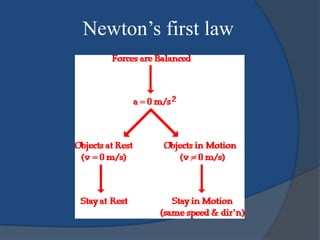
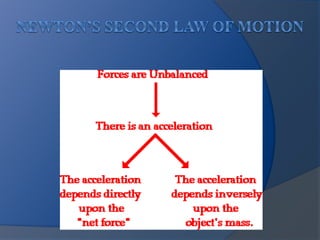
Isaac Newton was an influential English scientist born in 1642 who made fundamental contributions to physics, including establishing the laws of motion and universal gravitation. He formulated laws of motion and universal gravitation, published in his work "Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica", demonstrating that the motions of celestial bodies and objects on Earth could be explained by the same principles. Newton also made advances in optics and mathematics, developing calculus independently of Gottfried Leibniz. His work was revolutionary and had a major impact on scientific thought.