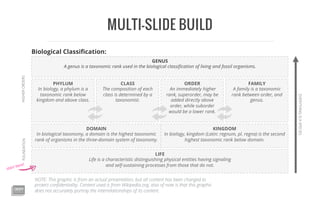
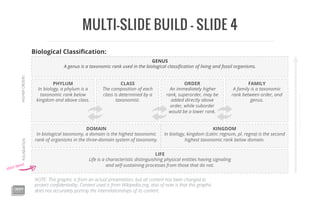
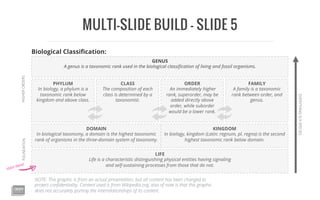
The document outlines the hierarchical structure of biological taxonomy, explaining key taxonomic ranks such as domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, and genus. It highlights that a domain is the highest taxonomic rank in the three-domain system and provides definitions for each rank. Additionally, it notes that the graphic content is altered to maintain confidentiality and may not accurately represent the relationships among the taxonomic categories.