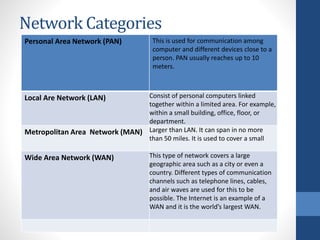
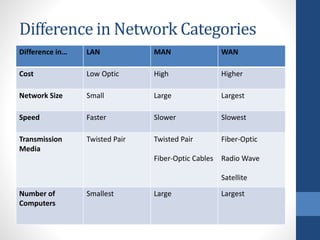
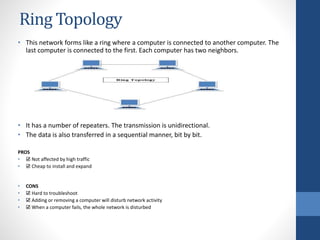
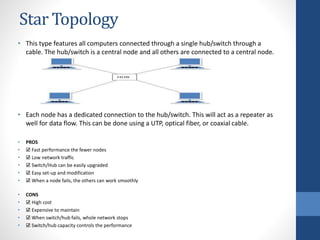
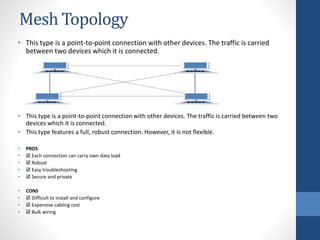
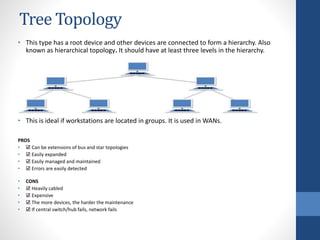
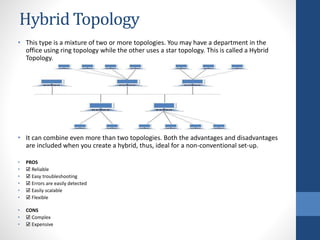
This document discusses configuring computer networks. It describes different types of computer networks including personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). It also discusses different network topologies such as bus, ring, star, mesh, tree, and hybrid and compares their pros and cons. The goal is to provide basic information about setting up computer networks at home using a few basic hardware pieces to connect computers and devices to each other and the internet.