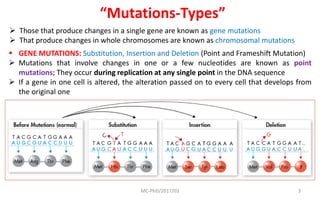
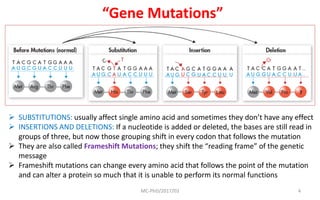
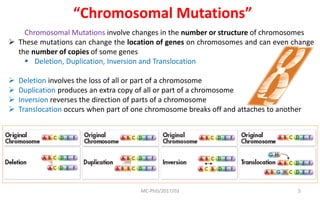
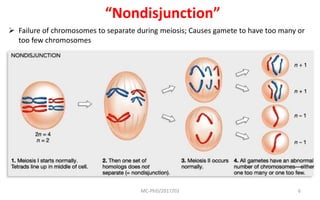
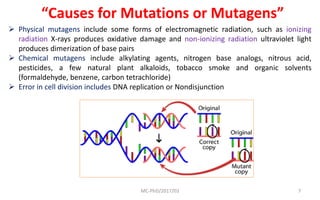
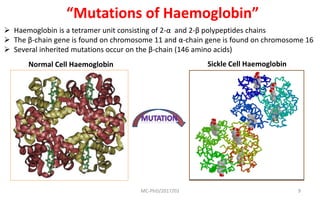
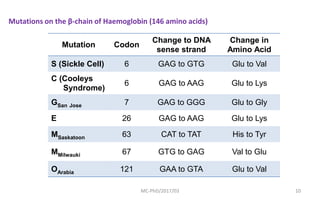
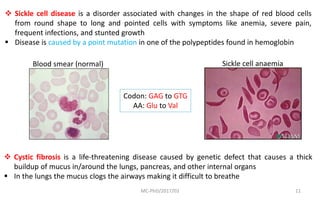
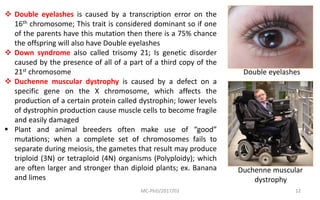
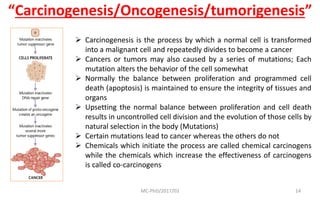
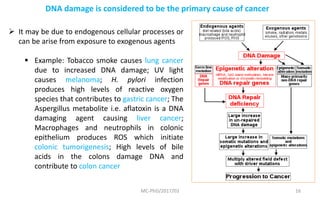
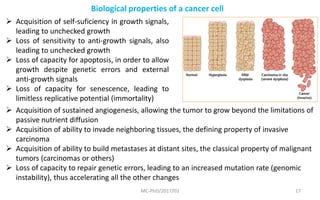
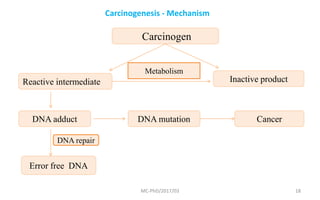
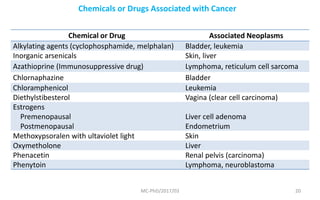
Mutations are changes in genetic material that can be caused by errors in DNA replication or by exposure to mutagens. There are several types of mutations including substitutions, insertions, deletions, and chromosomal mutations. Mutations can have varying effects, from being harmless to causing genetic disorders or cancer. Carcinogenesis is the process by which normal cells are transformed into cancer cells through a series of mutations that disrupt the balance between cell proliferation and cell death.