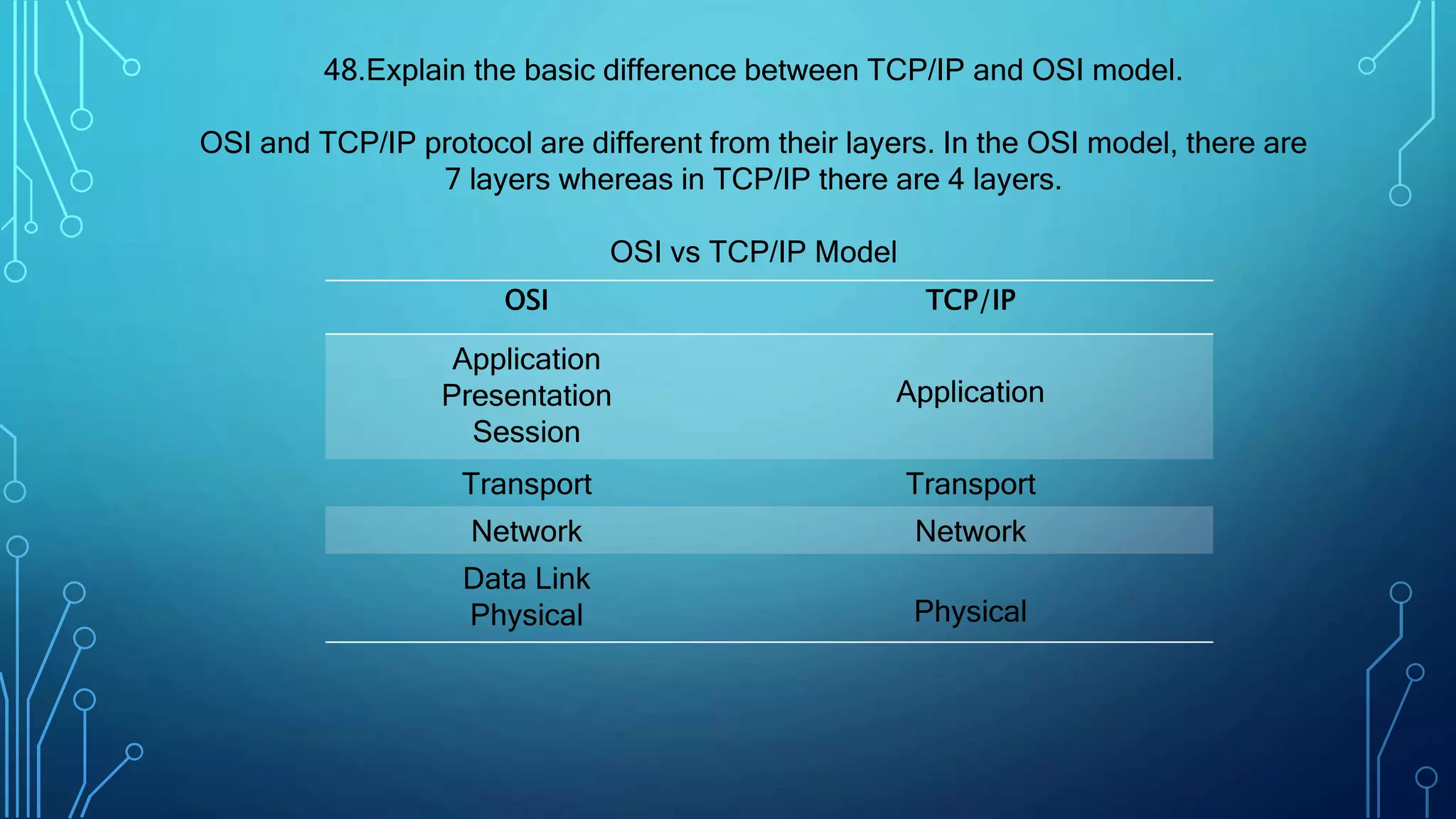
The document contains an extensive list of over 50 questions and answers focused on CCNA topics, specifically the 200-301 exam. Key concepts discussed include networking types, memory types in routers, OSI model layers, the differences between switches, routers, and hubs, and various networking protocols. Additionally, it addresses IP addressing, data transfer methods, network topology, and essential networking standards and technologies.