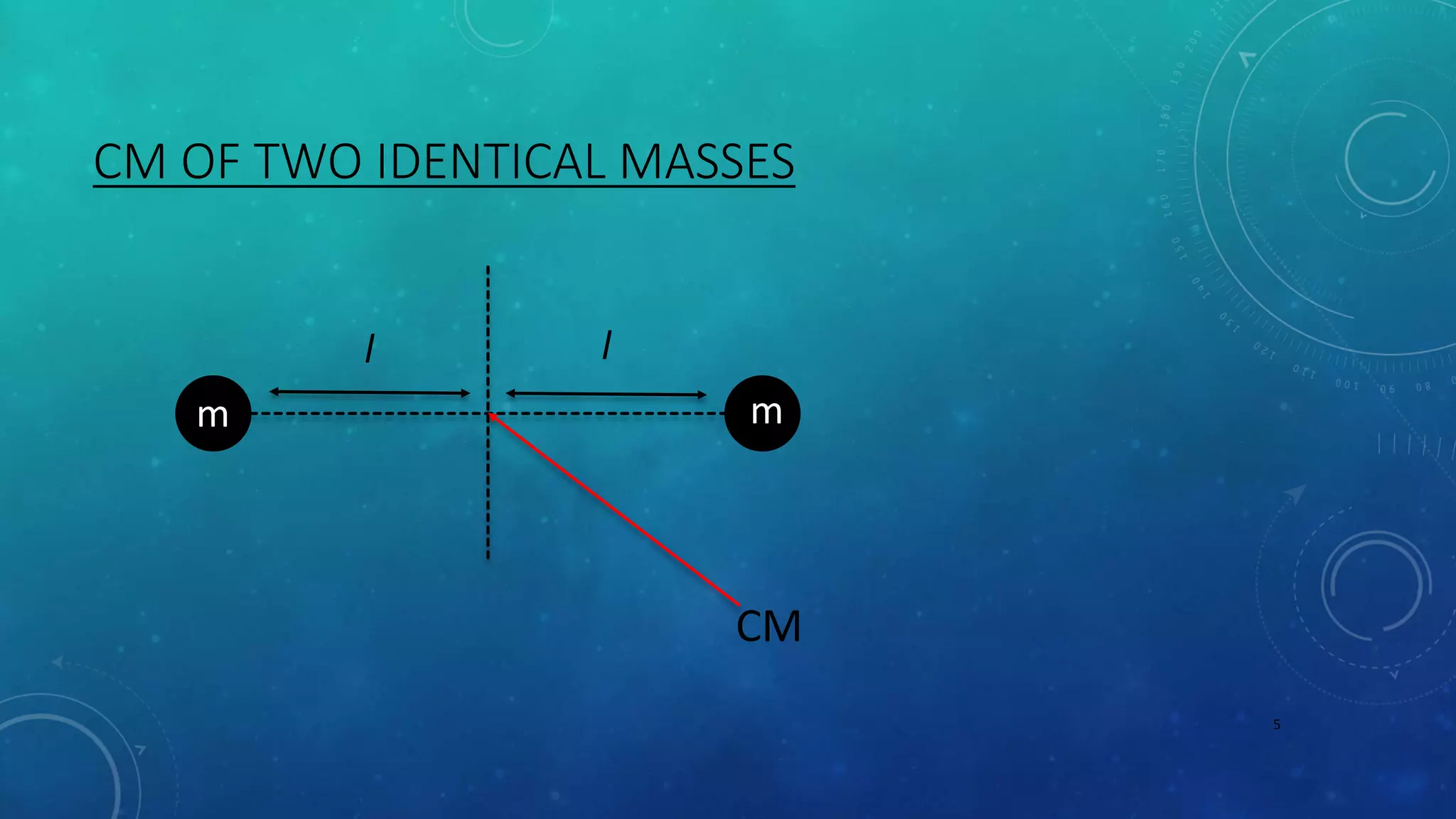
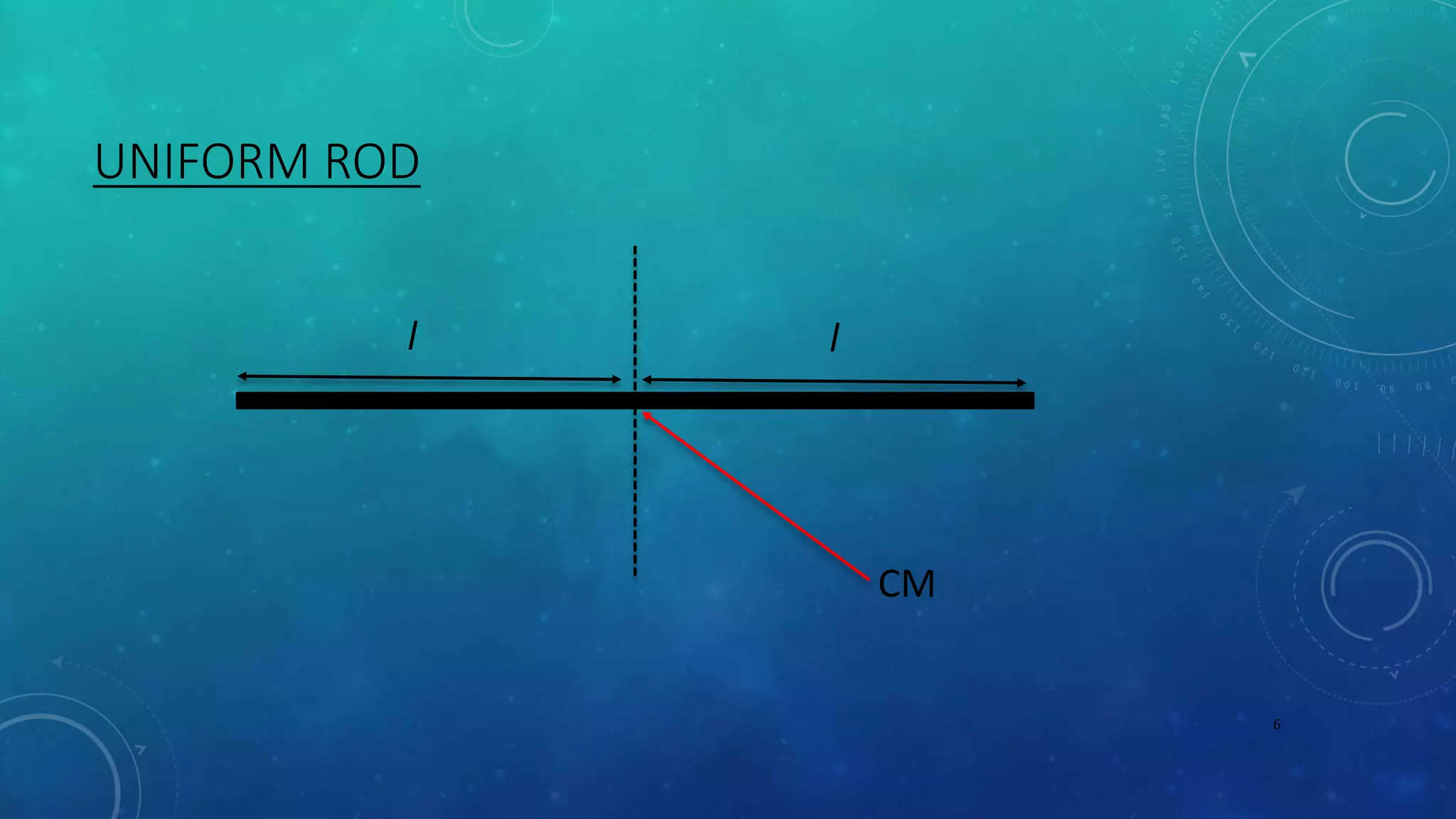
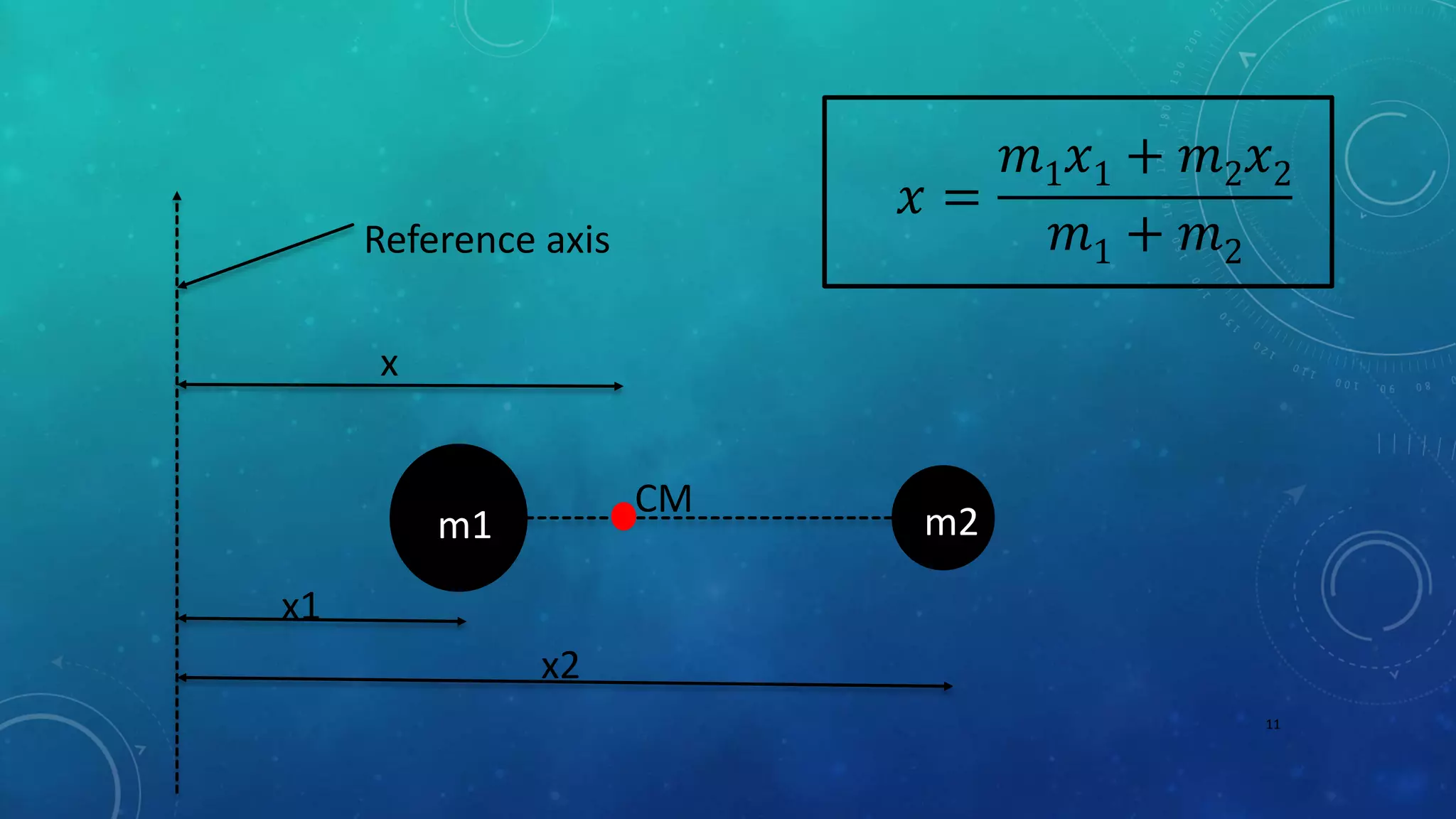
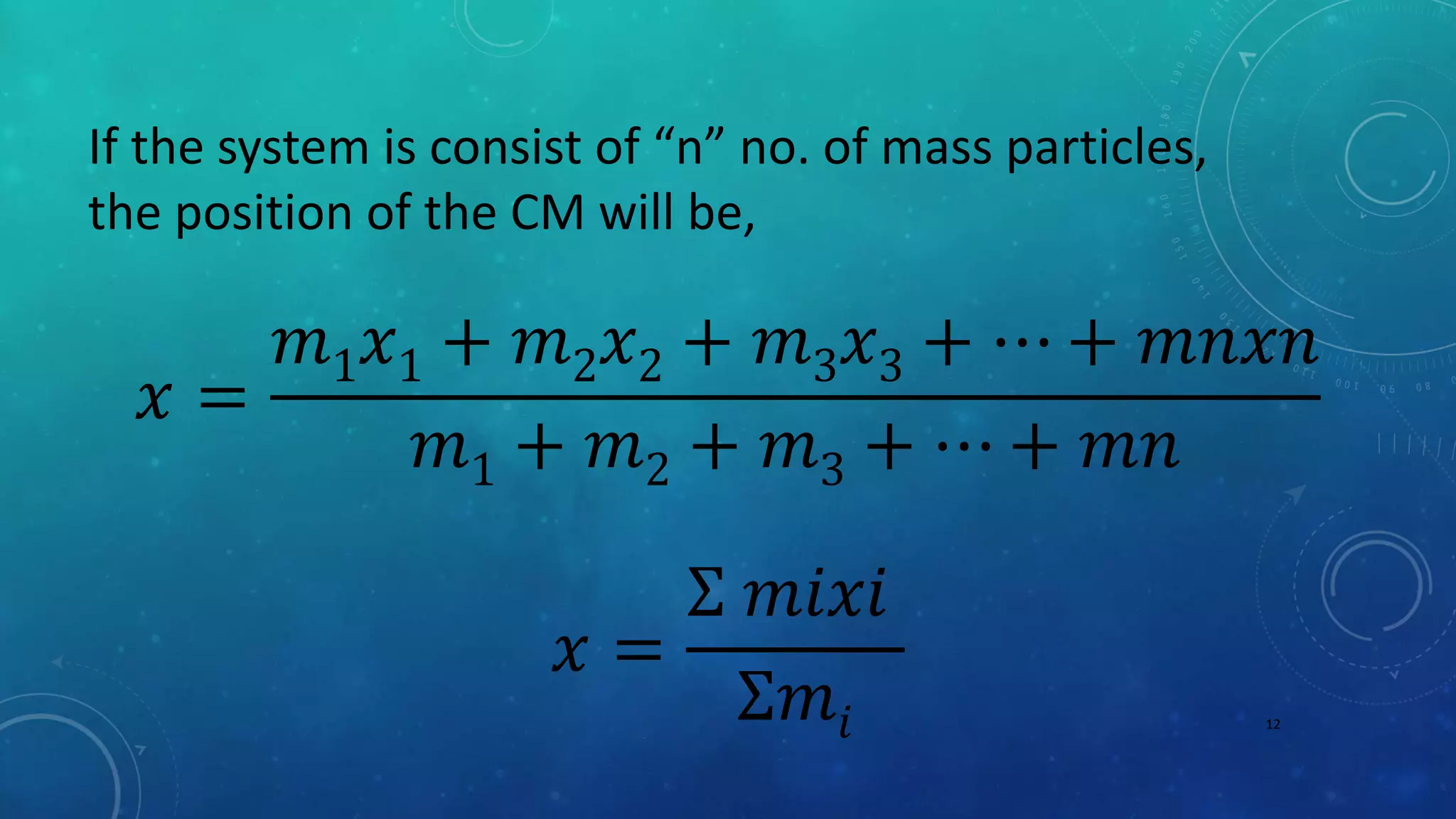The document discusses centre of mass and rocket propulsion. It defines centre of mass as the point where the entire mass of an object can be assumed to be concentrated and balances the distribution of mass. It provides examples of calculating the centre of mass for symmetrical shapes, uniform rods, triangles, circles, and cuboids. For a two-mass system, it gives the formula to find the centre of mass as a weighted average. Rocket propulsion is described as relying on conservation of momentum, where expelling mass in one direction causes the rocket to move in the opposite direction.