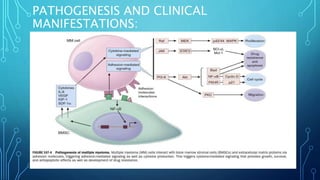
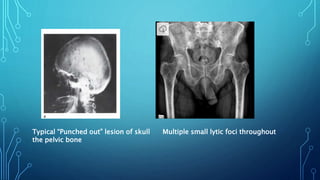
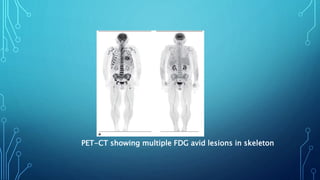
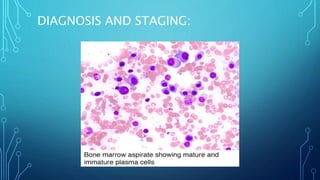
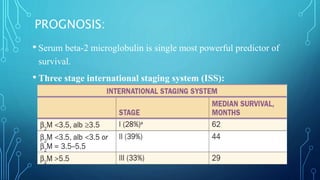
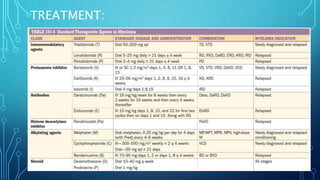
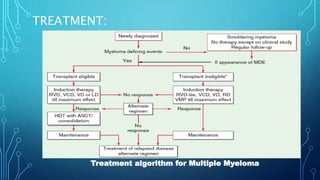
Multiple myeloma is a malignant proliferation of plasma cells that commonly affects bone. It causes bone pain, fractures, renal failure, anemia, and susceptibility to infection. The cause is unknown but genetic factors may be involved. Myeloma cells interact with bone marrow to increase osteoclast activity, causing lytic bone lesions. Diagnosis requires bone marrow plasmocytosis, serum/urine monoclonal protein, and end-organ damage. Risk is stratified using beta-2 microglobulin and FISH. Treatment involves induction, consolidation, and maintenance therapies such as bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone combinations. Supportive care focuses on complications like hypercalcemia, fractures, and anemia