Recommended
PPTX
PPTX
PPT
PPT
TAEM10:Intracranial emergency
PPT
DOC
PDF
Pharmacotherapy in patient with stroke 2555
PPT
PPS
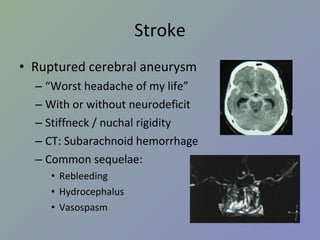
PPSX
USMLE -United States Medical License Examinations Orientation
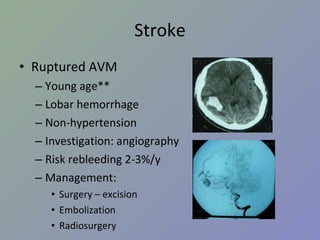
DOC
PDF
PPTX
PPT
ortho 02 orthopaedic complication & prevention + orthopaedic trauma (practica...
PPTX
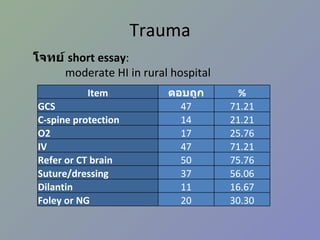
PPTX
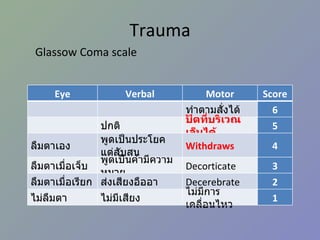
Cerebral Hemorrhage By Arlyn M. Valencia, M.D. Associate Professor Of Neurol...
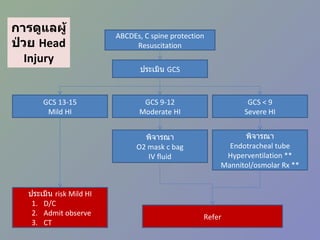
PDF
PPTX
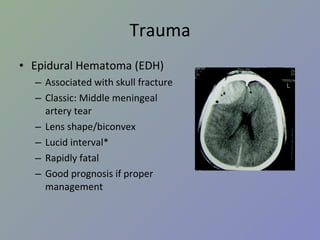
Arteriovenous Malformation
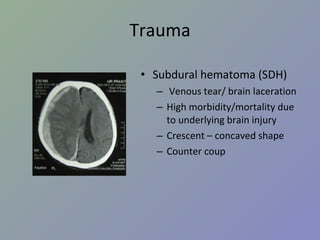
PPT
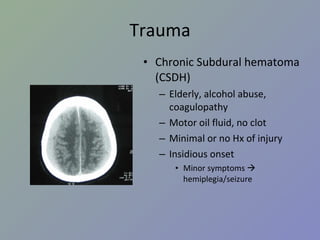
PDF
Mdcu Preventive Screening
PPT
PPT
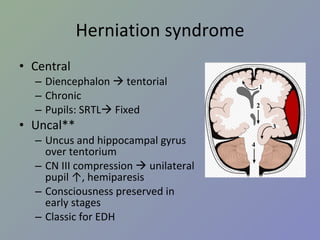
PDF
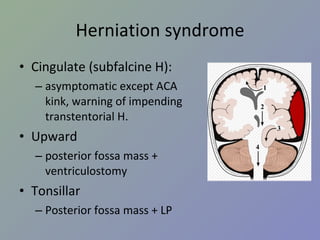
PPT
PDF
PDF
PPTX
Cerebral Hemorrhage By Arlyn M. Valencia, M.D. Associate Professor, Universit...
PPT
Tutorial national board 2010 Nephrology
PDF
Emergency care to head injured patient
PPTX
More Related Content
PPTX
PPTX
PPT
PPT
TAEM10:Intracranial emergency
PPT
DOC
PDF
Pharmacotherapy in patient with stroke 2555
PPT
Viewers also liked
PPS
PPSX
USMLE -United States Medical License Examinations Orientation
DOC
PDF
PPTX
PPT
ortho 02 orthopaedic complication & prevention + orthopaedic trauma (practica...
PPTX
PPTX
Cerebral Hemorrhage By Arlyn M. Valencia, M.D. Associate Professor Of Neurol...
PDF
PPTX
Arteriovenous Malformation
PPT
PDF
Mdcu Preventive Screening
PPT
PPT
PDF
PPT
PDF
PDF
PPTX
Cerebral Hemorrhage By Arlyn M. Valencia, M.D. Associate Professor, Universit...
