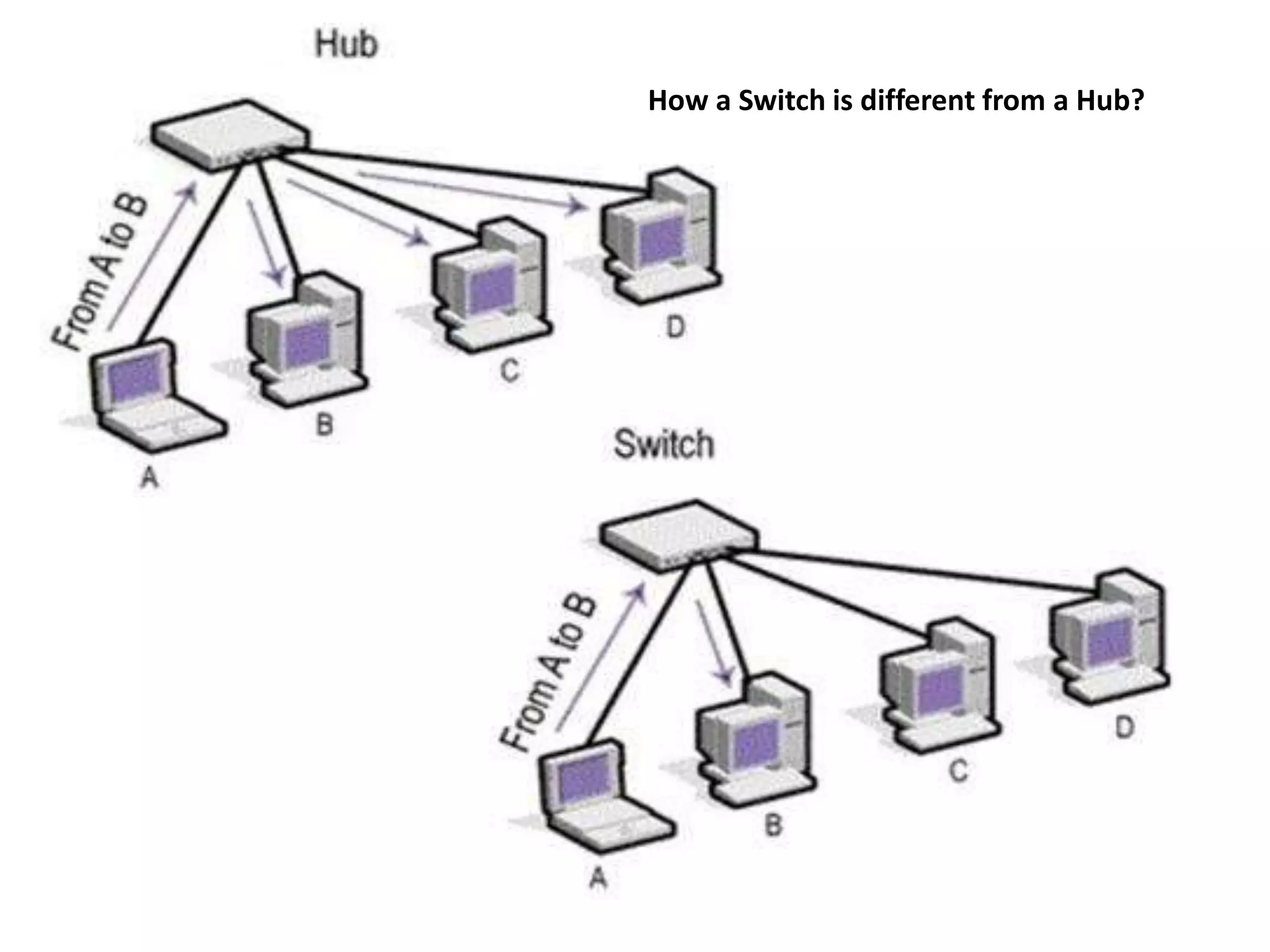
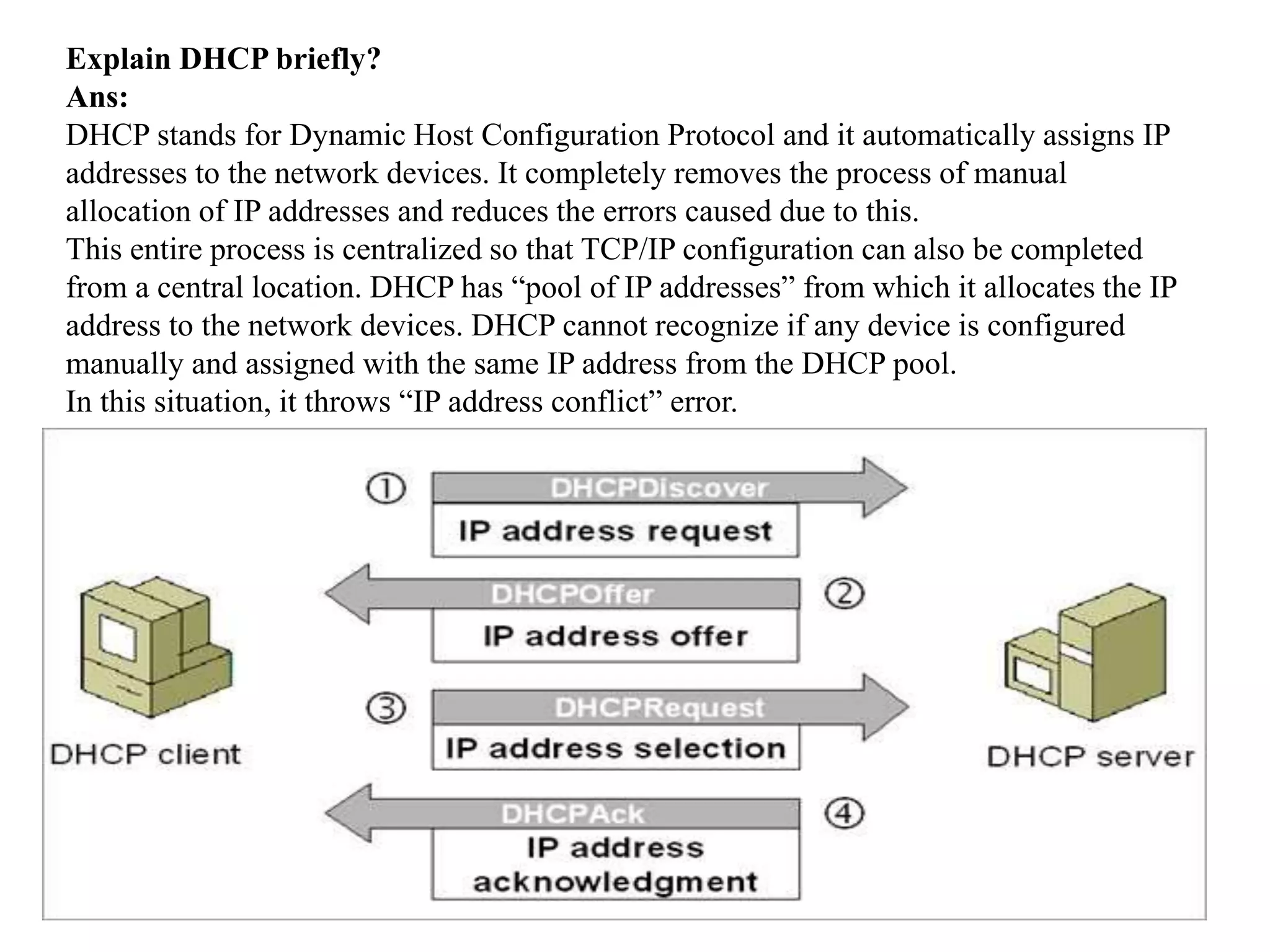
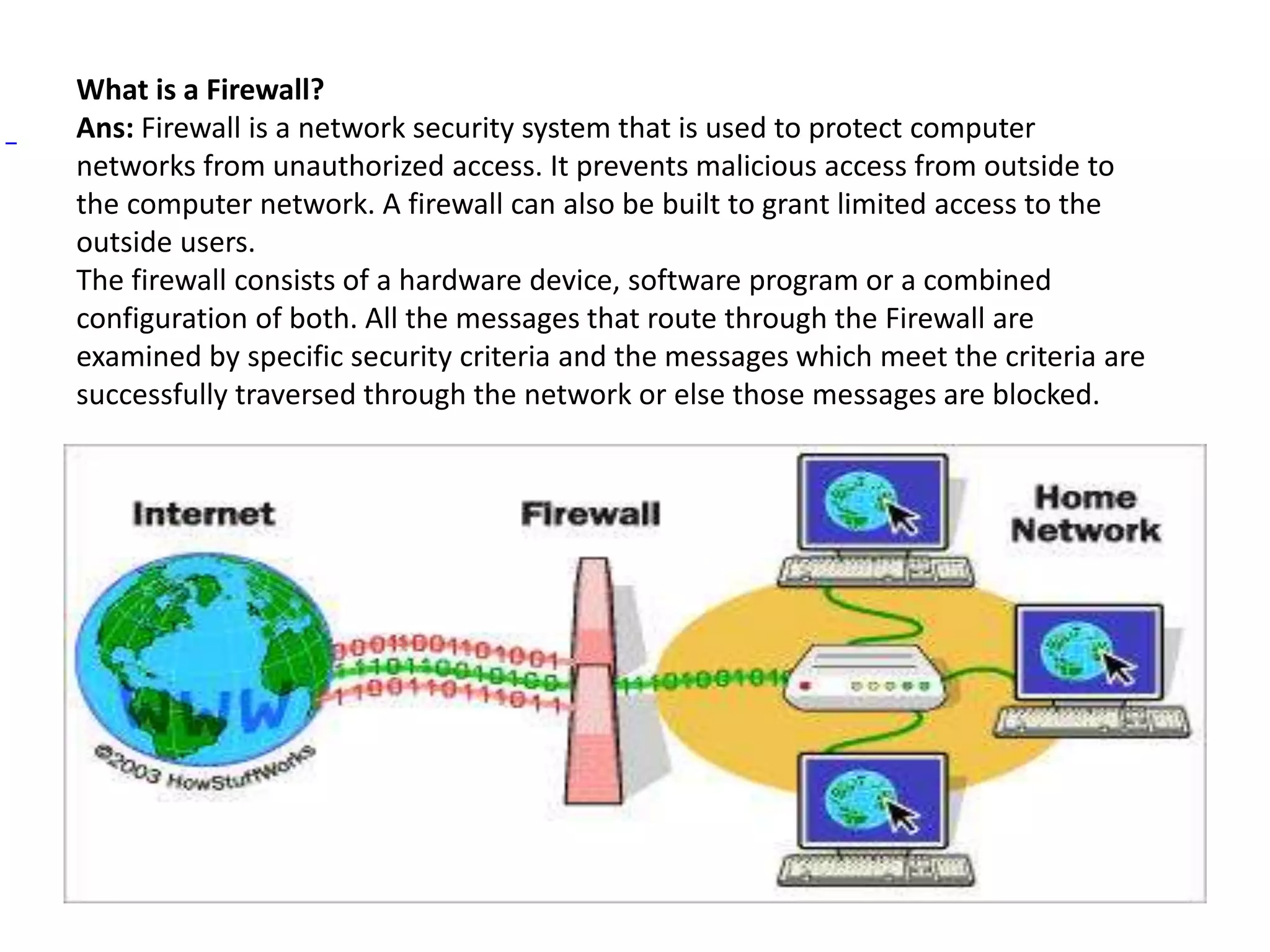
The document provides answers to various questions related to computer networks and networking concepts. It defines key terms like subnets, DNS, clients and servers. It describes the OSI model layers and transmission technologies. It also explains concepts like IP addresses, MAC addresses, switches, routers, firewalls, DHCP and more.