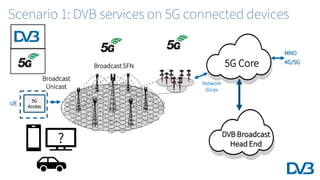
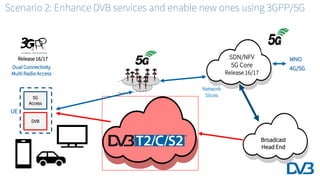
The document discusses the potential for 5G and broadcast technologies to work together. It provides background on past attempts at broadcast to handhelds that failed and lessons learned. 5G technologies like FeMBMS/enTV broadcast mode and network slicing could enable improved broadcast to mobile/indoor receivers. The DVB is analyzing scenarios for using 5G networks to distribute DVB services or enhance DVB services with 5G capabilities. Ongoing work includes defining collaboration between DVB providers and 5G operators.