PPT
Tutorial national board 2010 Nephrology
Similar to NeuroSx step2 Review
PDF
Emergency care to head injured patient
PPTX
PDF
Thai hemorrhagic stroke guideline 2008
PPTX
Neurosurgery topics for residents
PDF
CPG Thai Stroke infarct retrieved since 2555
PPTX
Clinical practice guidelines mild head injury
PPTX
2010_PMC Neurological Disease
PPT
Brain And Craniofacial (Thai)
PPT
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
Motor weakness and Cerebrovascular Disease
PPTX
PPT
PDF
Severe trauma and traumatic shock 14 พค.58
More from vora kun
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
Nt2553step3round1 28NOV2553
PDF
Osce ศรว ครั้งที่สอง 10jan53
PDF
PDF
PDF
Thai Osteoporosis guideline 2553
PPT
Abnormal pap smear ศิริราช ppt
PPT
ortho 02 orthopaedic complication & prevention + orthopaedic trauma (practica...
PPT
ortho 06 common ortho dis 2 edited 12 mar 10
PPT
ortho 05 common rheumatic dx rx
PPT
ortho 01 management of open fracture-update by kk 31052010
PPT
ortho 04 drugs in orthopaedic (principle & common use)
PPT
ortho 03 principle of closed reduction in fracture and dislocation
PDF
PDF
PDF
Step3 Tutorial by SWU book2
PDF
Step3 Tutorial by SWU book1
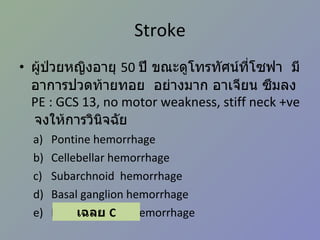
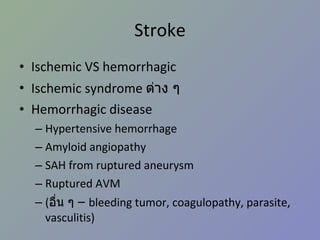
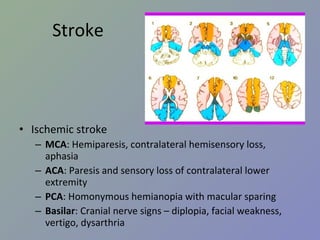
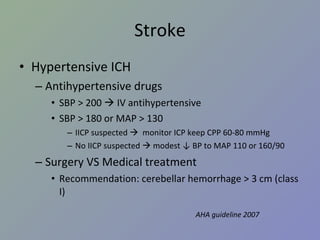
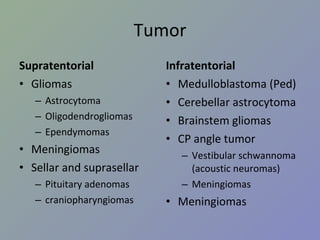
NeuroSx step2 Review 1. 2. I อาการ / ปัญหาสำคัญ ปวดศีรษะ มึนศีรษะ เวียนศีรษะ หน้ามืด เป็นลม กล้ามเนื้ออ่อนแรง ชัก สั่น กระตุก ชา ซึม ไม่รู้สติ 3. II โรค / ภาวะ / กลุ่มอาการฉุกเฉิน ( รวมทุกระบบ ) กลุ่ม 1 coma convulsion acute increased intracranial pressure Head injury 4. III โรคตามระบบ กลุ่ม 3 Benign and malignant neoplasm of brain Brain abscess Hydrocephalous Trigeminal neuralgia Head injury and spinal cord injury 5. Stroke ผู้ป่วยหญิงอายุ 50 ปี ขณะดูโทรทัศน์ที่โซฟา มีอาการปวดท้ายทอย อย่างมาก อาเจียน ซึมลง PE : GCS 13, no motor weakness, stiff neck +ve จงให้การวินิจฉัย Pontine hemorrhage Cellebellar hemorrhage Subarchnoid hemorrhage Basal ganglion hemorrhage Intraventricular hemorrhage เฉลย C 6. Stroke Ischemic VS hemorrhagic Ischemic syndrome ต่าง ๆ Hemorrhagic disease Hypertensive hemorrhage Amyloid angiopathy SAH from ruptured aneurysm Ruptured AVM ( อื่น ๆ – bleeding tumor, coagulopathy, parasite, vasculitis) 7. Stroke Ischemic VS hemorrhagic Hemorrhagic stroke มักมี sign of IICP ( ปวดหัว อาเจียน ซึมลง ) Ischemic stroke มักมาด้วย sudden neurodeficit Hemiparesis Apasia / apraxia Amaurosis fugax Onset แยกไม่ได้ Clinical แยกไม่ได้ 100% need investigation = CT 8. Stroke Ischemic stroke MCA : Hemiparesis, contralateral hemisensory loss, aphasia ACA : Paresis and sensory loss of contralateral lower extremity PCA : Homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing Basilar : Cranial nerve signs – diplopia, facial weakness, vertigo, dysarthria 9. Stroke Hemorrhagic stroke Hypertensive ICH Ruptured cerebral aneurysm Ruptured AVM Amyloid angiopathy Bleeding tumor Coagulopathy 10. Stroke Hypertensive ICH Hypertension > 90% IICP signs and symptoms (headache, vomiting, ↓consciousness) Common site: Basal ganglion – Hemiparesis, Aphasia (dominant hemisphere) Thalamus – hemianesthesia Cerebellar – ataxia, cerebellar sign +ve Pontine – pinpoint pupil 11. Stroke Hypertensive ICH Antihypertensive drugs SBP > 200 IV antihypertensive SBP > 180 or MAP > 130 IICP suspected monitor ICP keep CPP 60-80 mmHg No IICP suspected modest ↓ BP to MAP 110 or 160/90 Surgery VS Medical treatment Recommendation: cerebellar hemorrhage > 3 cm (class I) AHA guideline 2007 12. Stroke Ruptured cerebral aneurysm “ Worst headache of my life” With or without neurodeficit Stiffneck / nuchal rigidity CT: Subarachnoid hemorrhage Common sequelae: Rebleeding Hydrocephalus Vasospasm 13. Stroke Ruptured cerebral aneurysm Key point of management Refer to neurosurgeon ASAP (for clipping to prevent rebleeding) If clinical suspected but negative CT LP ดู xanthochromia Investigation of choice: 4 vessels angiography (alternative: CT angiography (CTA), MRA) 14. Stroke Ruptured AVM Young age** Lobar hemorrhage Non-hypertension Investigation: angiography Risk rebleeding 2-3%/y Management: Surgery – excision Embolization Radiosurgery 15. Stroke Investigation in intracerebral hemorrhage Consider Angiography CT angiography In Young age (< 45) Non hypertension Uncommon site (Lobar) 16. 17. Trauma ผู้ป่วยชายอายุ 50 ปี ขับรถยนต์ชนจักรยานยนต์ สลบไป 10 นาที ตื่นมารู้เรื่องดี หน่วยกู้ภัยนำส่งรพ . ตรวจร่างกายแรกรับปกติ อีก 2 ชั่วโมงซึมลง GCS E1V2M5, pupils right 3 mm, left 5 mm SRTL คิดถึงภาวะใดมากที่สุด Epidural hemorrhage Subdural hemorrhage Subarachnoid hemorrhage Intracerebral hemorrhage Diffuse axonal injury เฉลย a 18. Trauma Initial management* Epidural hematoma* Subdural hematoma* Traumatic intracerebral hematoma Traumatic SAH Skull fracture Sequalae 19. Trauma Initial management ABCDE Don’t miss! Collar (primary survey = A) ET tube in GCS ≤ 8 (primary survey = D) Search for other bleeding site in hypotensive patient GCS (Must remember!) 20. Trauma โจทย์ short essay : moderate HI in rural hospital Item ตอบถูก % GCS 47 71.21 C-spine protection 14 21.21 O2 17 25.76 IV 47 71.21 Refer or CT brain 50 75.76 Suture/dressing 37 56.06 Dilantin 11 16.67 Foley or NG 20 30.30 21. Trauma Glassow Coma scale Eye Verbal Motor Score ทำตามสั่งได้ 6 ปกติ ปัดที่บริเวณเจ็บได้ 5 ลืมตาเอง พูดเป็นประโยค แต่สับสน Withdraws 4 ลืมตาเมื่อเจ็บ พูดเป็นคำมีความหมาย Decorticate 3 ลืมตาเมื่อเรียก ส่งเสียงอืออา Decerebrate 2 ไม่ลืมตา ไม่มีเสียง ไม่มีการเคลื่อนไหว 1 22. การดูแลผู้ป่วย Head Injury ABCDEs, C spine protection Resuscitation ประเมิน GCS GCS < 9 Severe HI GCS 9-12 Moderate HI GCS 13-15 Mild HI ประเมิน risk Mild HI D/C Admit observe CT พิจารณา O2 mask c bag IV fluid Refer พิจารณา Endotracheal tube Hyperventilation ** Mannitol/osmolar Rx ** 23. Trauma Risk factors for Intracranial lesion for Mild HI Clinical findings GCS < 15 หลัง 1-2 ชั่วโมง * Amnesia ปวดศีรษะ อาเจียน มีประวัติหมดสติ มี Sign ของกะโหลกแตก ( skull Fx (Skull Base/Valve) ตรวจพบความผิดปกติทางระบบประสาท * Risk factors อายุ > 60 Coagulopathy (Warfarin, Hemophilia,etc) ชัก * ดื่มสุรา / ใช้สารเสพติด มีกลไกการบาดเจ็บที่รุนแรง เช่น โดนรถชนขณะเดินถนน 24. Trauma Epidural Hematoma (EDH) Associated with skull fracture Classic: Middle meningeal artery tear Lens shape/biconvex Lucid interval* Rapidly fatal Good prognosis if proper management 25. Trauma Subdural hematoma (SDH) Venous tear/ brain laceration High morbidity/mortality due to underlying brain injury Crescent – concaved shape Counter coup 26. Trauma Chronic Subdural hematoma (CSDH) Elderly, alcohol abuse, coagulopathy Motor oil fluid, no clot Minimal or no Hx of injury Insidious onset Minor symptoms hemiplegia/seizure 27. Trauma Skull Fracture Skull Fx ↑ risk of intracranial bleeding 5 times Skull base fracture CSF rhinorrhea, otorrhea Battle’s sign, Raccoon’s eye (anterior skull base) Facial weakness (petrous part of temporal bone) 28. Trauma Sequelae of head injury Increased intracranial pressure ( > 20 mmHg) General: sedation, analgesia, elevate head, avoid hypoxia Ventricular drainage Mannitol Hyperventilation 2 nd tier Phenobarb coma Decompressive craniectomy 29. Trauma Sequelae of head injury Electrolyte imbalance – hyponatremia Seizure Antiepileptic drug - ↓ early seizure Prophylaxis 7 days I/C: GCS≤10, intracranial lesion, penetrating injury, depressed skull fracture Carotid-cavernous fistula Posttrauma 2-3 mo Unilateral chemosis, proptosis Bruit/thrill at the orbit Ix: angiography Management: balloon embolizaion 30. Herniation syndrome Central Diencephalon tentorial Chronic Pupils: SRTL Fixed Uncal** Uncus and hippocampal gyrus over tentorium CN III compression unilateral pupil ↑, hemiparesis Consciousness preserved in early stages Classic for EDH 31. Herniation syndrome Cingulate (subfalcine H): asymptomatic except ACA kink, warning of impending transtentorial H. Upward posterior fossa mass + ventriculostomy Tonsillar Posterior fossa mass + LP 32. Tumor Supratentorial Gliomas Astrocytoma Oligodendrogliomas Ependymomas Meningiomas Sellar and suprasellar Pituitary adenomas craniopharyngiomas Infratentorial Medulloblastoma (Ped) Cerebellar astrocytoma Brainstem gliomas CP angle tumor Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuromas) Meningiomas Meningiomas 33. Tumor Most common brain tumor Metastasis Most common primary brain tumor Astrocytoma Most common primary brain tumor in children Medulloblastoma Glioblastoma multiforme Grade IV of astrocytoma Poor prognosis. 2 yr survival 11 mo for total resection 34. Tumor DDx for patient with progressive hemiparesis and IICP Supratentorial tumor (Metas, gliomas, meningioma, etc) Brain abscess (ped. With rt to lt shunt eg TOF) DDx for patient with bitemporal hemianopia => sellar and suprasellar tumor Pituitary adenoma Craniopharyngioma Meningioma 35. Hydrocephalous Mechanism Obstruction at CSF pathway: Obstructive hydrocephalous CSF pathway: tumor, blood, etc Obstruction at arachnoid granulation Communicating hydrocephalous Overproduction: choroid plexus papilloma Treatment Remove etiology Drainage Ventriculostomy (temporary) Shunting VP shunt VA shunt Ventriculo-pleural shunt 36. 37.