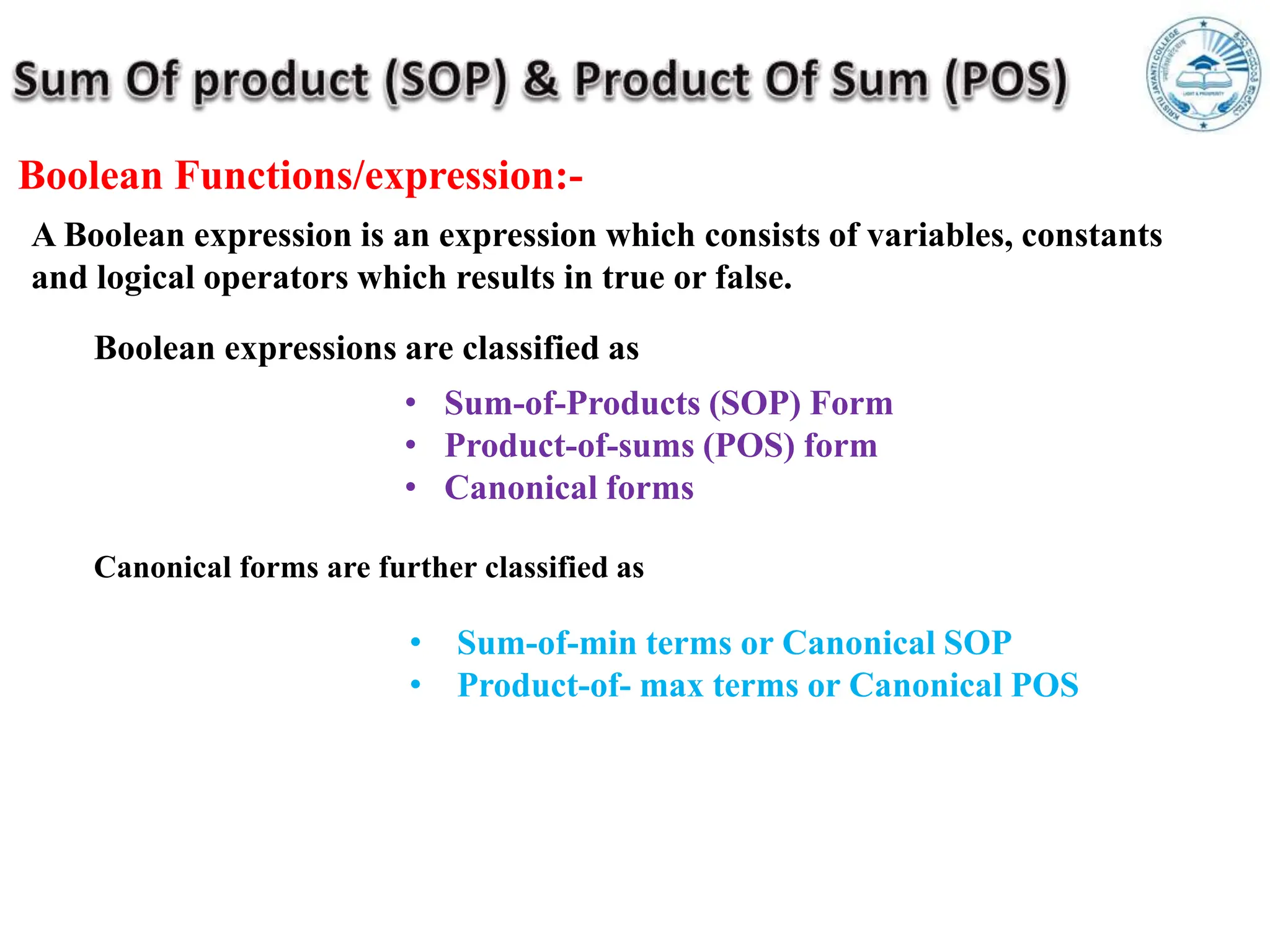
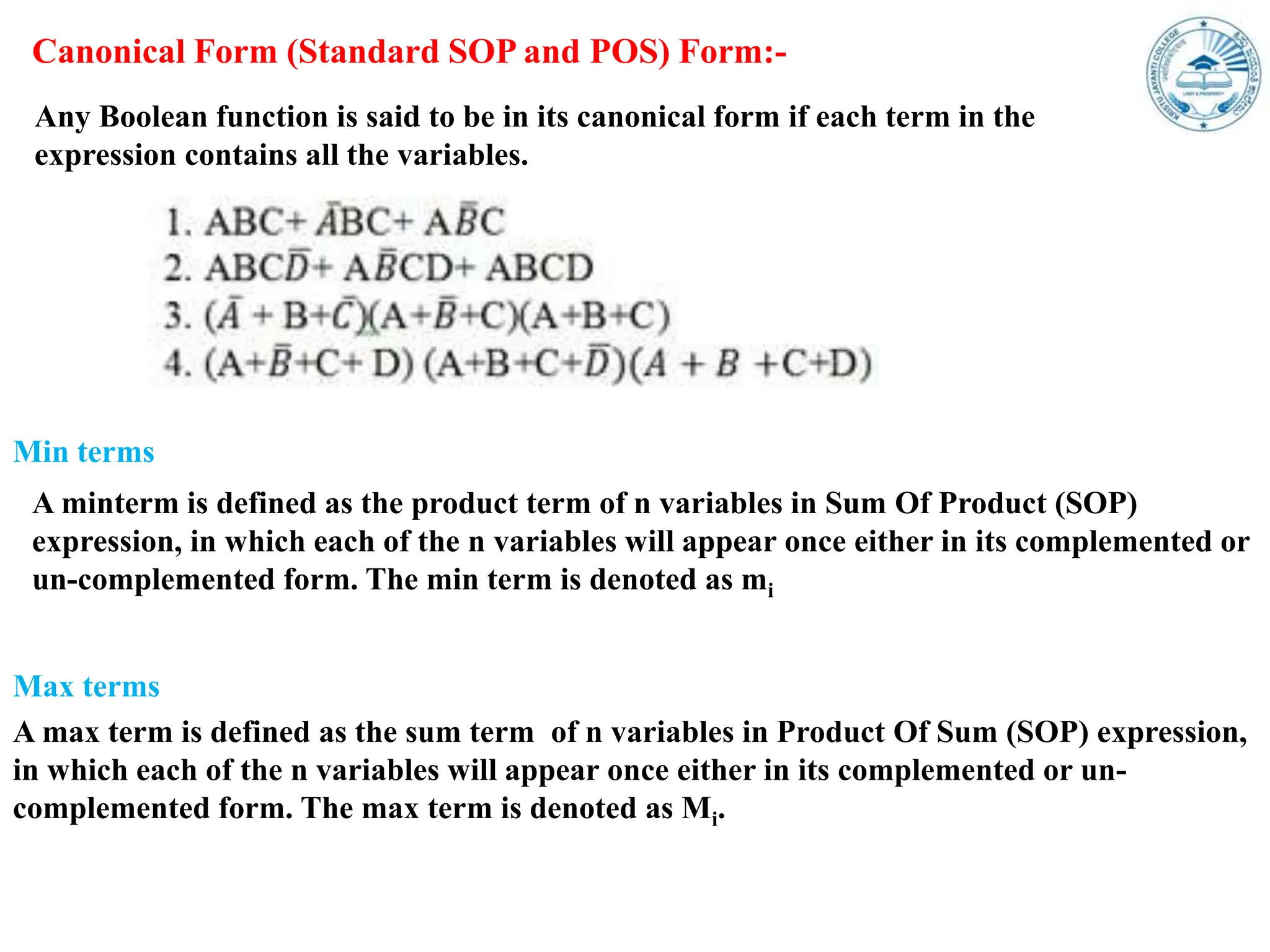
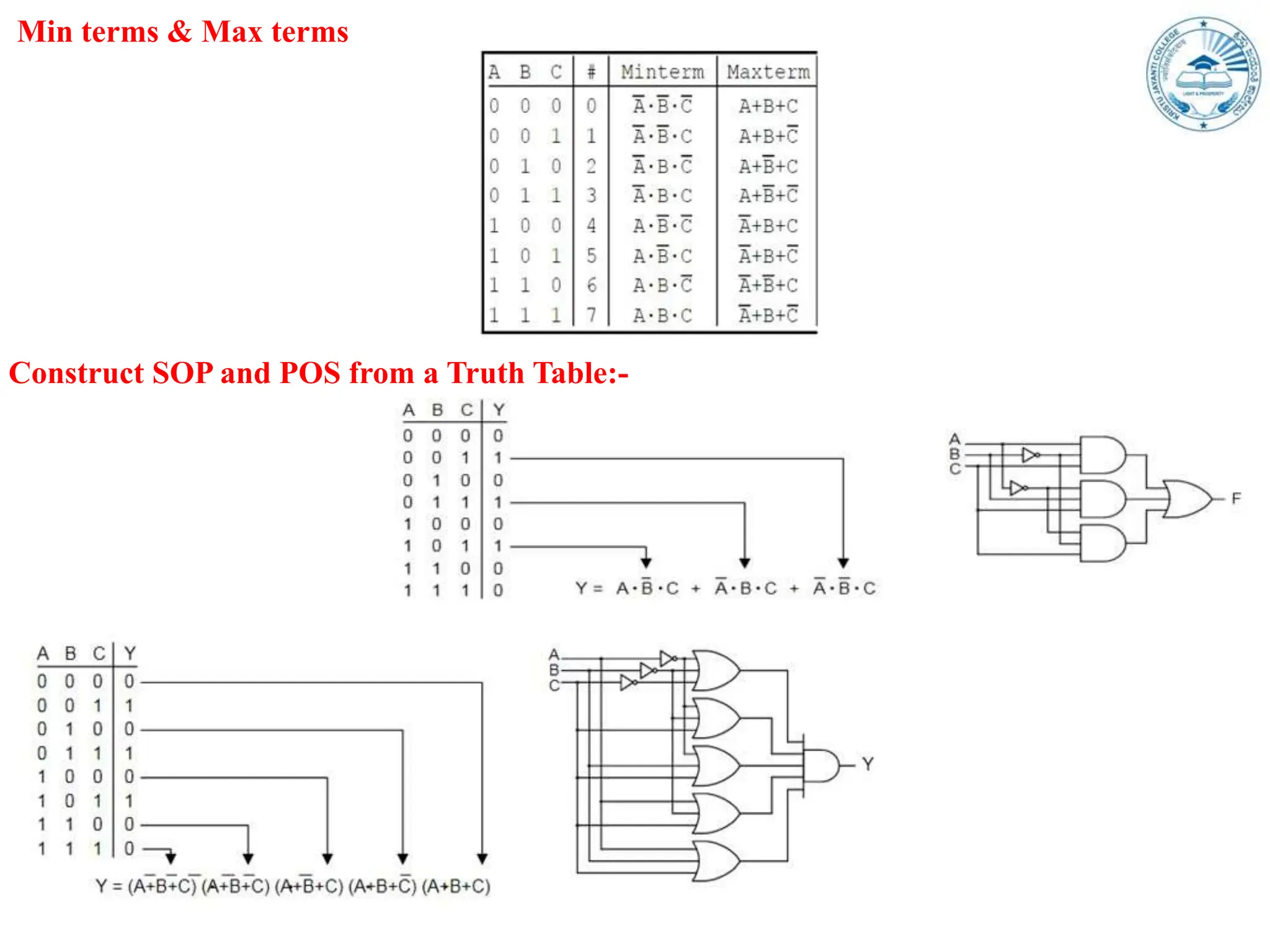
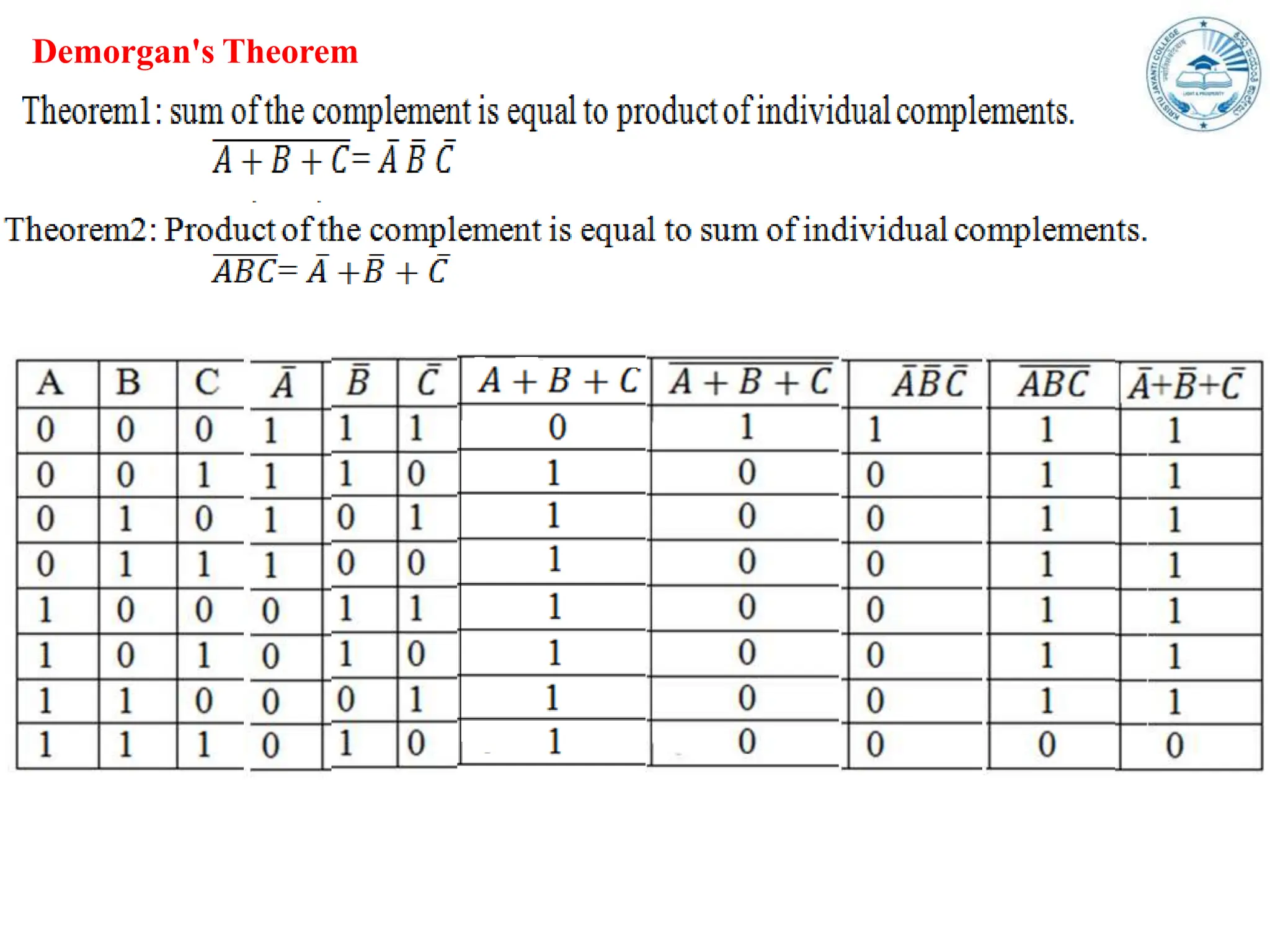
