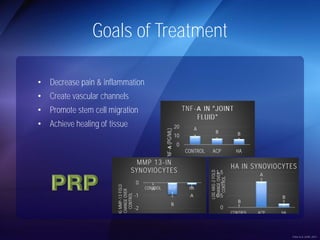
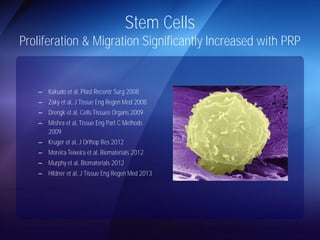
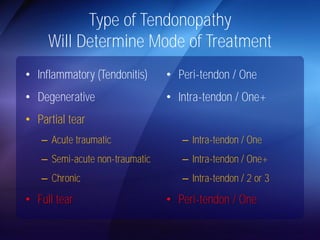
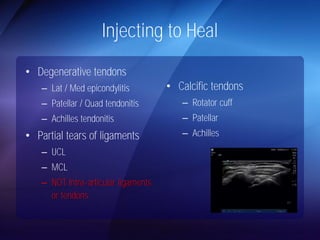
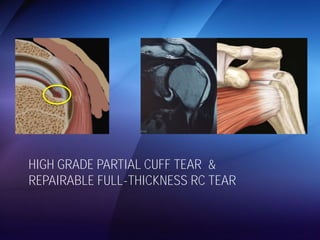
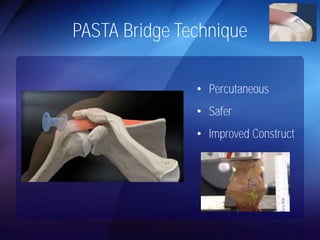
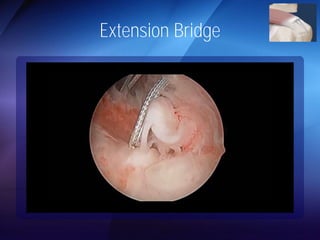
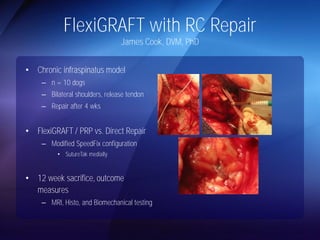
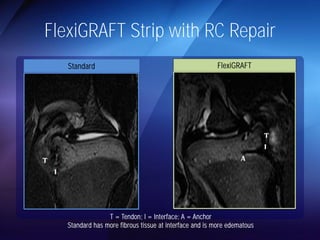
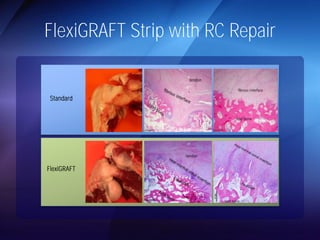
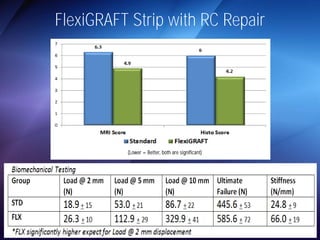
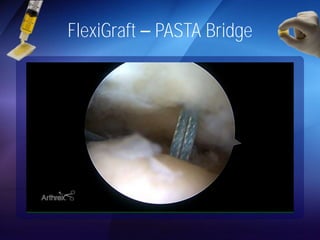
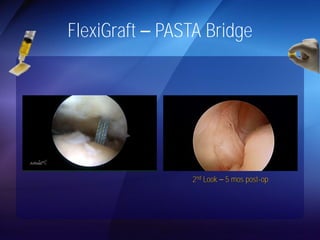
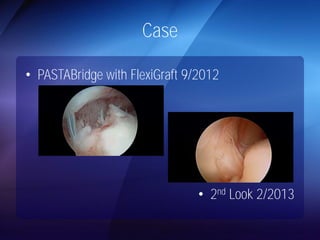
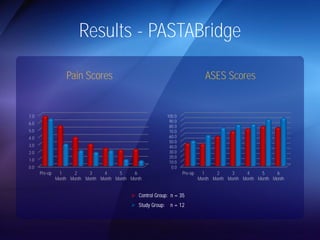
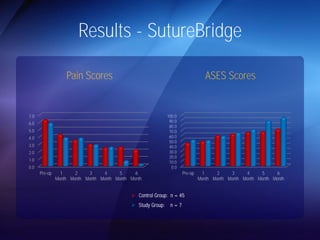
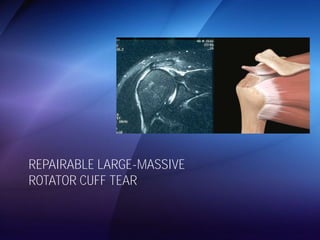
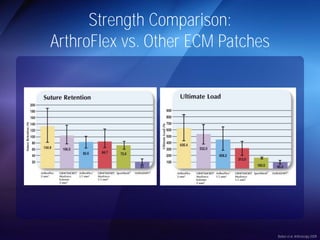
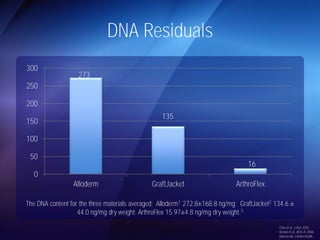
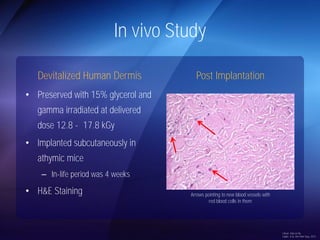
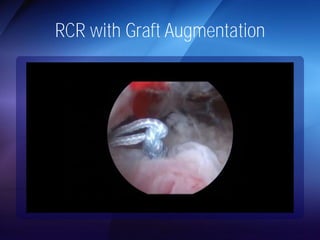
