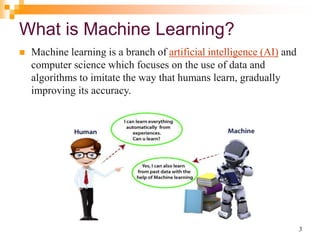
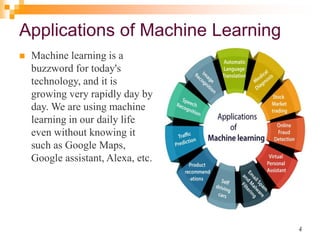
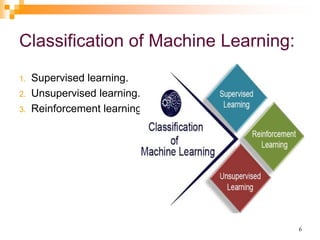
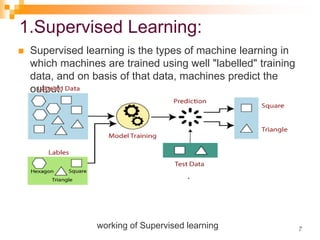
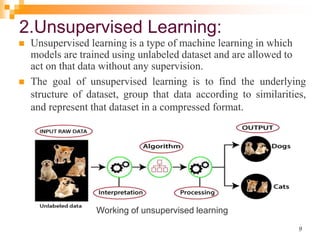
The document provides an introduction to machine learning, emphasizing its definition as a branch of artificial intelligence that improves through data and algorithms. It outlines applications such as Google Assistant and Alexa, and categorizes machine learning into supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, explaining each type's mechanisms and purposes. Key features include the ability to learn from data, detect patterns, and the similar nature to data mining.