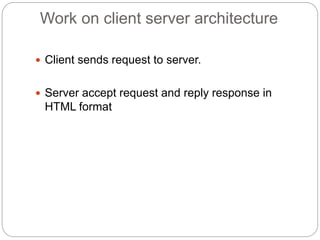
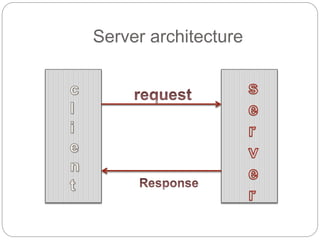
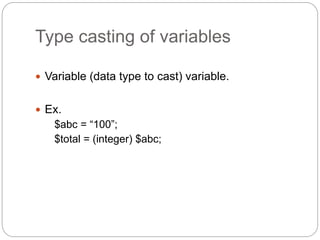
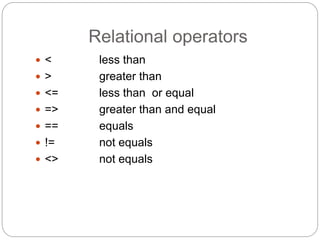
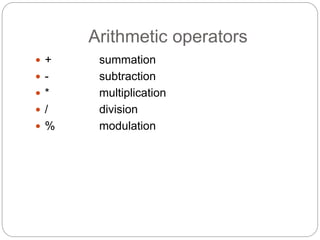
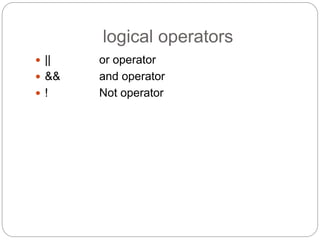
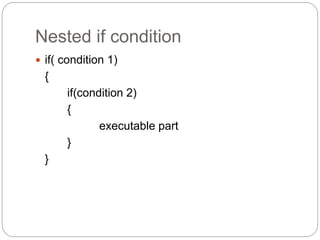
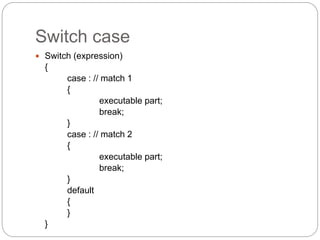
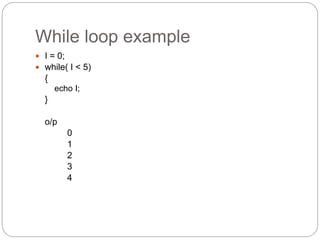
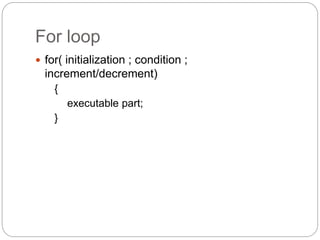
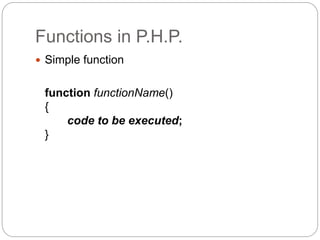
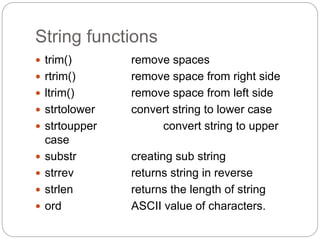
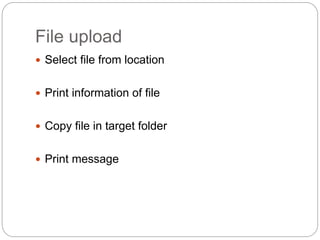
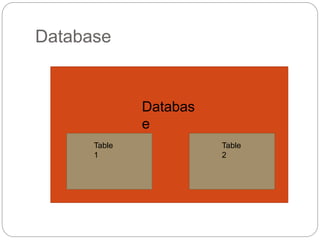
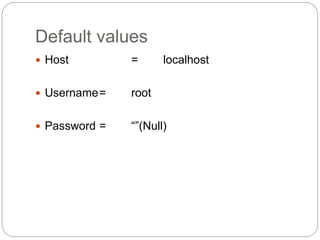
This document provides information about PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor), including its history, uses, syntax, variables, data types, operators, conditional statements, arrays, loops, functions, and more. Some key points:
- PHP is a widely-used scripting language for building dynamic web pages and applications. It was created in 1995 and runs on web servers.
- PHP code is embedded into HTML files and interpreted by the server before the page is sent to the browser. It allows for the creation of dynamic content.
- PHP is free, runs on most servers, and provides tools for database connectivity, security, and dynamic web page creation. It has advantages over competitors like ASP.









