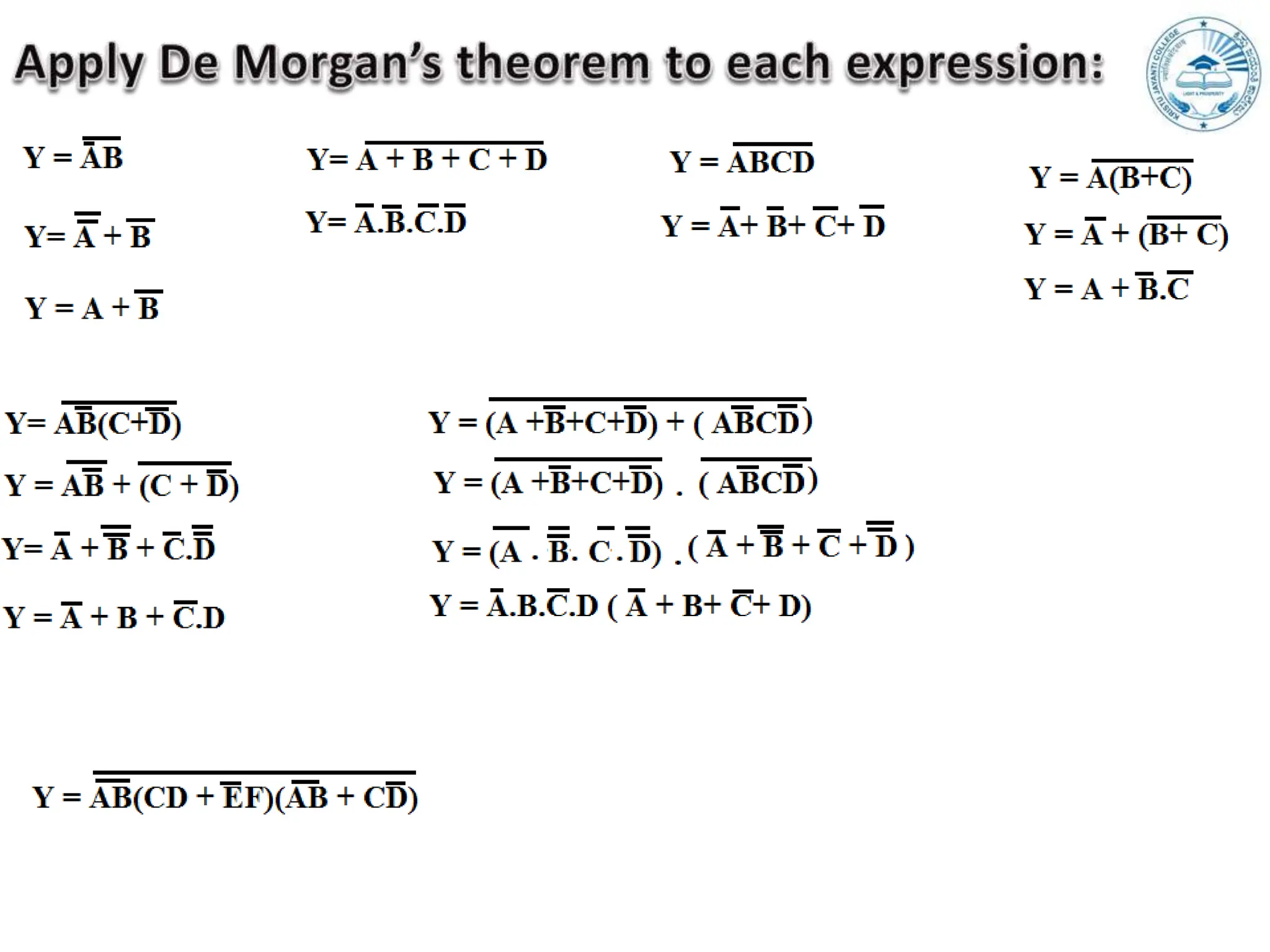
Boolean expressions use variables, constants, and logical operators to evaluate to true or false. They can be expressed in Sum-of-Products (SOP) form or Product-of-Sums (POS) form, and are classified as canonical (standard) SOP or POS. Canonical forms have each term containing all variables. SOP represents the function as a sum of product terms, while POS is the opposite as a product of sum terms. Boolean expressions are also represented using truth tables, min/max terms, Demorgan's theorem, and derived gates.