Embed presentation
Downloaded 148 times

![Register Indirect – the address of the source or destination is specified in registers Uses registers R0 or R1 for 8-bit address: mov psw, #0 ; use register bank 0 mov r0, #0x3C mov @r0, #3 ; memory at 3C gets #3 ; M[3C] 3 Uses DPTR register for 16-bit addresses: mov dptr, #0x9000 ; dptr 9000h movx a, @dptr ; a M[9000] Note that 9000 is an address in external memory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inst-100102041825-phpapp02/85/mup-7-320.jpg)
![Register Indexed Mode – source or destination address is the sum of the base address and the accumulator(Index) Base address can be DPTR or PC mov dptr, #4000h mov a, #5 movc a, @a + dptr ; a M[4005]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inst-100102041825-phpapp02/85/mup-8-320.jpg)
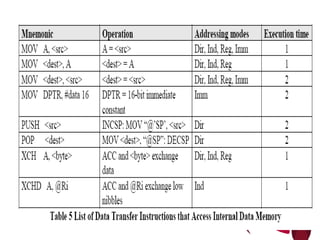
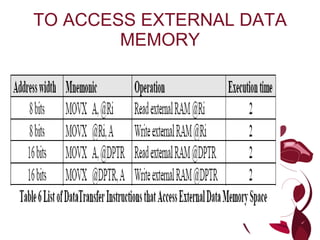
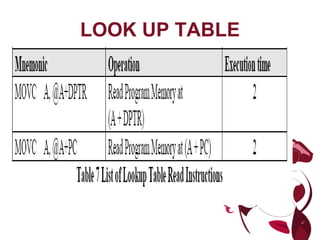
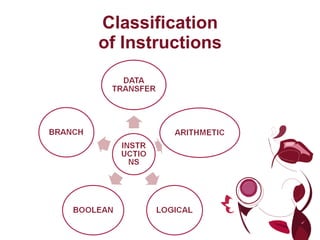
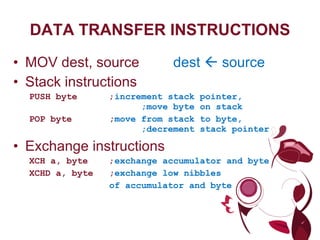
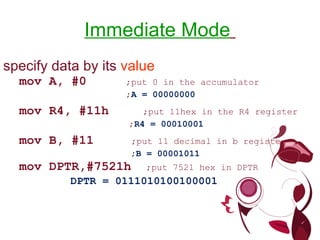
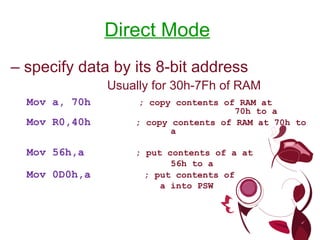
The document describes different types of instructions for the 8051 microcontroller including: 1. Data transfer instructions like MOV to move data between registers and memory locations. It also describes stack instructions like PUSH and POP. 2. Immediate mode instructions specify data using a value like MOV A,#0 to move the value 0 to the accumulator register. 3. Register addressing uses source or destination CPU registers like MOV R0,A to move the accumulator to register R0. 4. Direct mode specifies data using an 8-bit address in memory from 30h to 7Fh like MOV a,70h to copy memory at 70h to register a. 5.






![Register Indirect – the address of the source or destination is specified in registers Uses registers R0 or R1 for 8-bit address: mov psw, #0 ; use register bank 0 mov r0, #0x3C mov @r0, #3 ; memory at 3C gets #3 ; M[3C] 3 Uses DPTR register for 16-bit addresses: mov dptr, #0x9000 ; dptr 9000h movx a, @dptr ; a M[9000] Note that 9000 is an address in external memory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inst-100102041825-phpapp02/85/mup-7-320.jpg)
![Register Indexed Mode – source or destination address is the sum of the base address and the accumulator(Index) Base address can be DPTR or PC mov dptr, #4000h mov a, #5 movc a, @a + dptr ; a M[4005]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inst-100102041825-phpapp02/85/mup-8-320.jpg)


