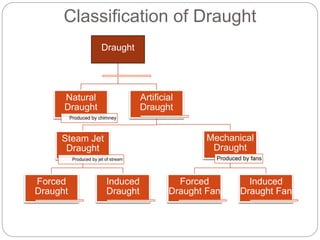
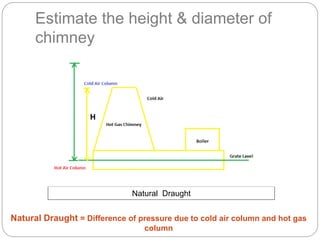
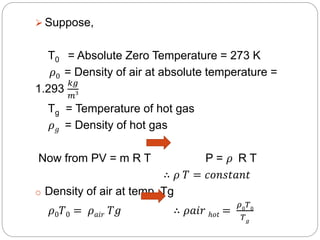
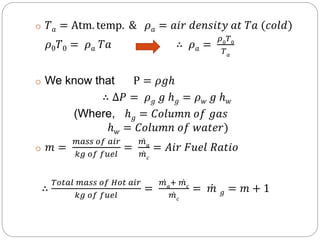
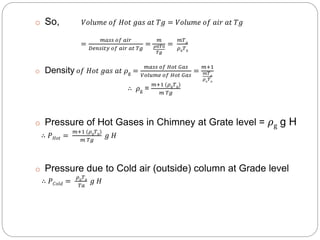
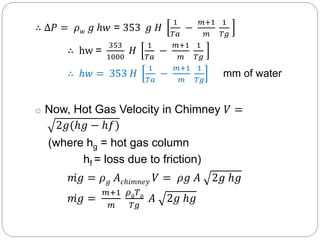
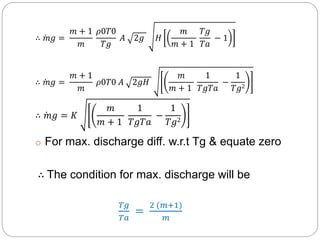
This document discusses natural draught systems used in power plant boilers. It defines draught as the pressure difference needed to maintain air and gas flow through a boiler. Natural draught uses the density difference between hot flue gases in a chimney and cold outside air to create this pressure. The document estimates the height and diameter of a chimney needed using formulas involving gas temperature, air temperature, and flow rates. It also discusses conditions for maximum discharge through a chimney and the low efficiency of natural draught systems. Advantages include low cost and maintenance while limitations include dependence on atmospheric conditions and inability to increase draught during peak loads.



![Losses in the air – gas circuit of Boiler:
Draught is nothing but pressure difference required to
accelerate the burnt gases to their final velocity and to
overcome the pressure losses in the boiler passage.
Draught = [head required to accelerate the gases] +
[head losses in the path
of flue gases]
ℎ 𝑓 = ℎ 𝑣 + ℎ 𝑎 + ℎ 𝑔 + ℎ 𝑑
Where, ℎ 𝑓 = total draught required or total loss
ℎ 𝑣 = pressure loss due to gas exit velocity from
chimney
ℎ 𝑎 = pressure loss on air side
ℎ 𝑔 = pressure loss in gas side
ℎ 𝑑 = pressure losses in chimney and gas ducts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppefinal-160929093757/85/Natural-Draught-4-320.jpg)