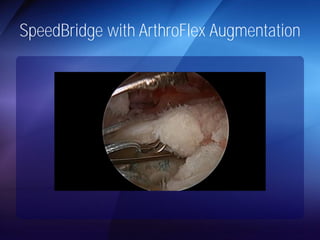
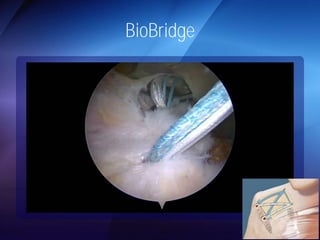
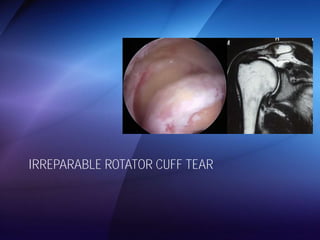
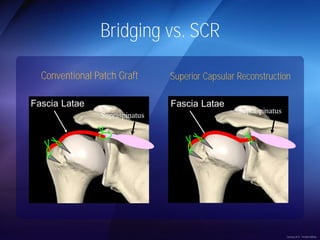
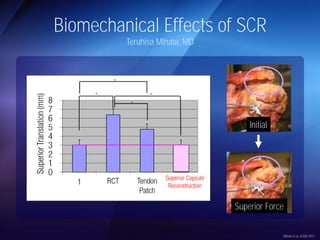
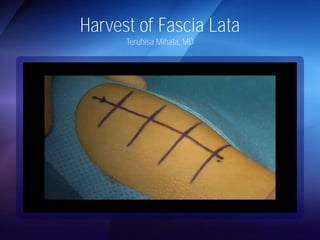
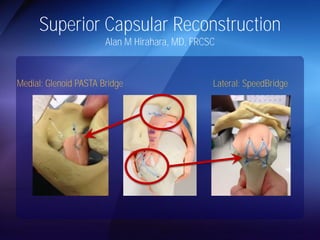
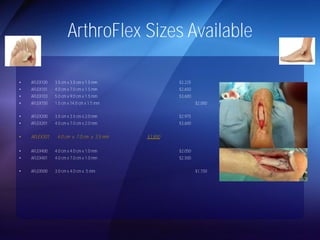
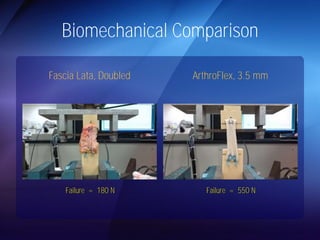
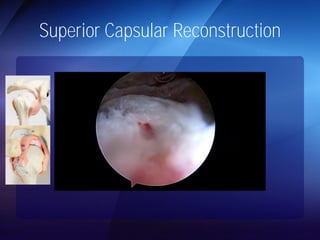
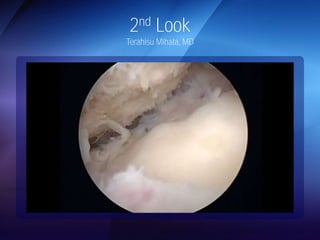
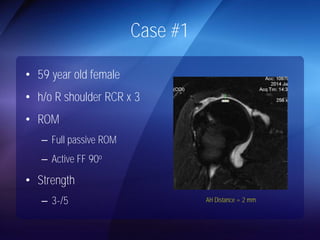
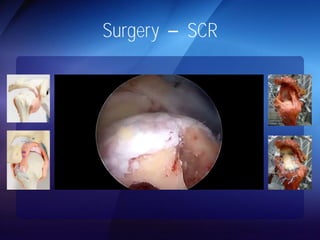
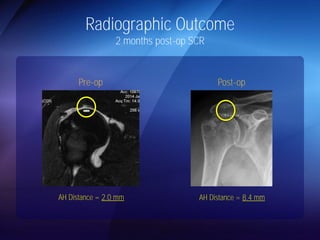
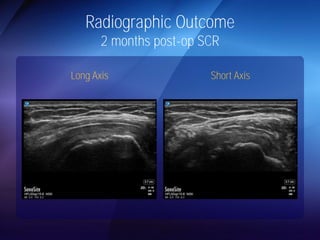
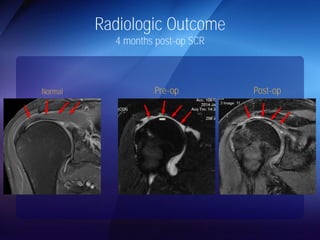
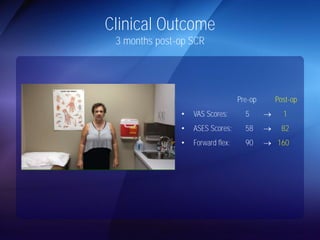
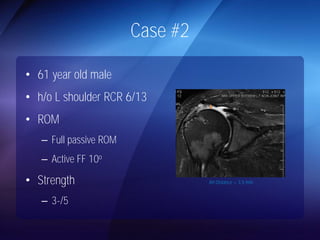
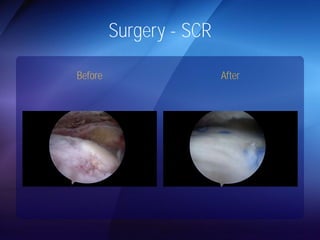
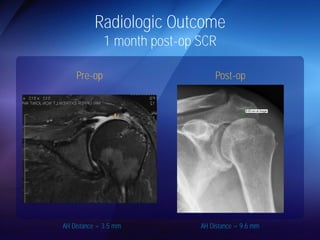
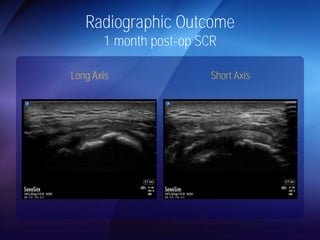
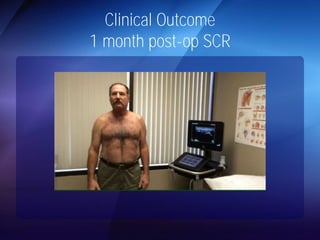
