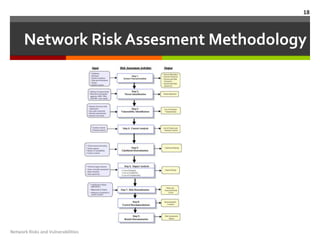
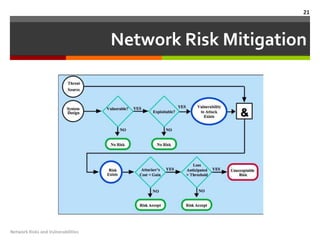
This document discusses network risks and vulnerabilities. It begins by defining vulnerabilities as software flaws or misconfigurations that weaken security. It then examines various types of vulnerabilities like design flaws, viruses, impersonation, worms, port scanning, man-in-the-middle attacks, denial-of-service attacks. The document also covers network risk assessment methodology and impact analysis. It concludes with a brief mention of network risk mitigation as a way to reduce risks.