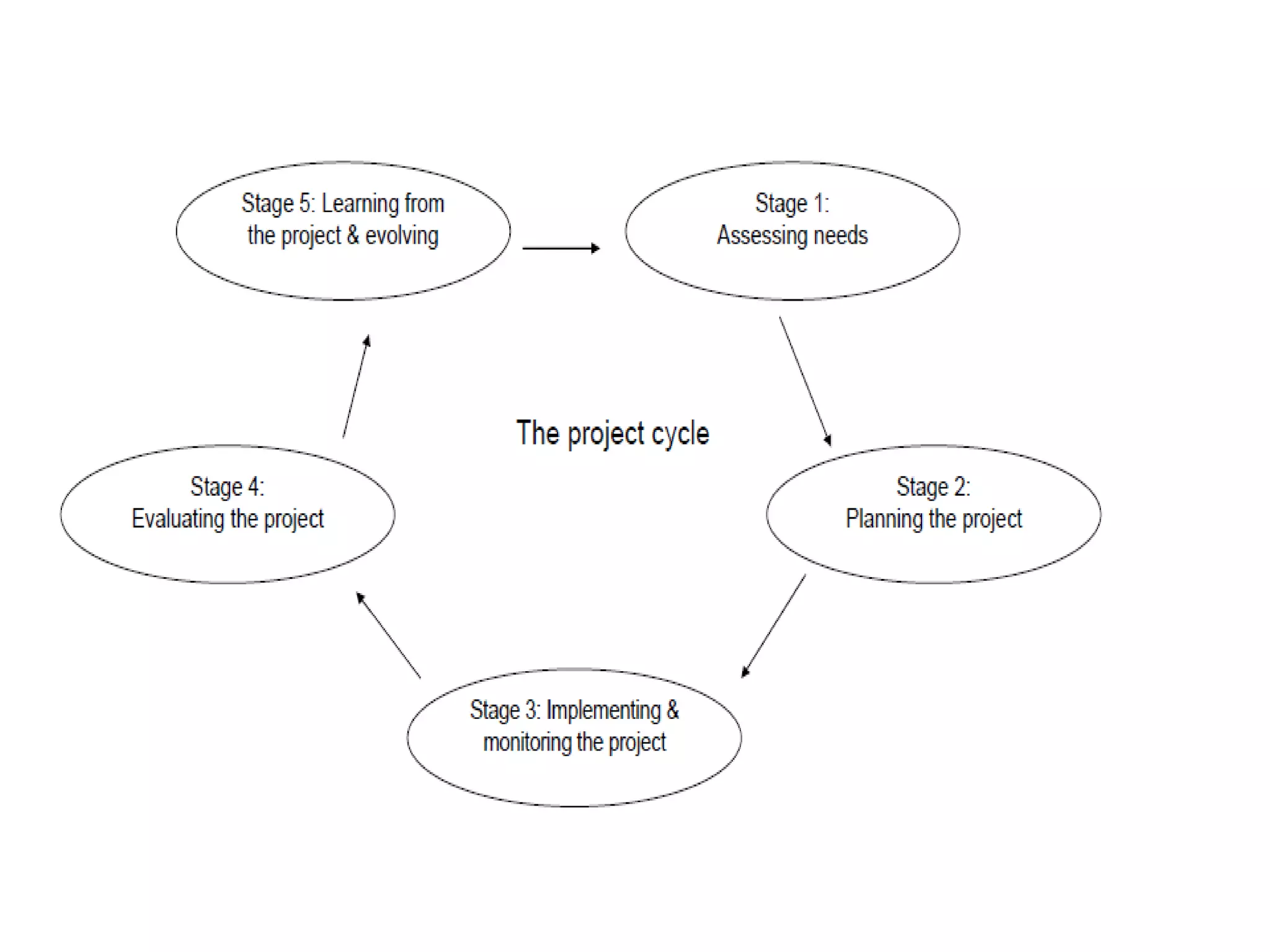
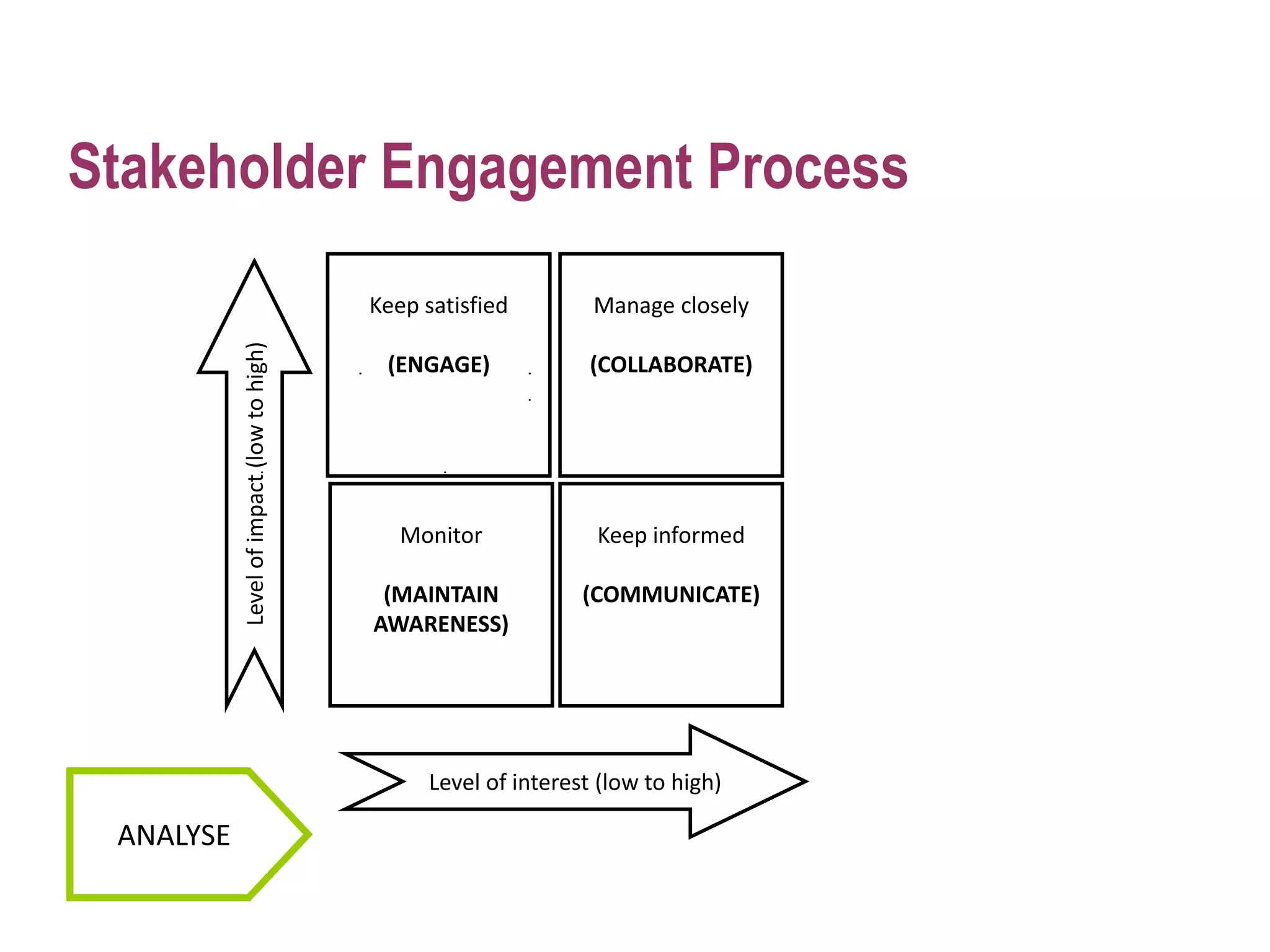
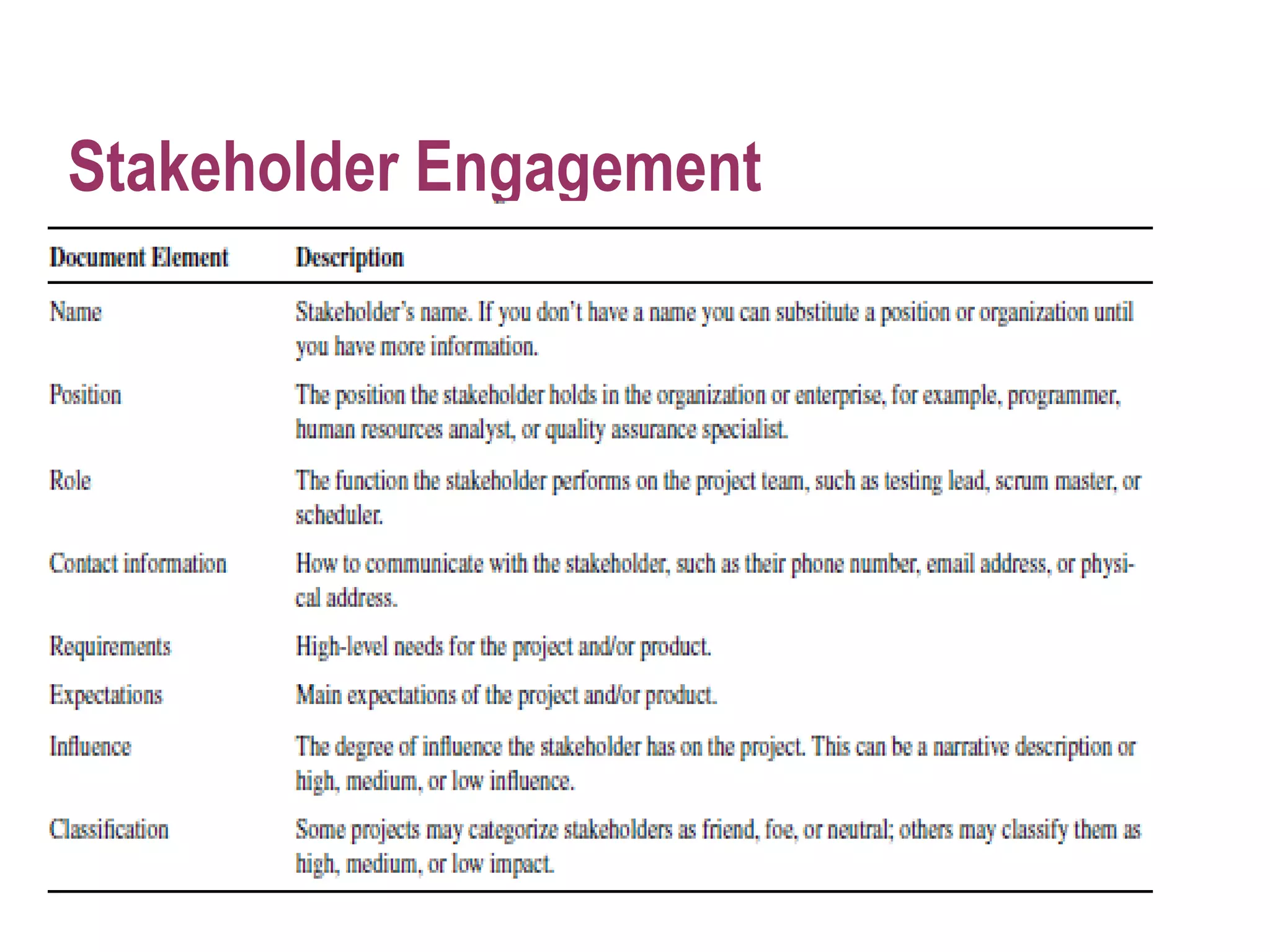
The document discusses project management and stakeholder engagement. It provides information on identifying, analyzing, planning and engaging stakeholders. The stakeholder engagement process involves identifying who will be impacted and involved, analyzing their interests and impact levels, and planning engagement strategies. The document also discusses principles of evaluation including relevance, efficiency, effectiveness, impact and sustainability as key criteria for evaluating development assistance programs and projects.