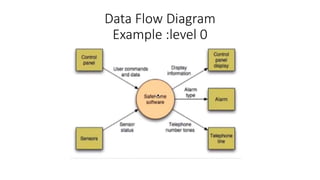
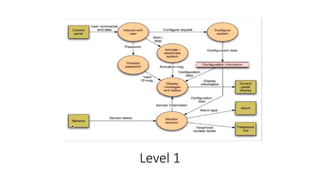
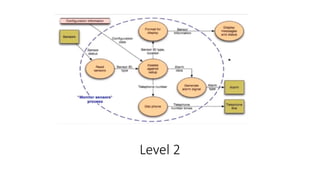
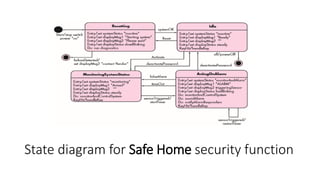
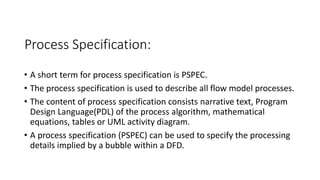
Flow Oriented Modeling uses data flow diagrams, control flow specifications, and process specifications. Data flow diagrams depict the system as bubbles divided into processes with inputs and outputs between levels. Control flow specifications represent system behavior through state diagrams showing state transitions triggered by events. Process specifications describe each process through narrative text, algorithms, equations, or activity diagrams.