Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times



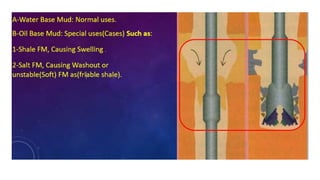


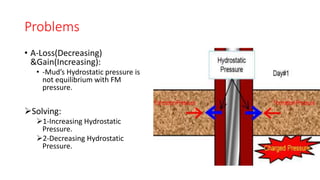
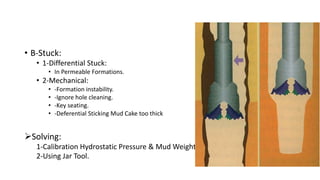
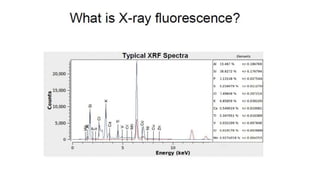

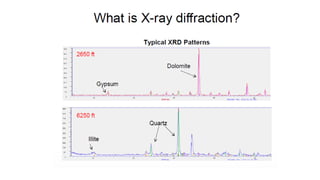
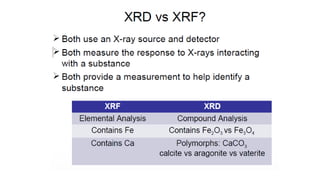





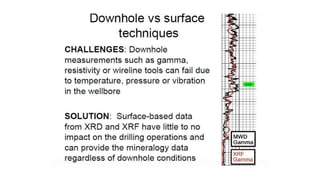



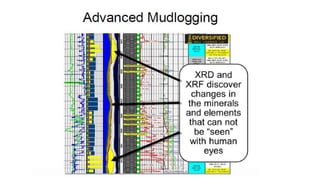

Mud logging involves monitoring drilling parameters and the lithology, gas content, and oil shows of downhole formations in real-time. A mud logger collects and examines rock cuttings for geological description and oil shows, monitors hydrocarbon gases and hydrogen sulfide levels, and tracks mud volume, drilling parameters, and trip sheets. Issues like losses or gains in mud volume and stuck pipe can occur due to pressure imbalances or poor hole cleaning and require solutions like adjusting mud weight or using a jar tool.























