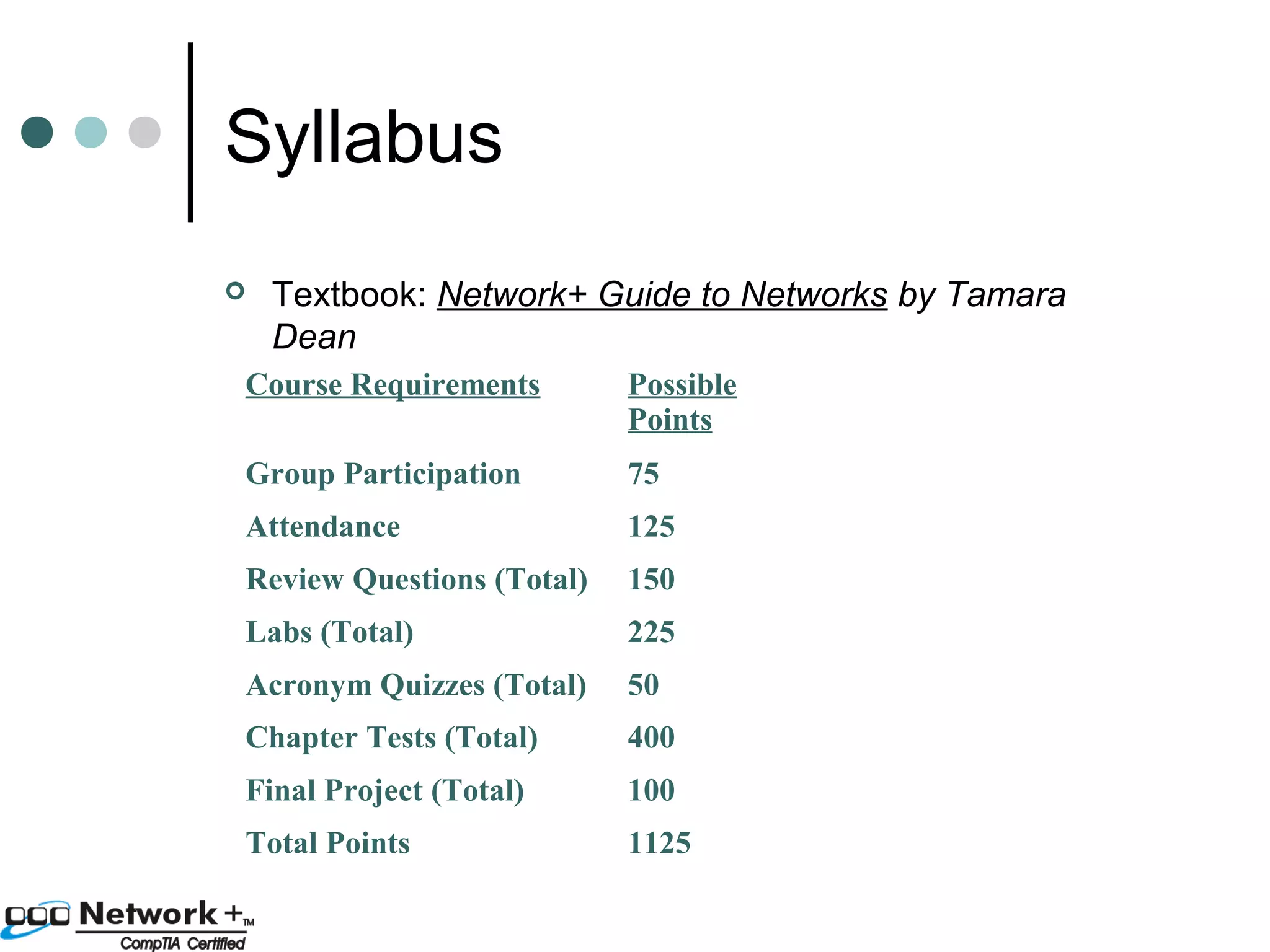
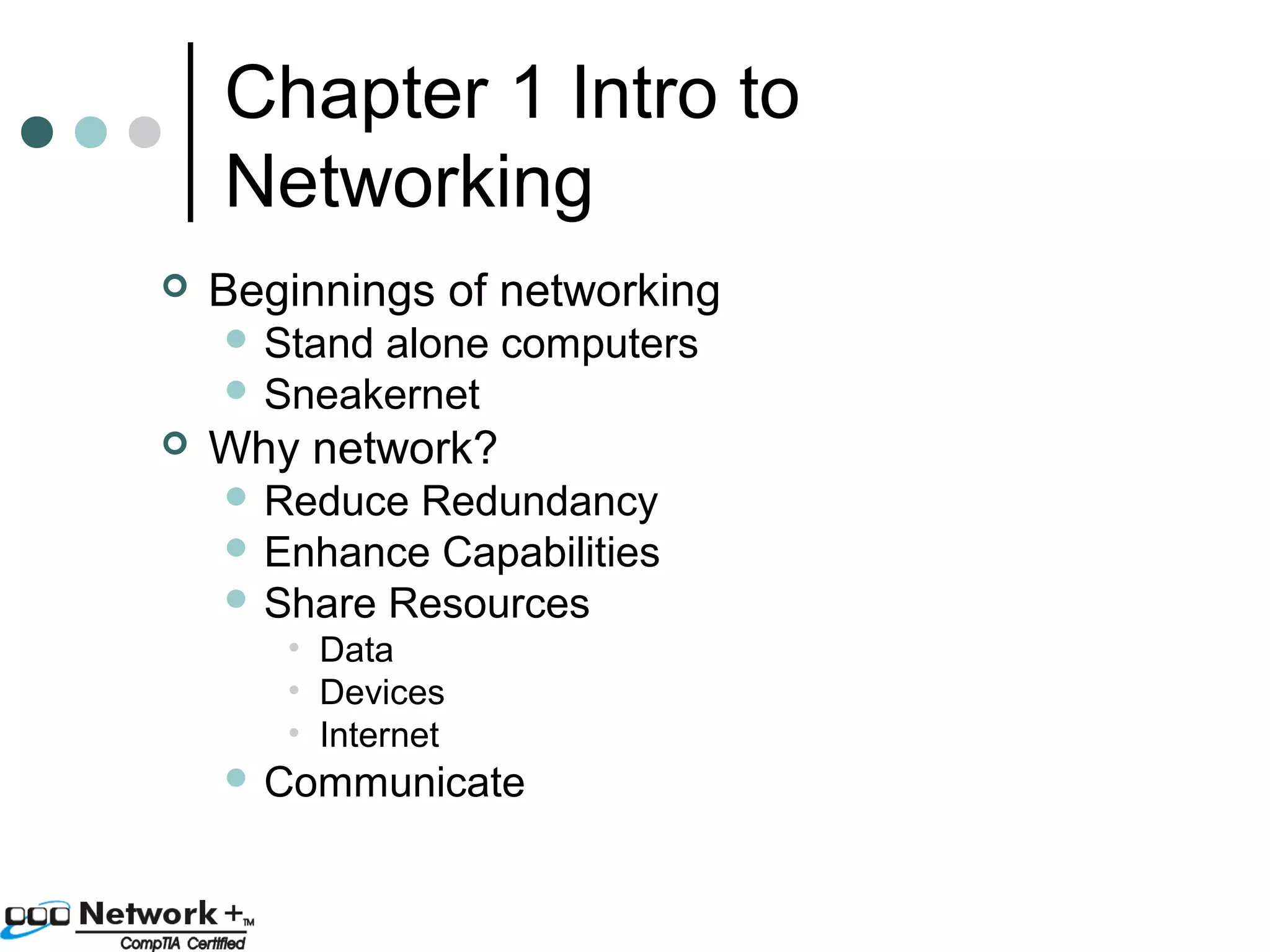
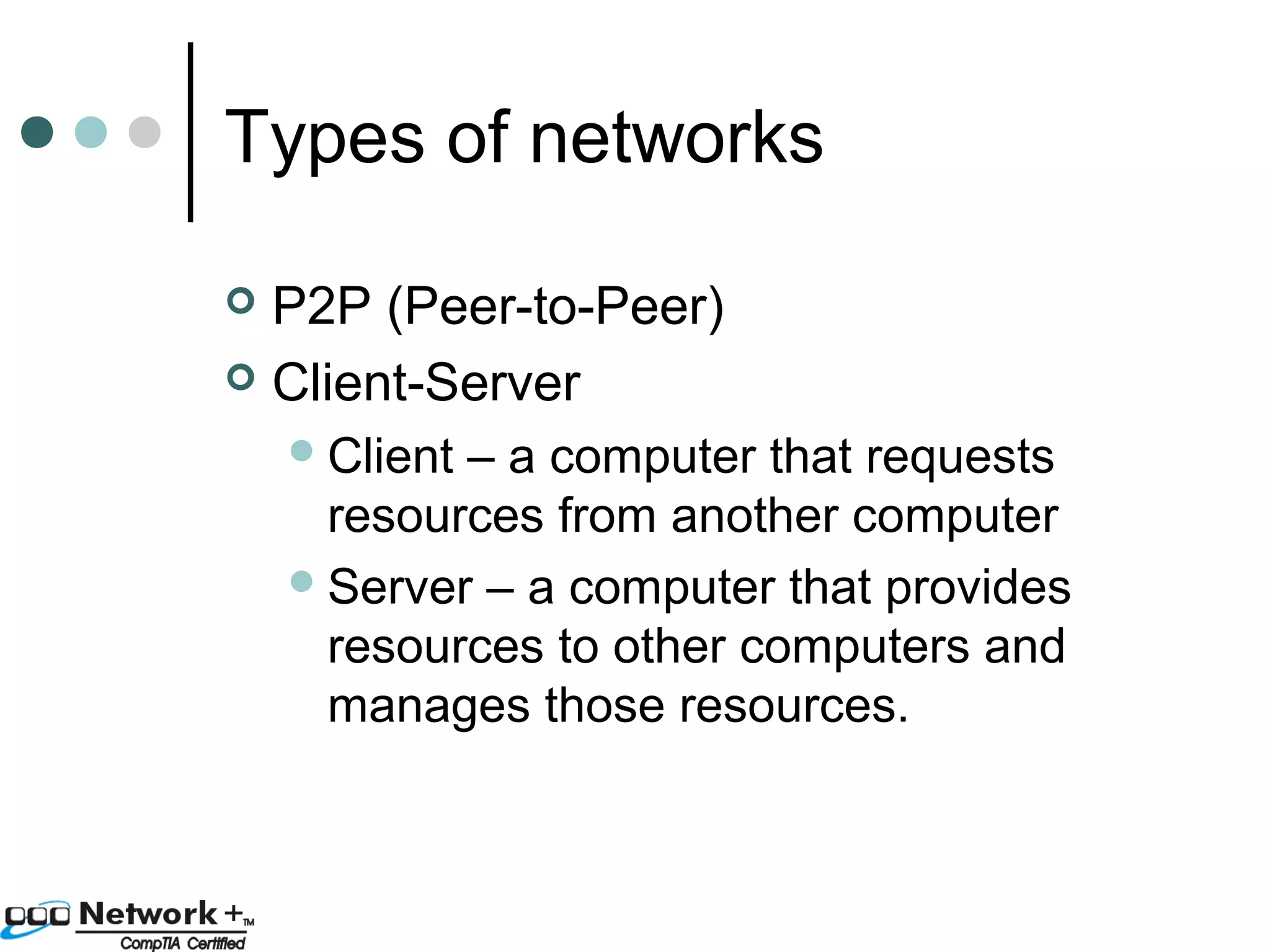
