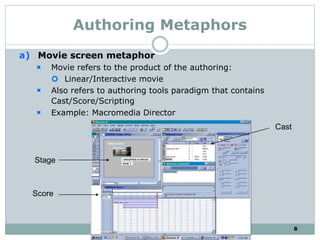
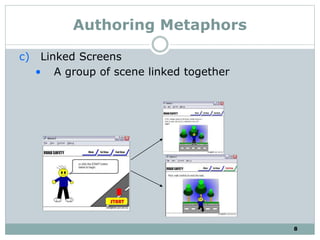
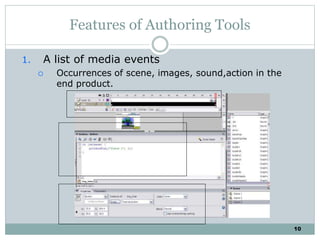
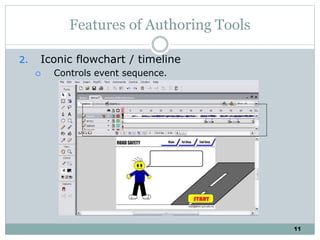
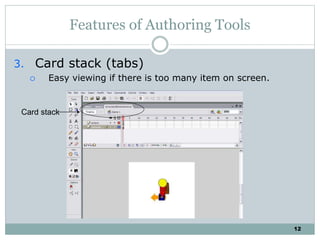
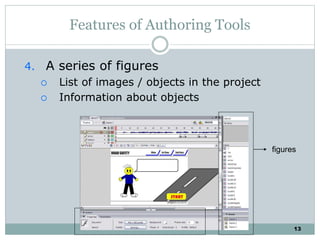
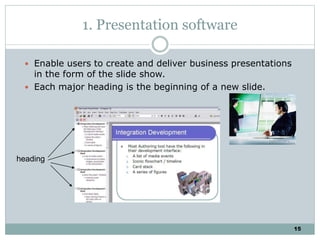
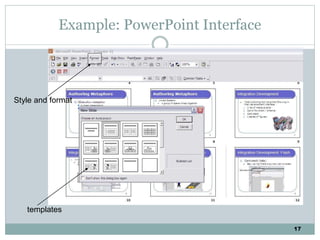
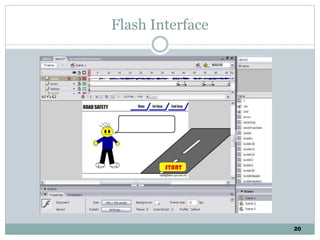
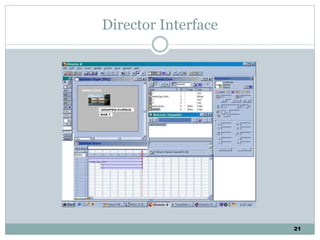
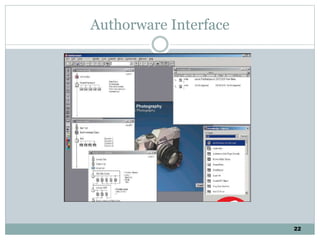
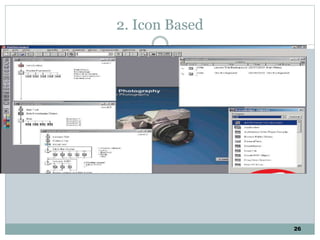
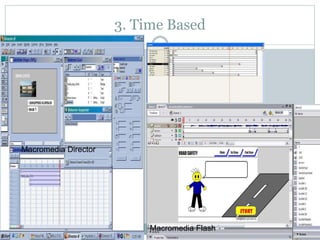
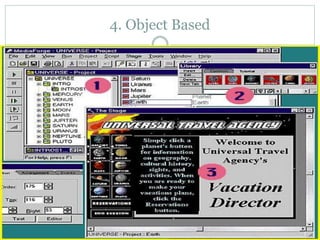
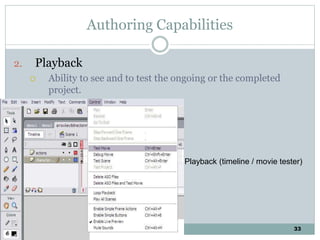
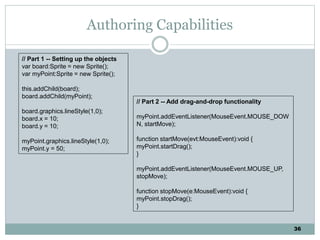
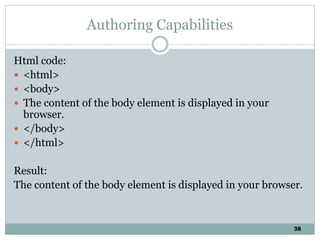
The document discusses multimedia authoring tools and their features. It begins by defining authoring tools as tools used to integrate various media components into a structured presentation. It then describes three common authoring metaphors: the movie screen metaphor exemplified by tools like Director, the slide show metaphor used in tools like PowerPoint, and linked screens. The document also outlines key features of authoring tools like media events lists, timelines, card stacks, and object listings. It categorizes tools as used for presentations, productions, or interactive education and provides examples like PowerPoint, Director, and Flash. Finally, it discusses capabilities of authoring tools such as interactivity, playback, editing, programming, cross-platform use, and distribution.