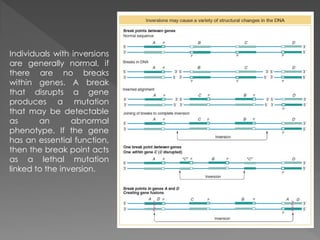
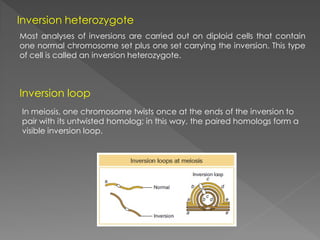
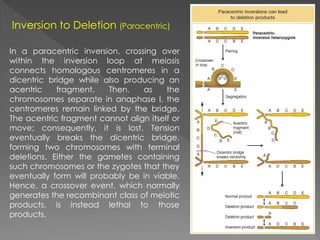
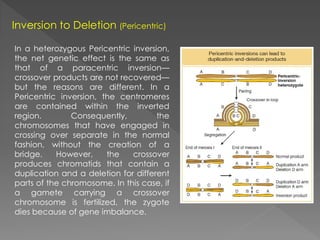
A mutation is a permanent alteration in the DNA sequence of a gene that differs from what is typically found. Mutations can range in size from a single DNA building block to a large chromosome segment including multiple genes. There are several types of chromosomal mutations, including deletions, duplications, inversions, translocations, and disjunctions. An inversion occurs when a chromosome segment is cut out, flipped, and reinserted. Inversions are either paracentric or pericentric depending on if the centromere is inside or outside the inverted region. During meiosis, inversions can lead to deletions or gene imbalances if crossovers occur within the inverted region, resulting in non-viable gametes or z