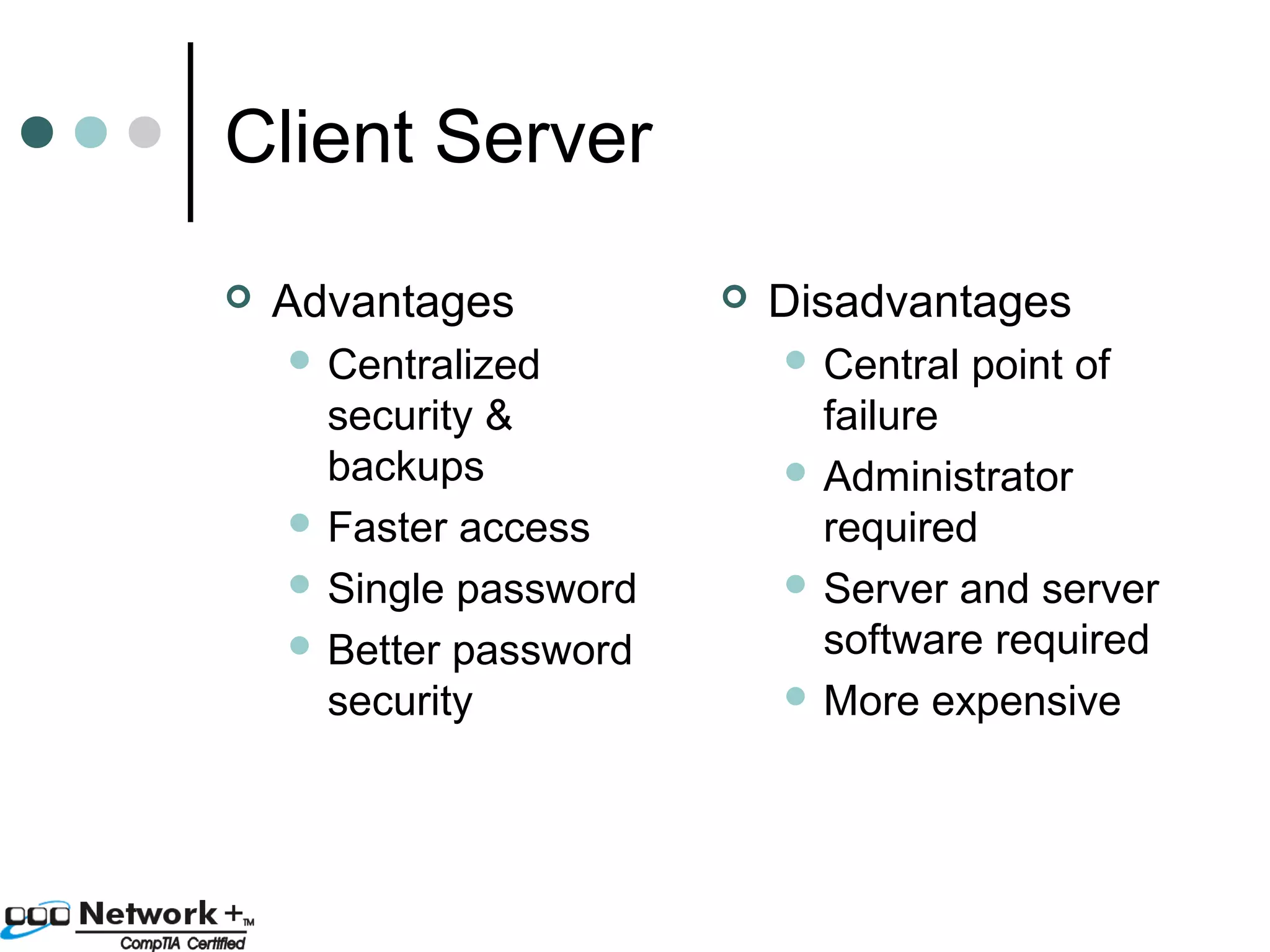
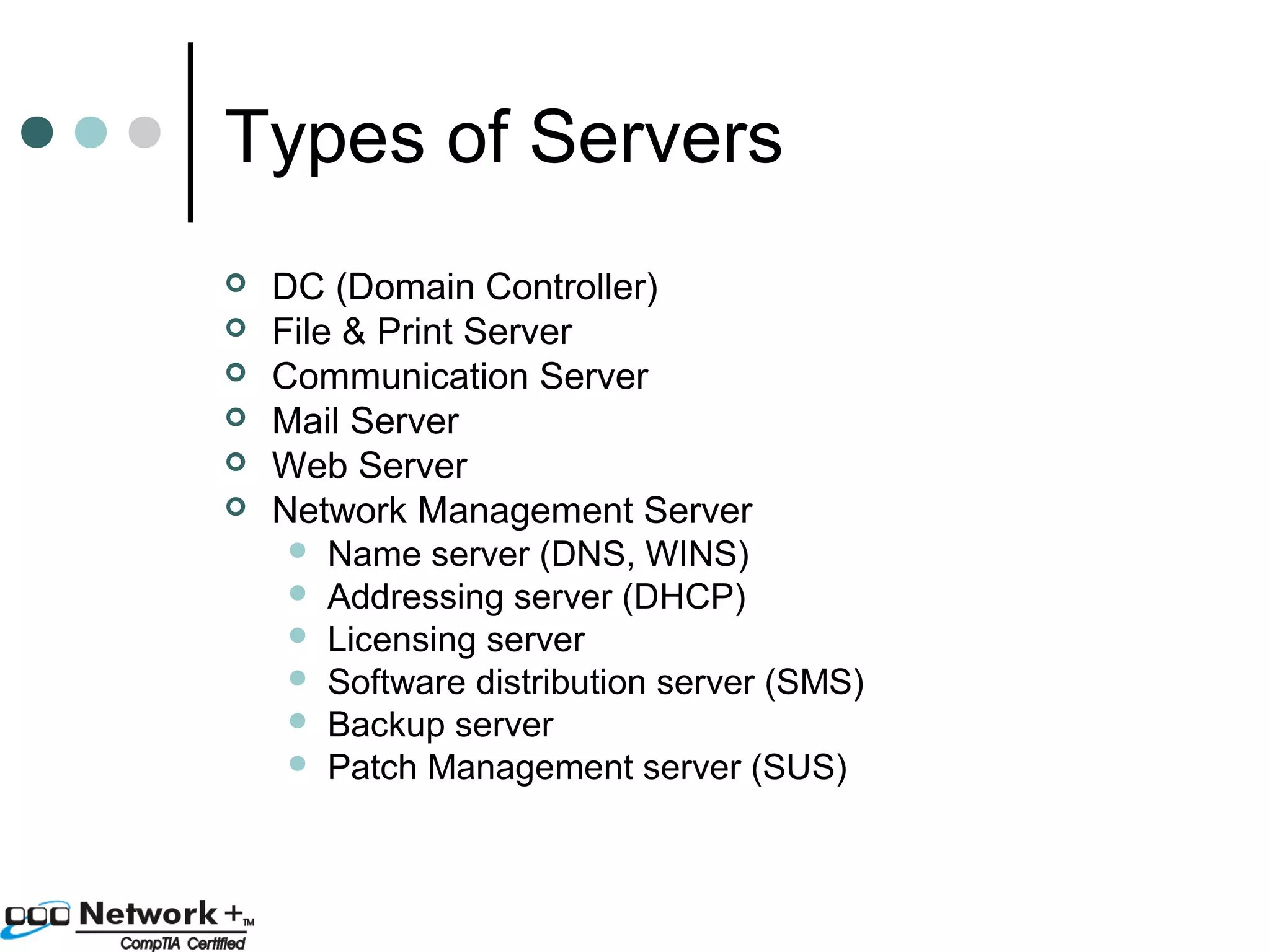
