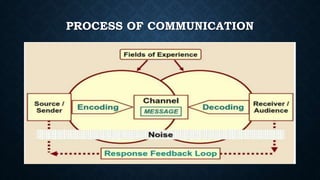
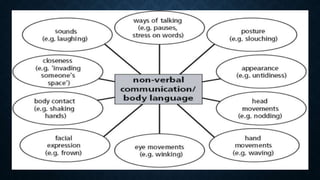
The document discusses international communication. It defines communication as the exchange of information, ideas, thoughts, feelings and emotions. International communication occurs across borders and is used to communicate beyond national boundaries. It involves government to government, business to business, and people to people interactions at a global level. The historical context discusses how communication evolved from smoke signals, shouting, clay tablets, and developed with technologies like the telegraph, radio, television and internet. Key tools of international communication include cultural exchange, mass media, news agencies, and news channels. Actors, technology, and modes of production are elements, while its scope includes promoting understanding and influencing policies across political, social, cultural, economic and military spheres.