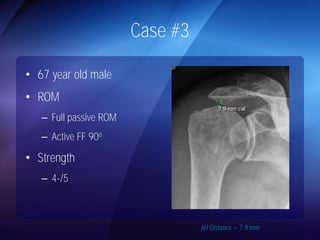
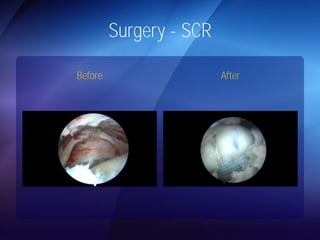
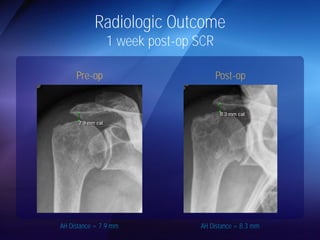
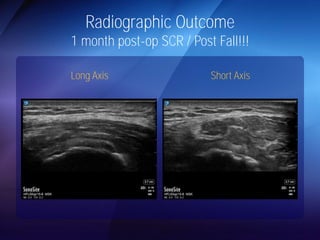
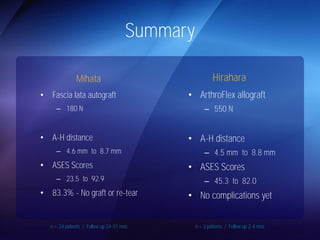
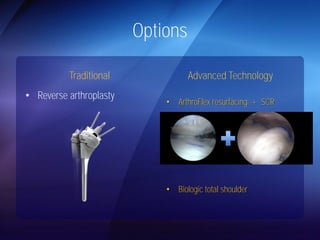
The document discusses advanced techniques for shoulder joint preservation, focusing on rotator cuff pathology, its diagnosis, and both conservative and surgical treatment options. It emphasizes the role of traditional methods alongside innovative technologies such as platelet-rich plasma and stem cell therapies for better outcomes in treating shoulder conditions. Additionally, it compares various surgical techniques, including superior capsular reconstruction and the use of grafts for irreparable rotator cuff tears, highlighting the importance of tailored approaches based on the type and severity of the injury.