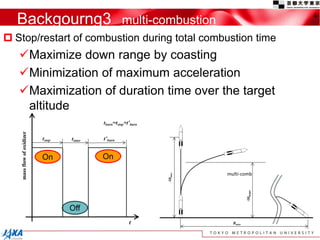
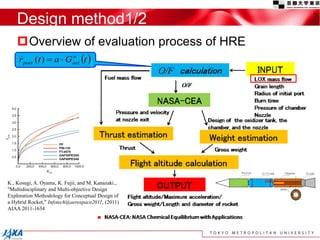
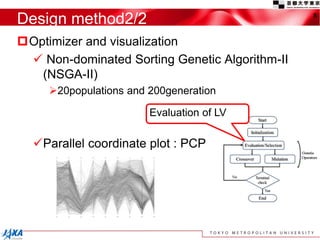
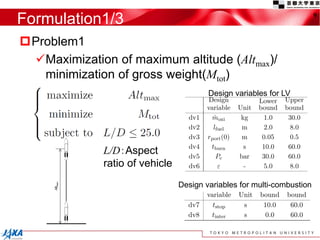
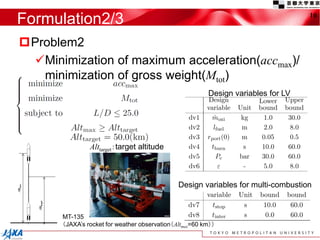
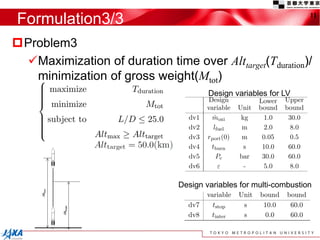
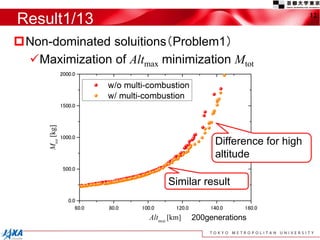
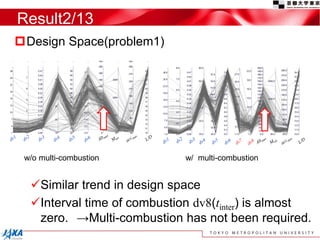
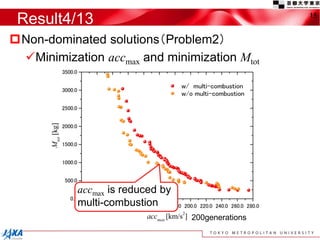
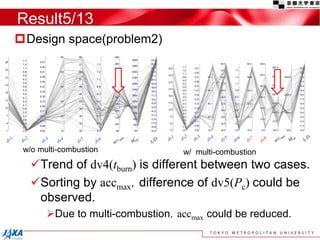
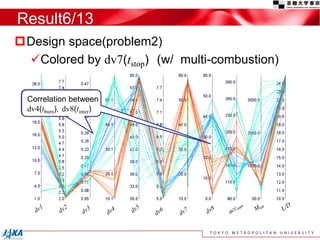
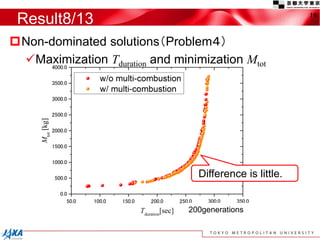
This document discusses the application of a multi-objective genetic algorithm for the conceptual design of single-stage rockets utilizing hybrid propulsion systems. It highlights the benefits and characteristics of hybrid rocket engines, compares them with solid and liquid rockets, and presents design optimization problems. The results indicate that while multi-combustion does not significantly enhance altitude or duration, it effectively minimizes maximum acceleration.