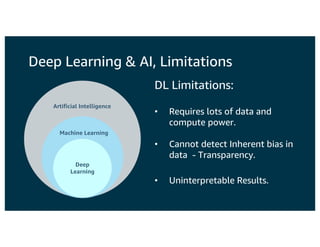
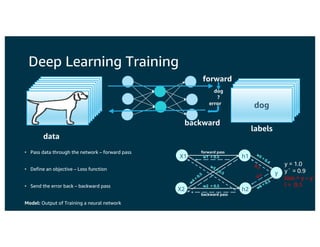
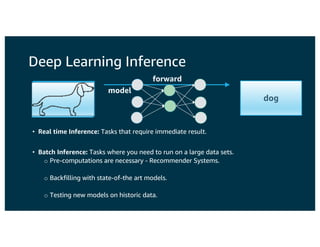
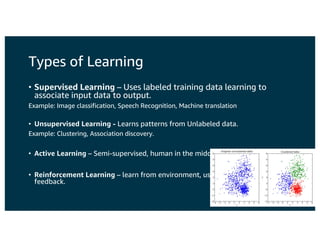
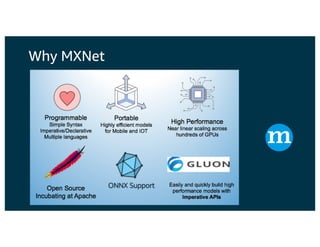
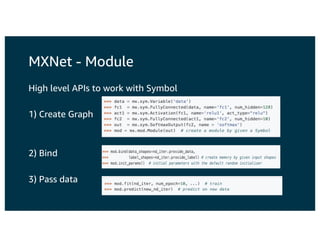
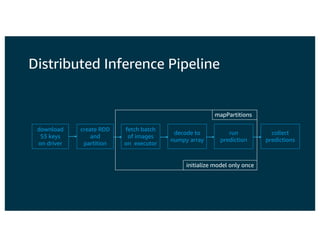
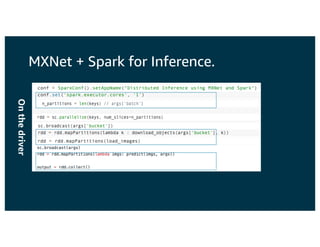
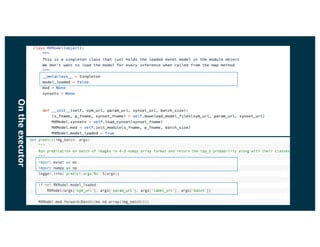
The document discusses the principles and implementations of distributed deep learning inference using Apache MXNet and Apache Spark, underlining the significance of deep learning in various sectors. It addresses different learning types, the MXNet framework capabilities, and the challenges faced in distributed inference. Additionally, it highlights future developments, including new APIs and community involvement for advancing AI.