![Receive data with all methods
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["fname"]; ?>!<br
/>
You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old
Welcome <?php echo $_GET["fname"]; ?>!<br />
You are <?php echo $_GET["age"]; ?> years old..
Welcome <?php echo $_REQUEST["fname"];
?>!<br />
You are <?php echo $_REQUEST["age"]; ?>
years old.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-61-320.jpg)
![Receiving parameters
Data.php
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["fname"]; ?>!<br
/>
You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years
old.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-62-320.jpg)




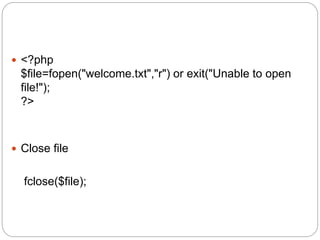






![Read cookies
<?php
// Print a cookie
echo $_COOKIE["user"];
// A way to view all cookies
print_r($_COOKIE);
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-75-320.jpg)
![Another example of cookies
<?php
if (isset($_COOKIE["user"]))
echo "Welcome " .
$_COOKIE["user"] ;
else
echo "Welcome guest!<br />";
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-76-320.jpg)


![Creating a new session in P.H.P.
$_SESSION[“ name of your session ”] = “value of
session”
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-79-320.jpg)
![Access session
$variable name = $_SESSION[“session name”];
Delete session
unset(“name of your session”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-80-320.jpg)





![Select database from entire
system
mysql_select_db(“database name", [ reference of
database]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-88-320.jpg)
![Example to insert data in table
<?php
$con = mysql_connect("localhost",“root","");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
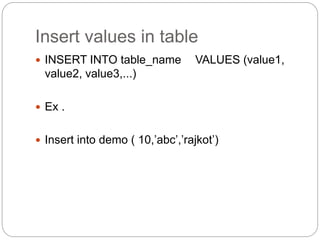
$sql="INSERT INTO Persons (FirstName, LastName, Age)
VALUES('$_POST[firstname]','$_POST[lastname]','$_POST[age]')";
if (!mysql_query($sql,$con))
{
die('Error: ' . mysql_error());
}
echo "1 record added";
mysql_close($con);
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-90-320.jpg)
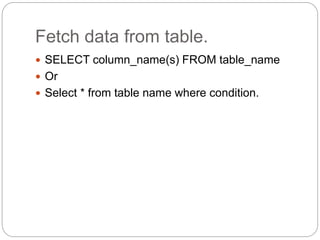
![Where clause
$con = mysql_connect("localhost",“root","");
if (!$con)
{
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
mysql_select_db("my_db", $con);
$result = mysql_query("SELECT * FROM Persons
WHERE FirstName=‘abc'");
while($row = mysql_fetch_array($result))
{
echo $row['FirstName'] . " " . $row['LastName'];
echo "<br />";
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-92-320.jpg)
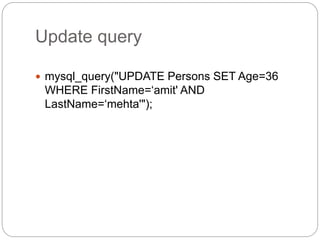

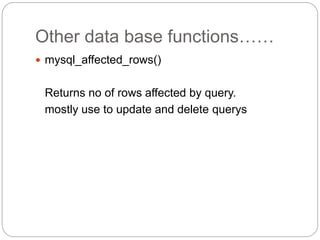






![SERVER object
Methods
$_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT']
Returns path of document root
$_SERVER['HTTP_USER_AGENT']
returns browser information
$_SERVER['REMOTE_PORT']
returns port number](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-102-320.jpg)
![$_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']
returns ip address of server
$_SERVER['SERVER_NAME']
returns name of server
$_SERVER['SCRIPT_FILENAME']
returns path of current file with file name](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-161226121409/85/Php-103-320.jpg)