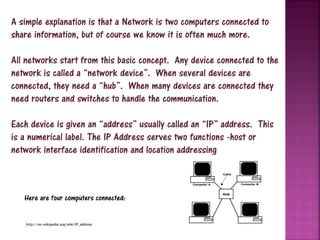
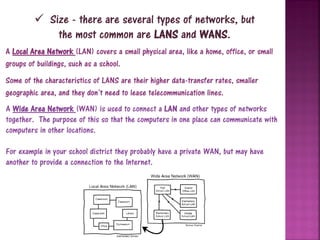
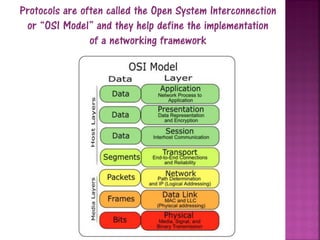
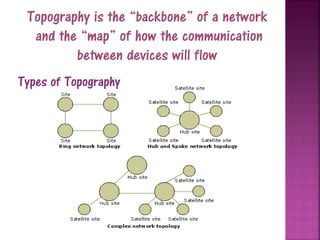
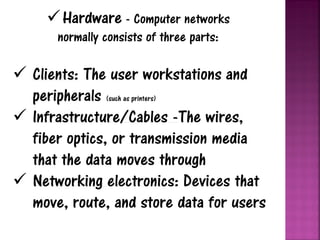
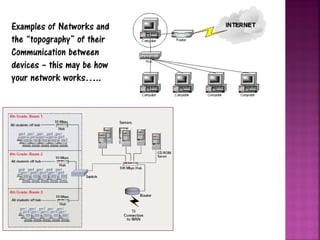
This document provides an overview of computer networks. It defines a network as two or more connected computers that share information. All networks require devices, hubs or switches to connect multiple devices, and routers to handle communication as more devices connect. Each device needs an IP address for identification and location. The document discusses key aspects of networks including size (LANs and WANs), protocols, topology, hardware components, and cabling infrastructure. It provides examples of how different types of networks are structured. The purpose of networks is to facilitate communication, sharing of hardware, files and software between connected devices.