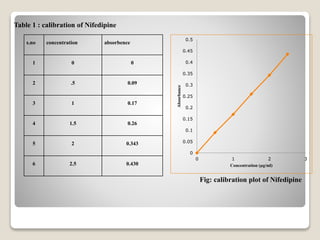
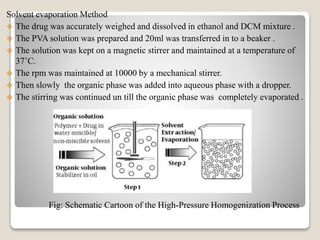
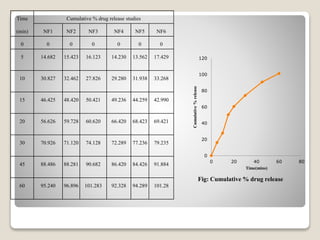
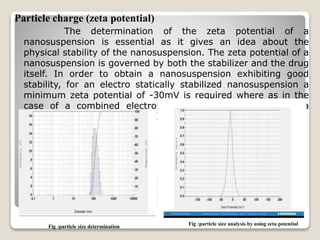
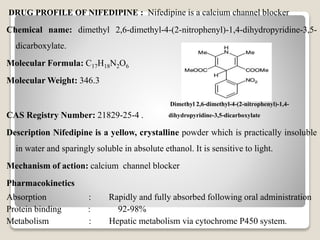
This document provides an introduction and project report on the preparation and evaluation of a nifedipine nanosuspension using the solvent evaporation method. It begins with background information on nanosuspensions and how they can be used to improve the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. The aim and objectives are to prepare and evaluate a nifedipine nanosuspension using solvent evaporation. Literature is reviewed on previous studies related to nanosuspensions and the drug nifedipine. The nanosuspension is formulated and characterized through in vitro drug release studies and measurement of particle size and zeta potential.







![POLYMER PROFILE OF POLYVINYLALCOHOL
Nonproprietary Names:
PhEur: Poly (vinylis acetas) USP: Polyvinyl alcohol
Chemical Name and CAS Registry Number
Ethanol, homopolymer [9002-89-5]
Structual Formula
Description:
Polyvinyl alcohol occurs as an odorless, white to cream-colored granular powder.
Melting point:
2280C for fully hydrolyzed grades;180–1900C for partially hydrolyzed grades.
Refractive index: nD
25 = 1.49–1.53
Solubility
soluble in water. slightly soluble in ethanol (95%). insoluble in organic solvents.
Dissolution requires dispersion (wetting) of the solid in water at room temperature followed
by heating the mixture to about 900C for approximately 5 minutes. Mixing should be
continued while the heated solution is cooled to room temperature.
Specific gravity
1.19–1.31 for solid at 250C; 1.02 For 10% w/v aqueous solution at 250C.
Specific heat: 1.67 J/g (0.4 cal/g)
Functional Category
Coating agent, lubricant, stabilizing agent, viscosity-increasing agent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nanosuspension-copy-160910100221/85/Nano-suspension-copy-9-320.jpg)