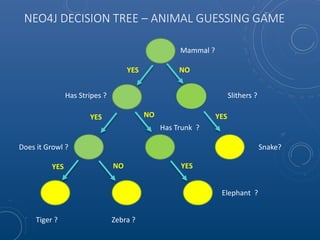
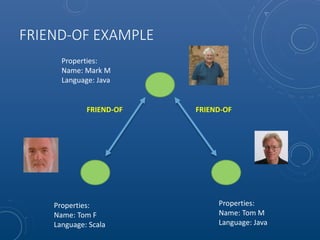
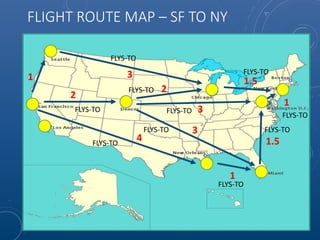
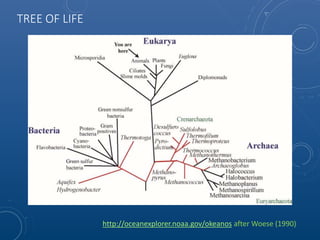
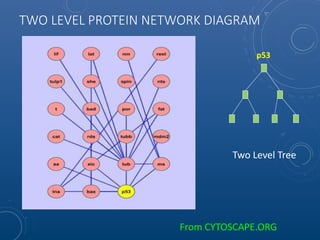
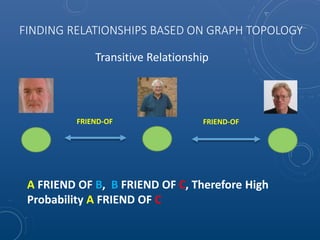
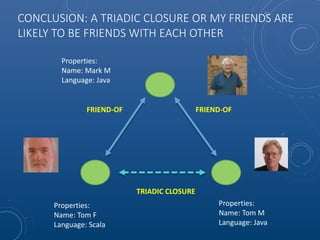
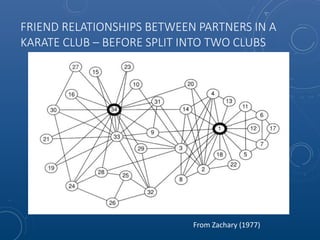
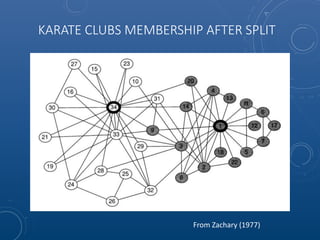
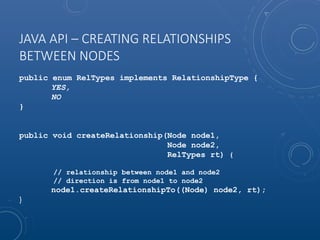
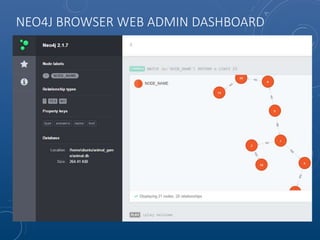
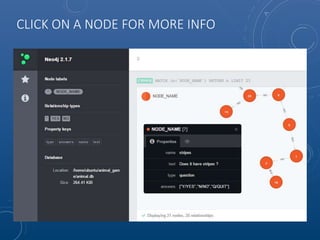
Mark Maslyn presented an introduction to Neo4j, an open-source graph database, covering its applications, advantages, and Java API syntax. The presentation emphasized the utility of graph databases in various fields like social media and fraud detection, demonstrating their natural representation of data and faster query responses. A live demo of an animal guessing game using Neo4j showcased its decision tree capabilities.















![NEO4J SERVER RESTFUL API – DRILLING DOWN FOR
META-DATA FROM ANIMAL DATABASE
REQUEST: http://localhost:7474/db/data/relationship/types
JSON RESPONSE:
[
"YES",
"NO"
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jopensourcegraphdatabase-150907153053-lva1-app6892/85/Neo4J-Open-Source-Graph-Database-32-320.jpg)
![RETRIEVING A SINGLE NODE AND ITS PROPERTIES
REQUEST: http://localhost:7474/db/data/node/0
JSON RESPONSE:
{
…..
"metadata": {
"id": 0,
"labels": [
“ANIMALS"
]
},
"data": {
"text": "Does the animal live on land ?",
"name": "start",
"answers": [
"Y/YES",
"N/NO",
"Q/QUIT"
],
"type": "question"
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jopensourcegraphdatabase-150907153053-lva1-app6892/85/Neo4J-Open-Source-Graph-Database-33-320.jpg)



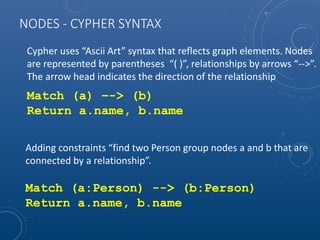
![RELATIONSHIPS - CYPHER SYNTAX
Anonymous relationships match all relationship and are indicated
by the arrow alone
This query syntax is used to find two nodes a and b that are
connected by the specific “ACTED_IN” relationship to match
actors with movies
Match (a) --> (b)
Match (a) –[:ACTED_IN]-> (b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jopensourcegraphdatabase-150907153053-lva1-app6892/85/Neo4J-Open-Source-Graph-Database-40-320.jpg)

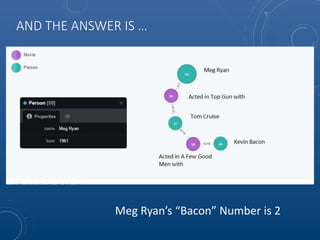
![CYPHER QUERY FOR SIX DEGREES OF KEVIN BACON
FOR MEG RYAN USING NEO4J SHORTEST PATH
FUNCTION
MATCH p=shortestPath(
(b:Person {name:"Kevin Bacon"})-[*]-(m:Person {name:"Meg
Ryan"})
)
RETURN p](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4jopensourcegraphdatabase-150907153053-lva1-app6892/85/Neo4J-Open-Source-Graph-Database-43-320.jpg)