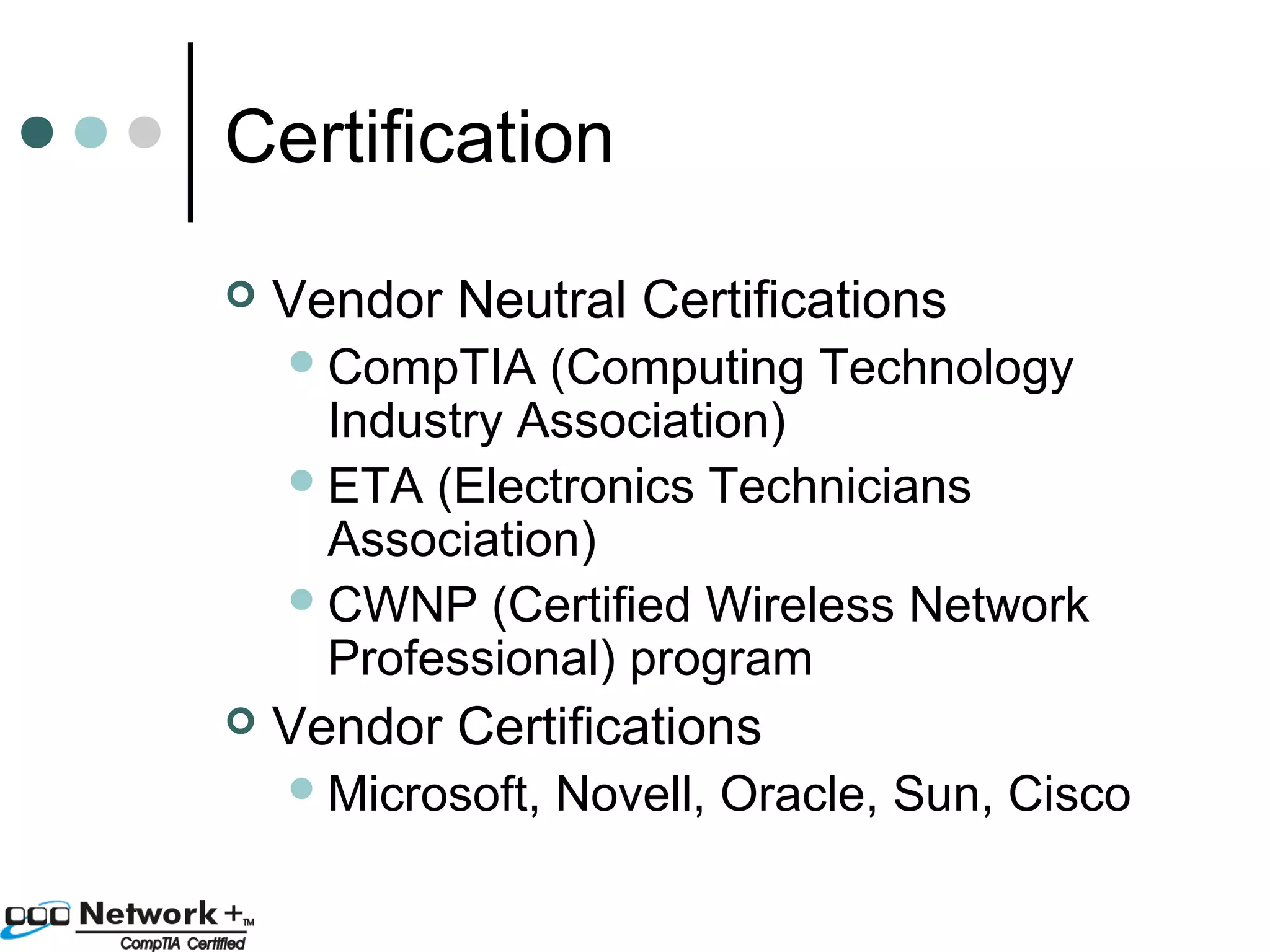
This document provides an introduction to a networking essentials class, including information about the instructor, class times and structure, textbook, and course outline. It also summarizes key topics that will be covered in the class, such as networking history, types of networks, network operating systems, networking terminology, roles of servers, skills required of network professionals, and certifications.