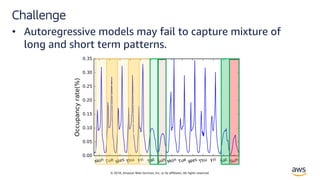
The document discusses the challenges and advancements in multivariate time series forecasting using autoregressive models, highlighting the limitations of existing methods such as the cold start problem and handling large datasets. It introduces 'DeepAR,' a forecasting model based on autoregressive recurrent neural networks, and outlines its advantages, including minimal manual feature engineering and the ability to forecast with little historical data. Additionally, it presents 'LSTNet,' a model designed to capture both long- and short-term patterns in time series data using a combination of convolutional and recurrent neural networks.

![© 2018, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
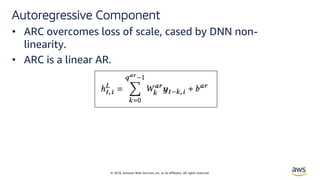
Autoregressive Models
• Hyndman[1] defines autoregressive models as:
’’ In an autoregression model, we forecast the variable of
interest using a linear combination of past values of the
variable. The term autoregression indicates that it is a
regression of the variable against itself.’’
• AR(p) model:
?@ = B + DE?@FE + D?@FG + … + D?@FH + I@](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/time-series-180824184812/85/Multivariate-Time-Series-2-320.jpg)
![© 2018, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Auto Regressive Models
!" = 18 − 0.8!")* + ," !" = 8 + 1.3!" − 1 − 0.7 !")/ − 2 + ,"
• Autoregressive models are remarkably flexible at handling a wide range of
different time series patterns.
1,2: 4!56785 [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/time-series-180824184812/85/Multivariate-Time-Series-3-320.jpg)



![© 2018, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
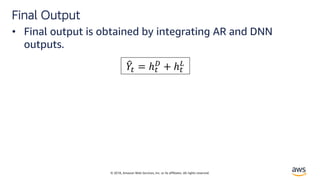
Solution
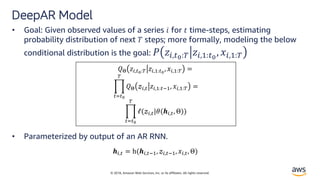
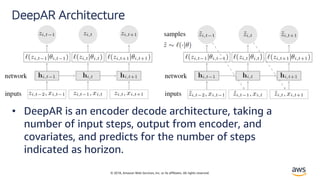
• DeepAR is a forecasting model based on autoregressive
RNNs, which learns a global model from historical data
of all time series in all datasets.[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/time-series-180824184812/85/Multivariate-Time-Series-7-320.jpg)

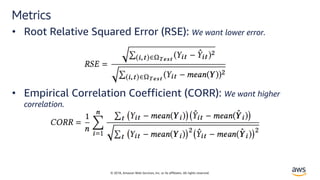
![© 2018, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
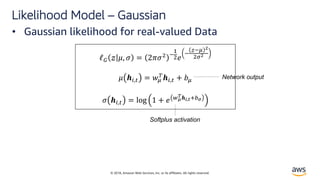
Likelihood Model – Negative Bionomial
• Negative-binomial likelihood for positive count data. The
Negative Binomial distribution is the distribution that
underlies the stochasticity in over-dispersed count
data.[3]
ℓ"# $ %, ' =
Γ $ +
1
'
Γ $ + 1 Γ
1
'
1
1 + '%
,
- '%
1 + '%
$
% ./,0 = log 1 + 4 56
7.8,9:;6
' ./,0 = log 1 + 4 5<
7.8,9:;<
• % =>? '=@4 ABCℎ BECFEC BG =
?4>H4 I=J4@ KLCℎ
HBGCFIEH =MCLN=CLB>
• ' HM=I4H N=@L=>M4 @4I=CLN4 CB
Cℎ4 O4=>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/time-series-180824184812/85/Multivariate-Time-Series-12-320.jpg)

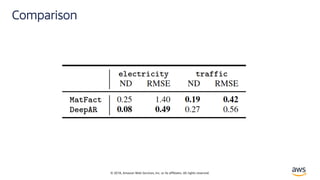


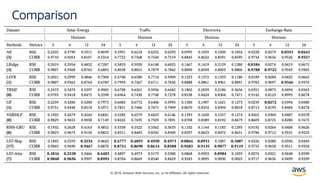
![© 2018, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
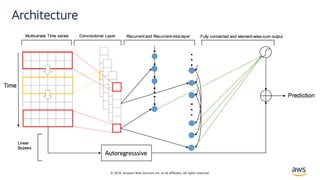
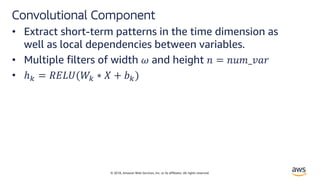
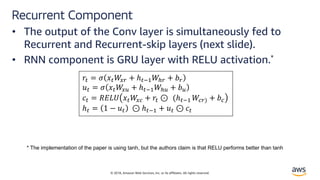
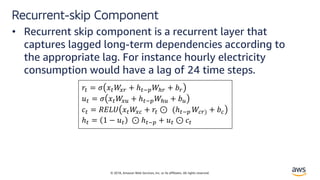
Solution – LSTNet[4]
• Long and Short Terms Time-series Networks is designed
to capture mix long- and short-term patterns in data for
multivariate time-series.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/time-series-180824184812/85/Multivariate-Time-Series-18-320.jpg)