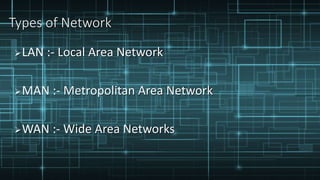
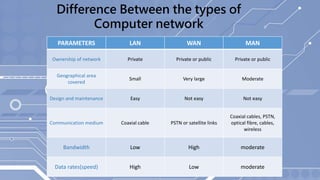
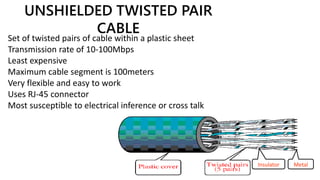
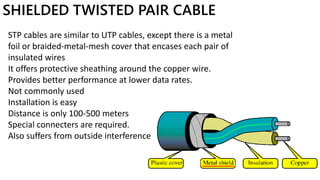
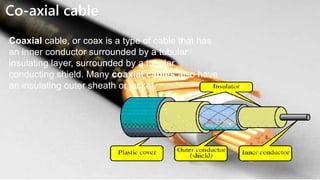
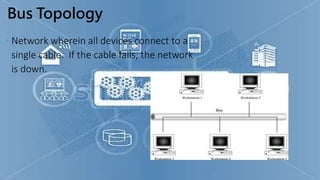
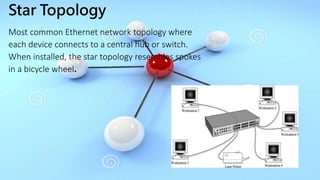
This presentation provides an overview of computer networks. It defines what a network is and discusses the main types: human networks and computer networks. It then covers the key aspects of computer networks including definitions of LANs, MANs, and WANs. The presentation outlines the basic components of a computer network, including hubs, switches, bridges, routers, repeaters, and gateways. It also discusses network topologies, media types, and the advantages and disadvantages of computer networks.